-
Posts
9251 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
369
Everything posted by anyweb
-
thanks, it's a requirement because Operating System Deployment requires it for the boot images needed to deploy both Windows 8.1 and Server 2012 R2 operating systems, in addition migration of data between those operating systems needs the newer version of USMT, Configuration Manager 2012 SP1 also required ADK 8.0 for the same reasons (support Windows 8/Server 2012)
-
after the time/date change did you confirm all servers have changed time ? have you tried rebooting them ?
-
what time does it say on the hyperv host ?
-
it's not available, if you want all the bitlocker actions then import the one i linked to above your post, it's all in that task sequence just remove the bits you don't need.
-

Slow image deployment download since SCCM 2012 R2 upgrade
anyweb replied to Gareth86's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
ok the problem has been identified apparently (on a separate list) and here's what they said so i guess a hotfix is coming cheers niall -

Server 2012 R2 & SCCM 2012 R2 - WDS Crash
anyweb replied to hoivikaj's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
have you tried uninstalling PXE on the dp, uninstalling WADK 8.1, reinstalling WADK 8.1 (make sure it's the newest version), re-enabling PXE on the dp ? -

Auto-assign computername in OSD Deployment with VB Script
anyweb replied to Bever87's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
have you added any connection capability in your boot wim ? you need to add the optional component (Winpe-mdac) ? -

Slow image deployment download since SCCM 2012 R2 upgrade
anyweb replied to Gareth86's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
I wonder if there is any update available for your vmware server solution ? can you tell us what version you are running ? -
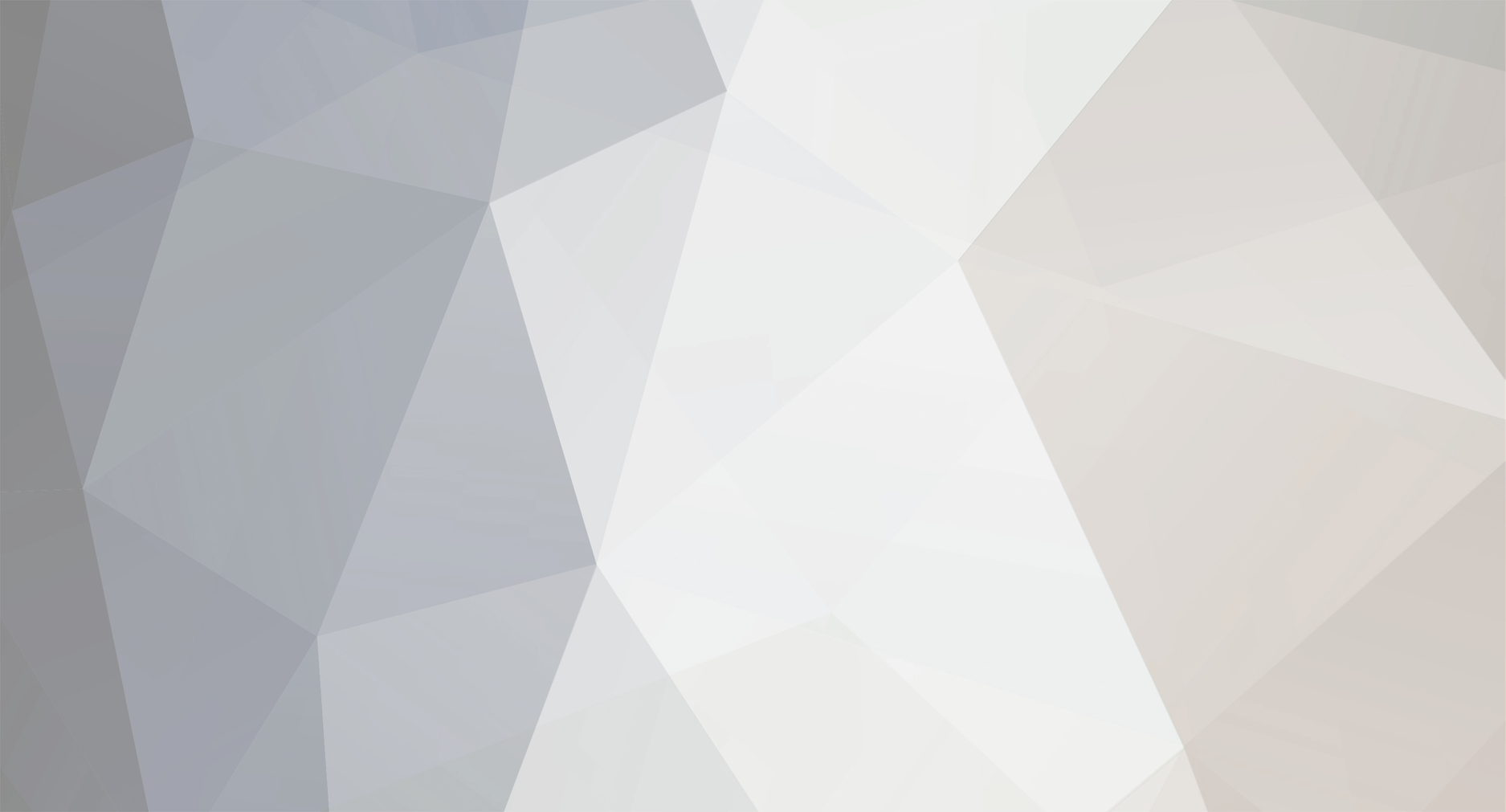
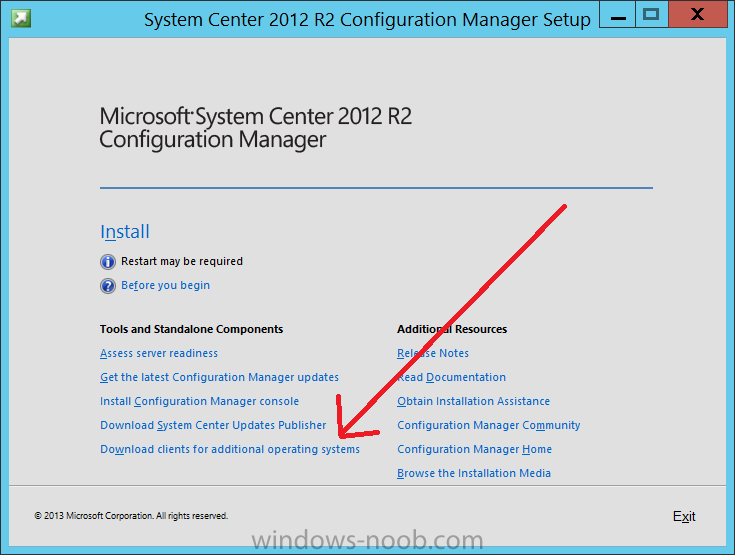
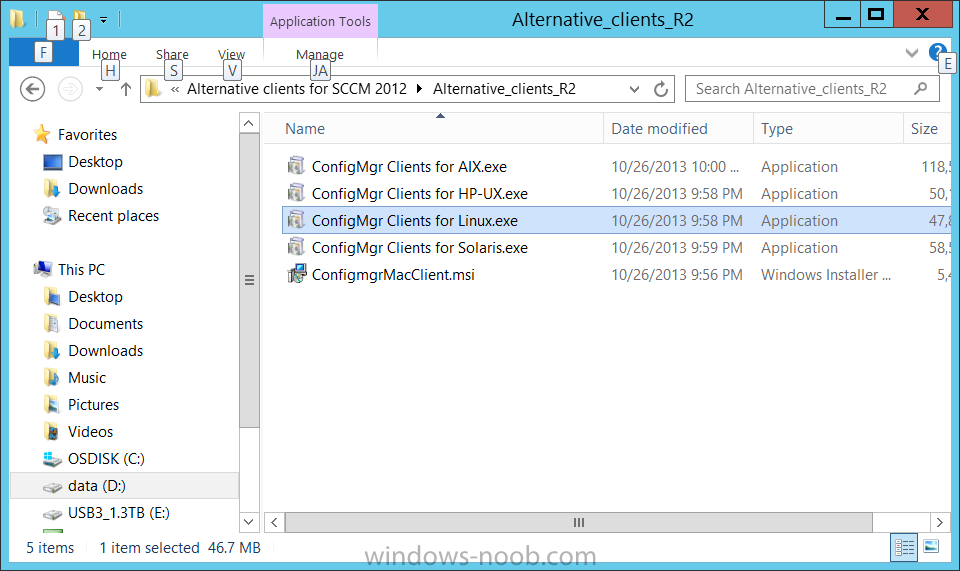
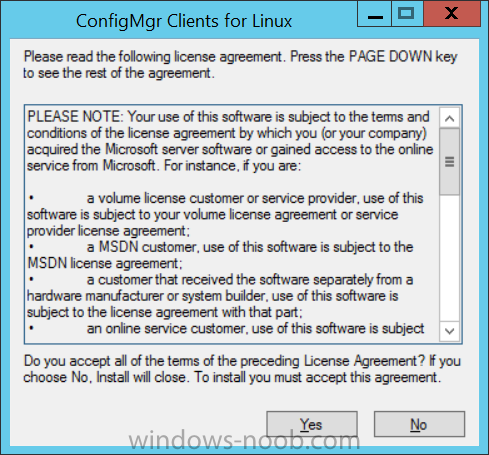
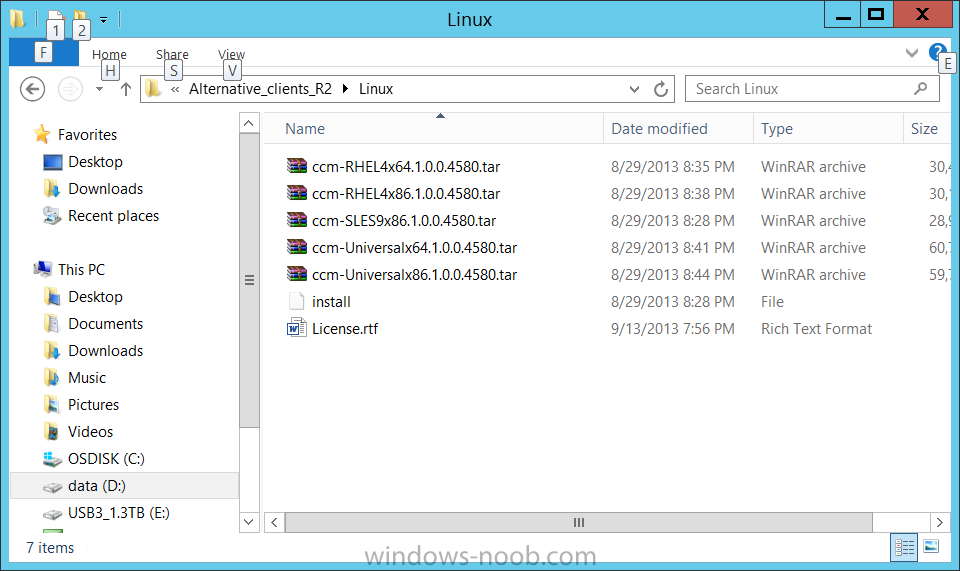
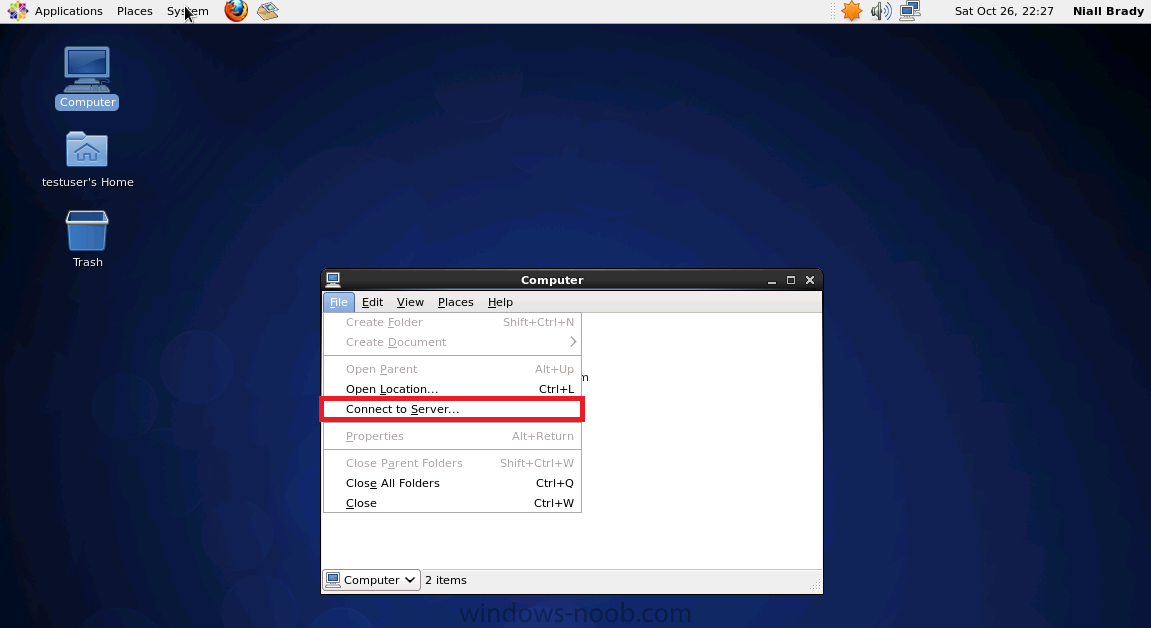
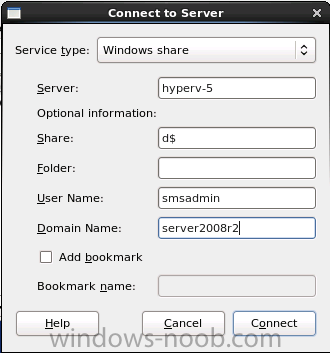
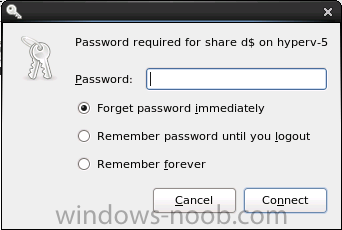
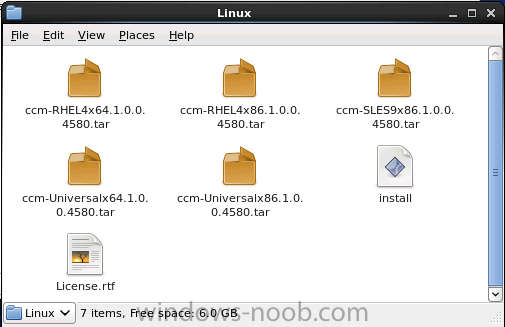
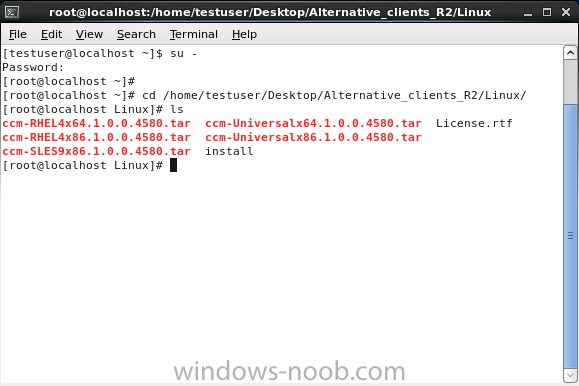
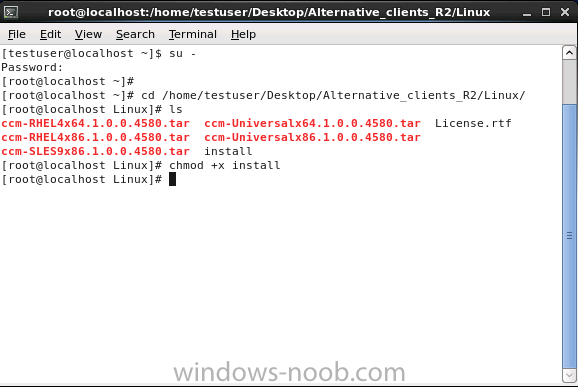
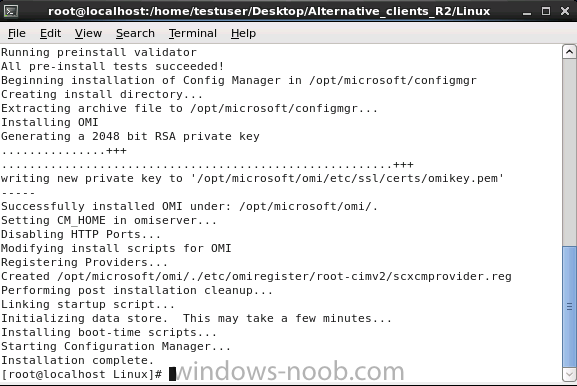
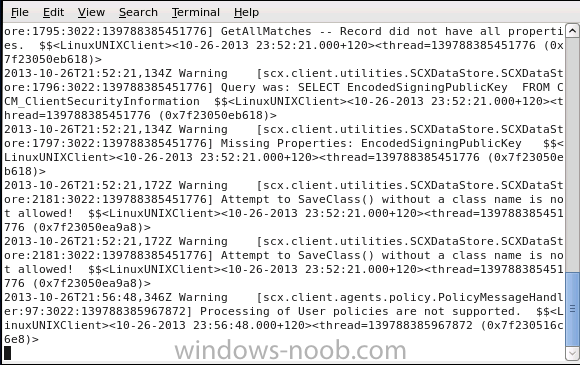
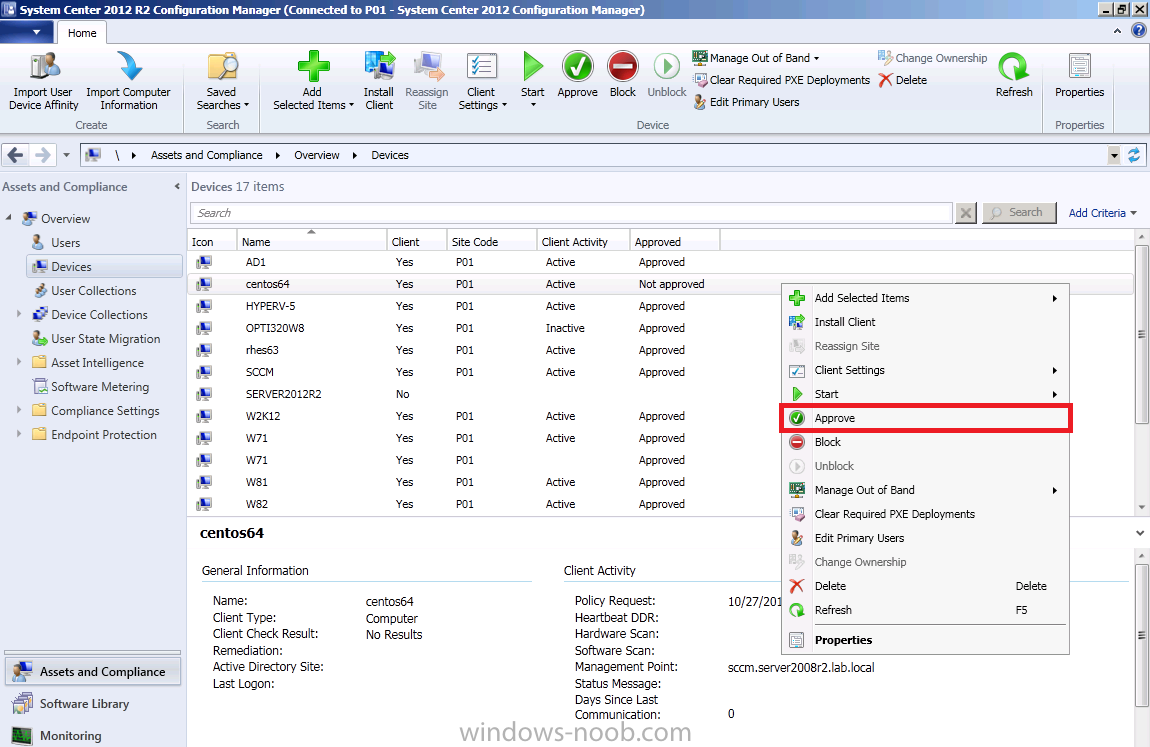
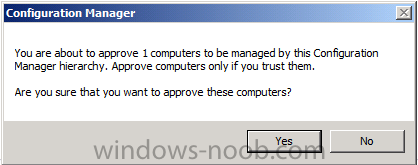
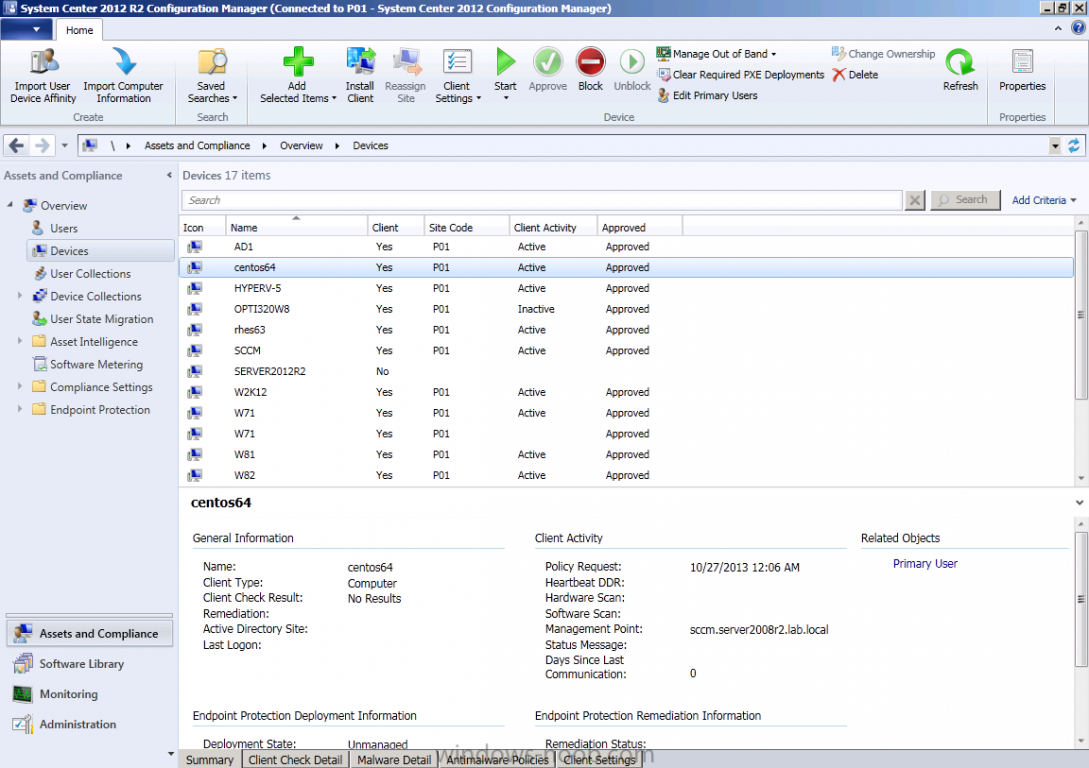
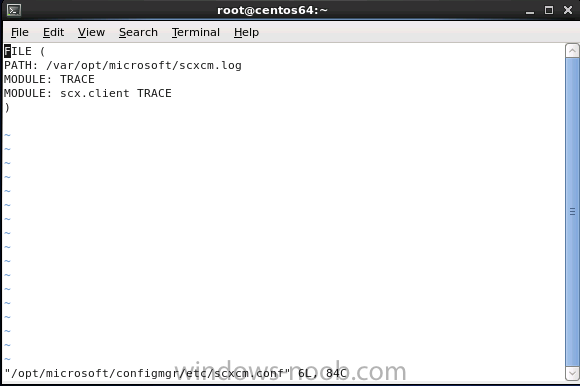
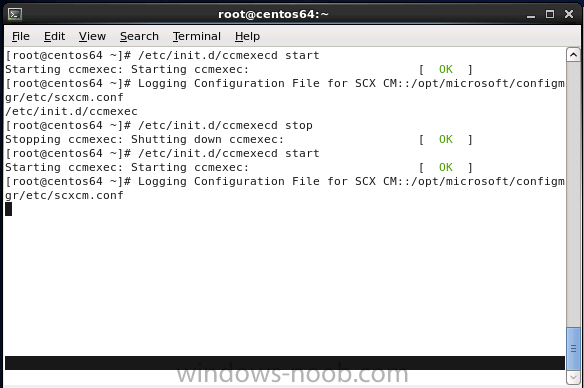
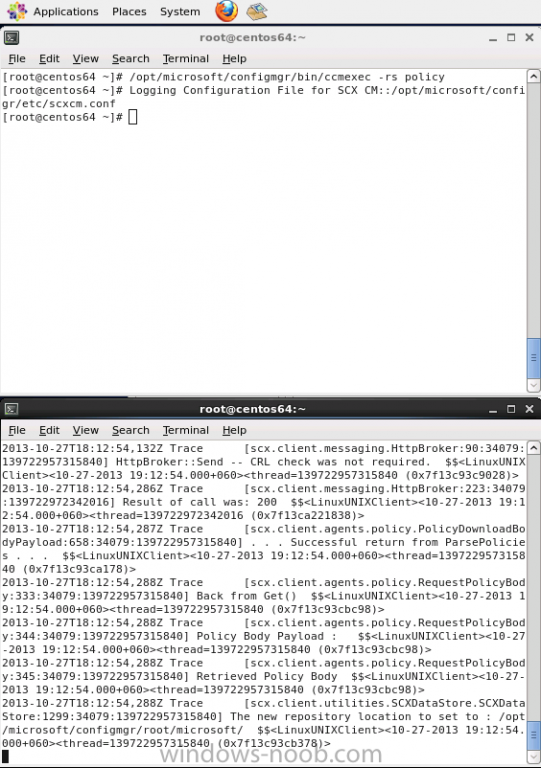
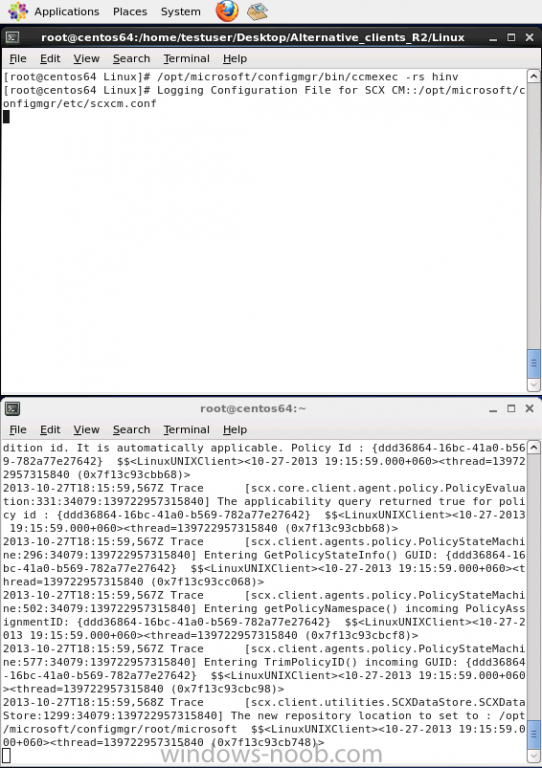
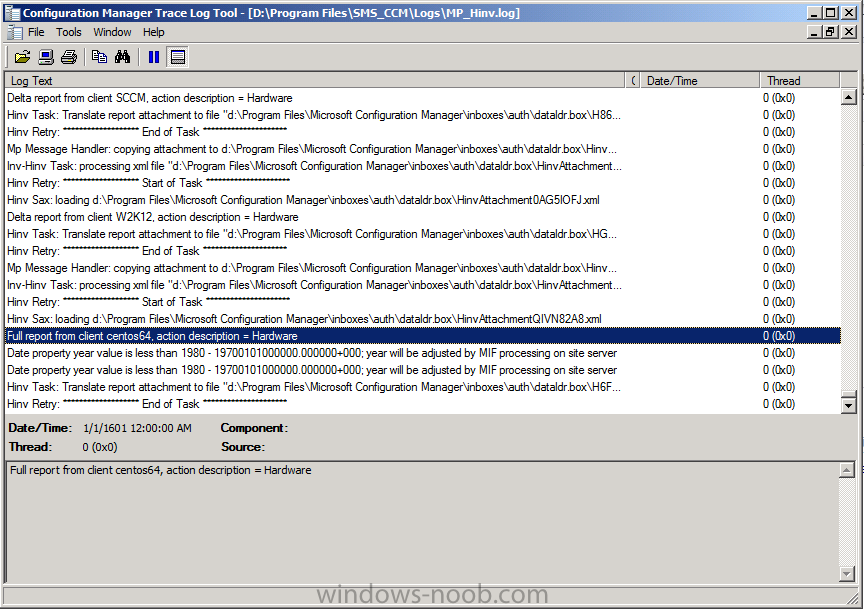
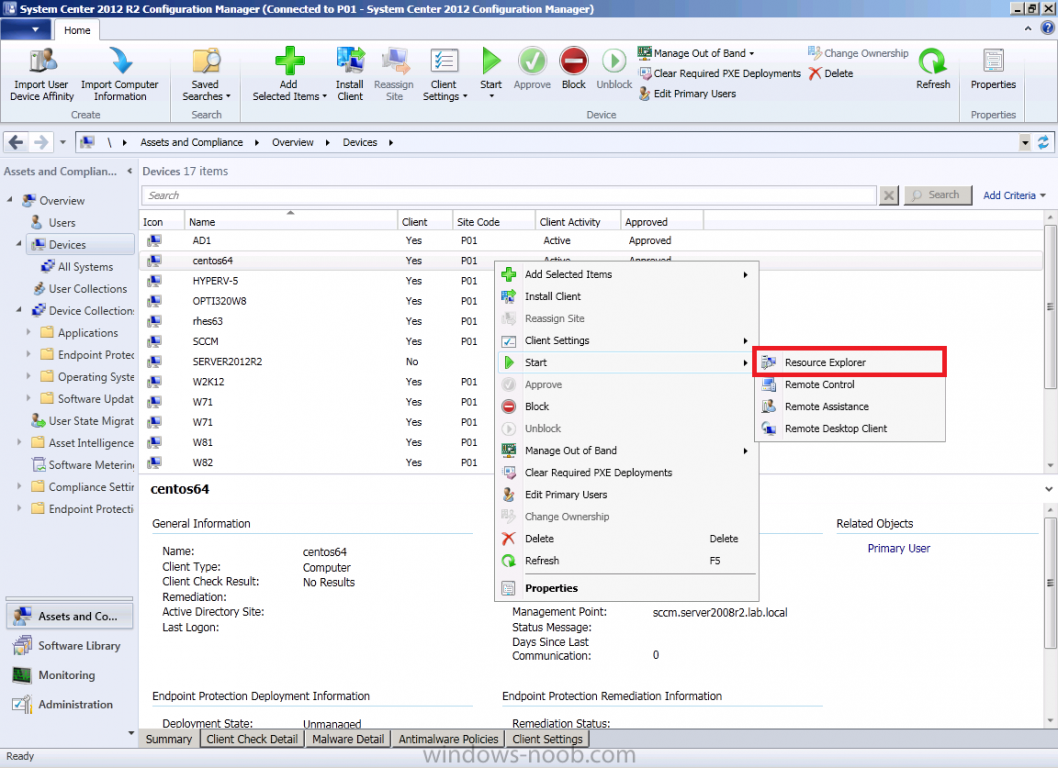
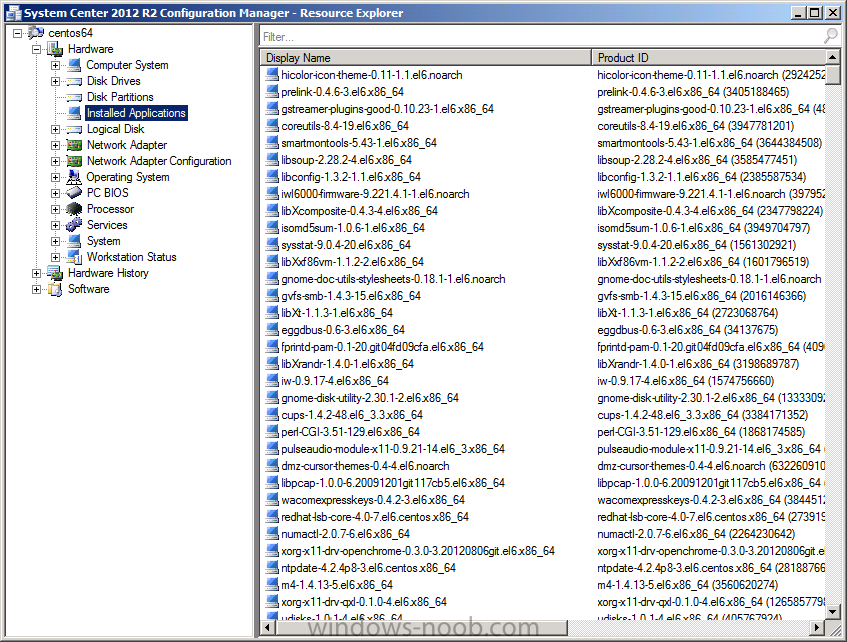
Introduction System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager supports a wide variety of operating systems including alternative operating systems such as the following:- Mac Client: Mac OS X 10.6 (Snow Leopard) Mac OS X 10.7 (Lion) Mac OS X 10.8 (Mountain Lion) UNIX/Linux Client: AIX Version 7.1, 6.1, 5.3 Solaris Version 11, 10, 9 HP-UX Version 11iv2 , 11iv3 RHEL Version 6 , 5, 4 SLES Version 11, 10, 9 CentOS Version 6, 5 Debian Version 6, 5 Ubuntu Version 12.4 LTS, 10.4 LTS Oracle Linux 6, 5 Note: A list of supported clients is available on Technet here. In this post I will show you how to install the Linux client on a popular Linux operating system (Centos 6.4) and do some basic actions like hardware and software inventory in System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager. This guide assumes you have already installed your Linux server and are ready for the next step. If you have not installed it yet just download the Live CD from here and boot from it, choose the option to Install to hard drive once the os has booted to the desktop. Step 1. Download the Alternative Client files Note: The download required will be different depending on which version of Configuration Manager you are using. Download the correct version matching the version you are running, so if for example you are running the Configuration Manager 2012 R2 CU1 use these updated clients. When you started the System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager installation you probably didn't notice that there was a link to download alternative clients on the splash screen highlighted in the screenshot below If you did click on the link it would bring you here so go ahead and download those client files. Update: check the following link for updated supported clients and click here for R2 SP1 or Current Branch clients. Step 2. Extract the Linux client files on a Windows computer On the computer you downloaded the alternative client files, locate the Linux client exe file and extract the contents somewhere local by double clicking on the ConfigMgr Clients for Linux.exe file. extract the files to somewhere useful. the files are extracted.. Step 3. Copy the linux client files to your linux server Logon as a testuser on the Centos server, click on the Computer icon, and click on File, then Connect to server enter the details required to connect to a server that has the client files downloaded from Step 1 above and click on connect (notice I chose windows shares in the service type drop down menu) then click on Connect you may be prompted for a password, enter it Locate the extracted files and copy them to your desktop Step 4. Install the Linux client To install the client we need the right permission, and the permission needed is that of root. We will install the Linux client using the command line. Start a terminal by clicking on Applications, System tools and choosing Terminal. become root (the Linux equivalent of Administrator) by typing su - This will prompt you for a password, enter the password for root. change directory (cd) to the directory that holds the client installation files. Linux is case sensitive so keep that in mind. make the installer executable by typing the following chmod +x install and then install the client using the following command (for an X64 server os, use the corresponding X86 file if it's 32 bit). Change the management point FQDN and sitecode to match your infrastructure. ./install -mp sccm.server2008r2.lab.local -sitecode P01 ccm-Universalx64.1.0.0.4580.tar After some moments you'll see Installation Complete, if you get a "Pre-Install validator failed. Please check the version of OpenSSL with CM installation requirements" try the -ignoreSHA256validation switch as specified here. You can review what's happening realtime via the log file using the following command tail -F /var/opt/microsoft/scxcm.log Tip: to uninstall the client use /opt/microsoft/configmgr/bin/uninstall Step 5. Change logging options Logging for the Linux based client is pretty much all done in one log file called scxcm.log contained in /var/opt/microsoft/. How that log file gets written to is governed by the following configuration file /opt/microsoft/configmgr/etc/scxcm.conf. Below is what the conf file looks like by default:- FILE ( PATH: /var/opt/microsoft/scxcm.log MODULE: WARNING MODULE: scx.client WARNING ) using vi or your favorite text editor in Linux, change it so that it now reads as follows FILE ( PATH: /var/opt/microsoft/scxcm.log MODULE: TRACE MODULE: scx.client TRACE ) save the changes and stop and then start (or simply restart) the Linux client To start the client: /etc/init.d/ccmexecd start To stop the client: /etc/init.d/ccmexecd stop Tip: The default logging mode for the scxcm.log file is WARNING which Indicates possible problems for the client operations. TRACE mode logs verbosely. As the log file is not trimmed in any way, when you are finished doing your diagnosis it is recommended to change it back to WARNING mode and restart the client daemon. Step 6. Approve the Linux client In the Configuration Manager console, locate the new linux client in Devices, and right click choose Approve. answer yes when prompted the client is now listed as Approved in the console Step 7. Request a machine Policy as root issue the following command /opt/microsoft/configmgr/bin/ccmexec -rs policy in the log file above you can see the word TRACE repeated over and over, this confirms that our change to the logging options were indeed processed and it's now in Trace mode. Step 8. Perform a hardware inventory Hardware inventory on a Linux or UNIX server runs according to the schedule you configure in client settings. By default, this is every seven days. The client for Linux and UNIX supports both full inventory cycles and delta inventory cycles. You can also force the client on a Linux or UNIX server to immediately run hardware inventory. To run hardware inventory, on a client use root credentials to run the following command to start a hardware inventory cycle: /opt/microsoft/configmgr/bin/ccmexec -rs hinv as root issue the following command /opt/microsoft/configmgr/bin/ccmexec -rs hinv on your Configuration Manager server, you can check the MP_HINV.log and look for the HINV details from our Centos computer coming in... now's a good time to start Resource Explorer in the console to see what info it has got and here is what the installed applications look like and that's it, you've installed the Alternative client on our Centos server and performed a Hardware Inventory and got the information uploaded to your Primary server. You can even install RPM packages using Packages (and programs). I'll deal with that in a separate post. until then, adios niall. Related Reading How to Install Clients on Linux and UNIX Computers in Configuration Manager - http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj573939.aspx Microsoft System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager - Clients for Additional Operating Systems - http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=39360# Hardware Inventory for Linux and UNIX in Configuration Manager - http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj573945.aspx ConfigMgr 2012 SP1 and UNIX/Linux Clients – Part 1: Introduction and Client - http://blogs.technet.com/b/manageabilityguys/archive/2013/04/11/configmgr-2012-sp1-and-unix-linux-clients-part-1-introduction-and-client.aspx ConfigMgr 2012 SP1 and UNIX/Linux Clients - Part 2: General Operations and Inventory - http://blogs.technet.com/b/manageabilityguys/archive/2013/05/03/configmgr-2012-sp1-and-unix-linux-clients-part-2-general-operations-and-inventory.aspx Get help with Linux - http://www.linux-noob.com
-

"IT Organization" Text SCCM 2012 SP1
anyweb replied to abremel's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
great, it works because the default client settings apply to everything in the hierarchy -

Slow image deployment download since SCCM 2012 R2 upgrade
anyweb replied to Gareth86's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
are all of you using vmware ? have you checked for any updates to vmware to support the newer boot images ? -

"IT Organization" Text SCCM 2012 SP1
anyweb replied to abremel's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
change it in the Default Client settings, then update your boot image(s) to your distribution points. -

Post Config Manager 2012 R2 Upgrade Errors - Help Needed
anyweb replied to TopherWilkes's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
ok thanks, i've filed a bug on connect and pointed to this post, thanks for your information and troubleshooting- 6 replies
-
- configuration manager 2012 r2
- configuration
-
(and 5 more)
Tagged with:
-

Post Config Manager 2012 R2 Upgrade Errors - Help Needed
anyweb replied to TopherWilkes's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
Hi David and Topher, can you please tell me what your patch statement said and where you had it defined (client installation properties ?), did both of you have Automatic client upgrade selected ? I'm raising a bug on connect for this issue cheers niall- 6 replies
-
- configuration manager 2012 r2
- configuration
-
(and 5 more)
Tagged with:
-
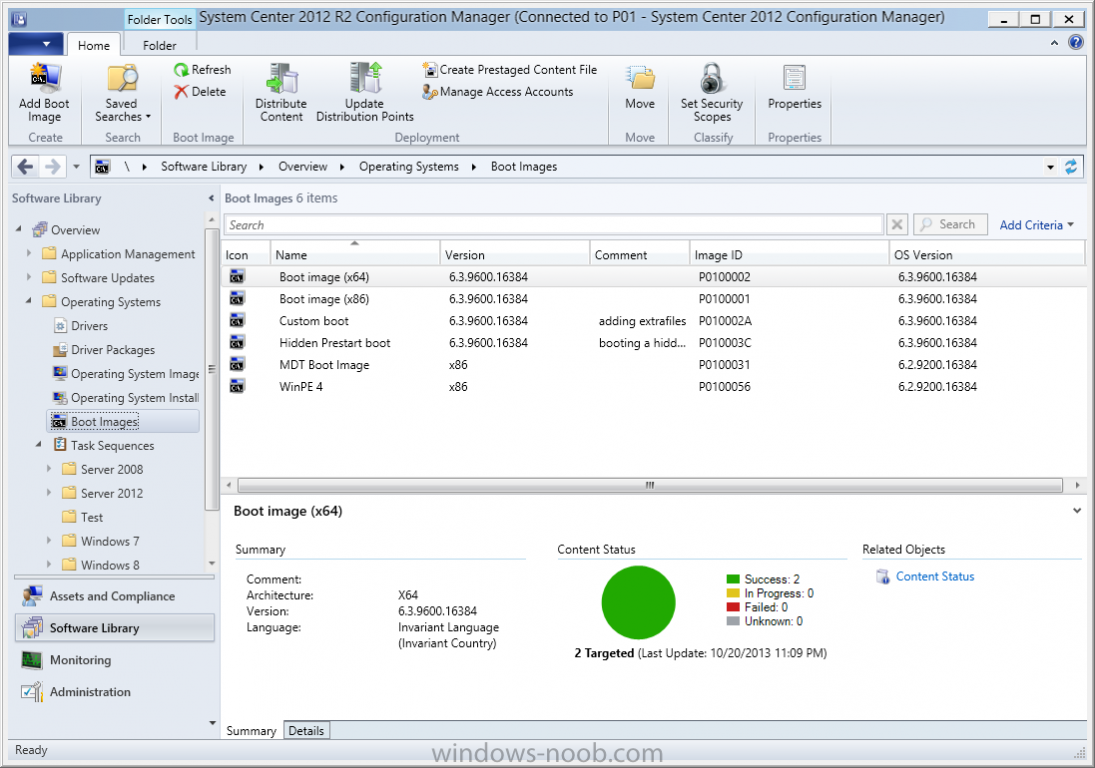
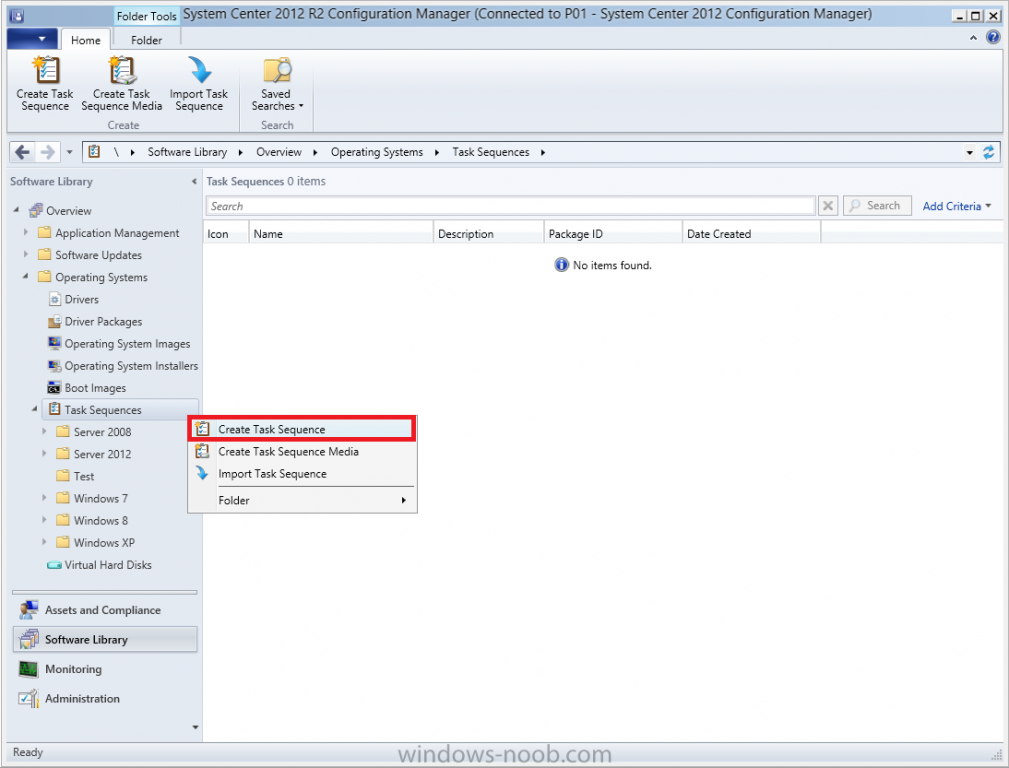
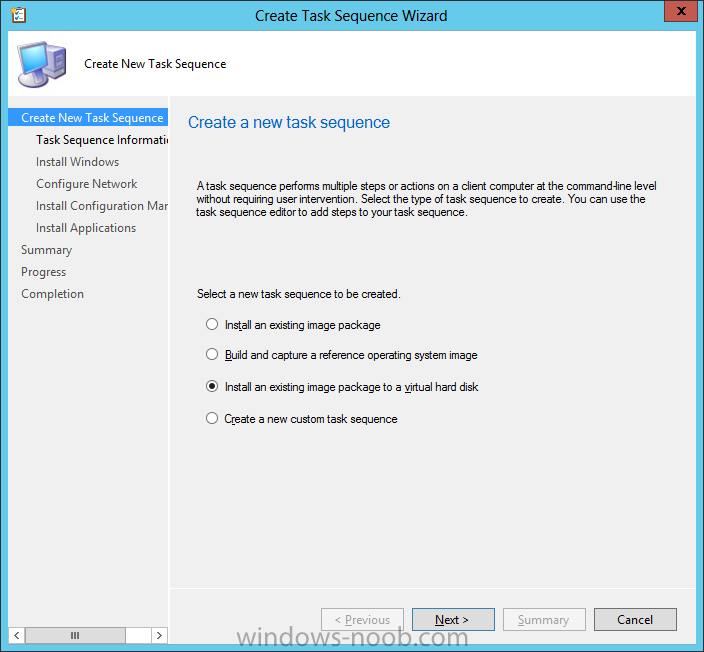
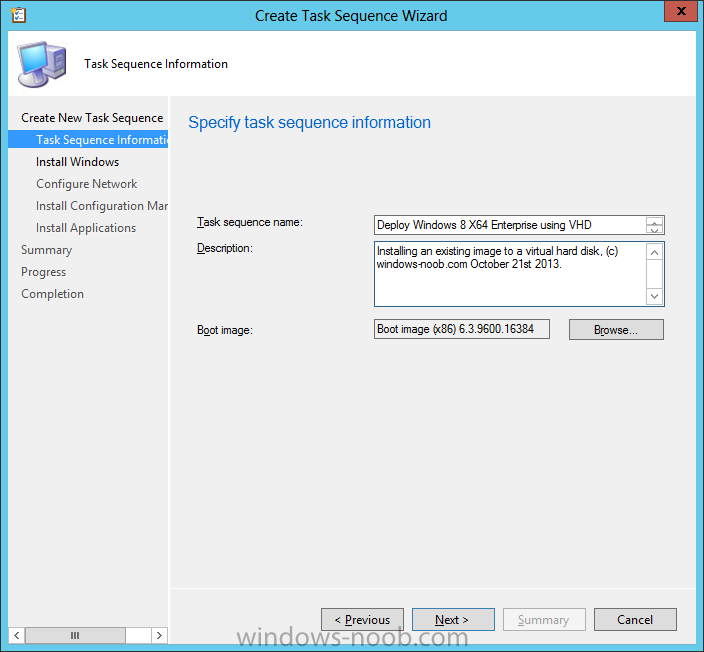
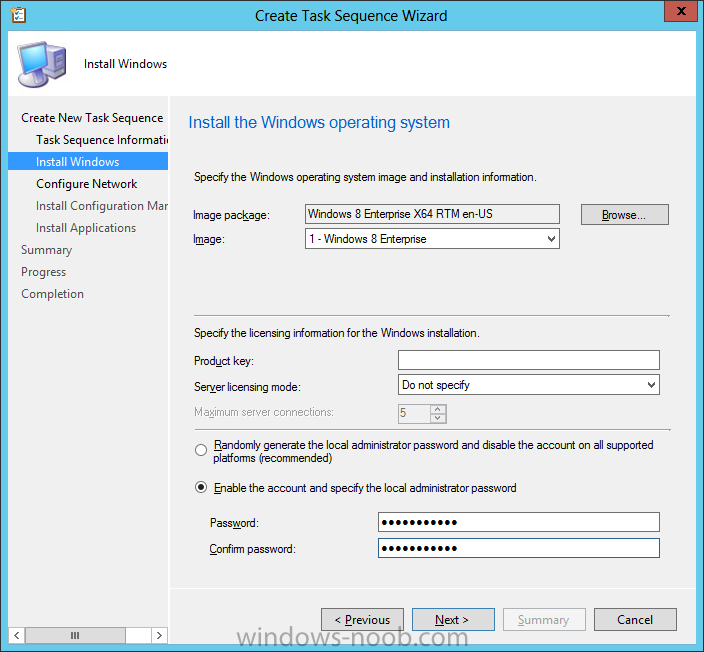
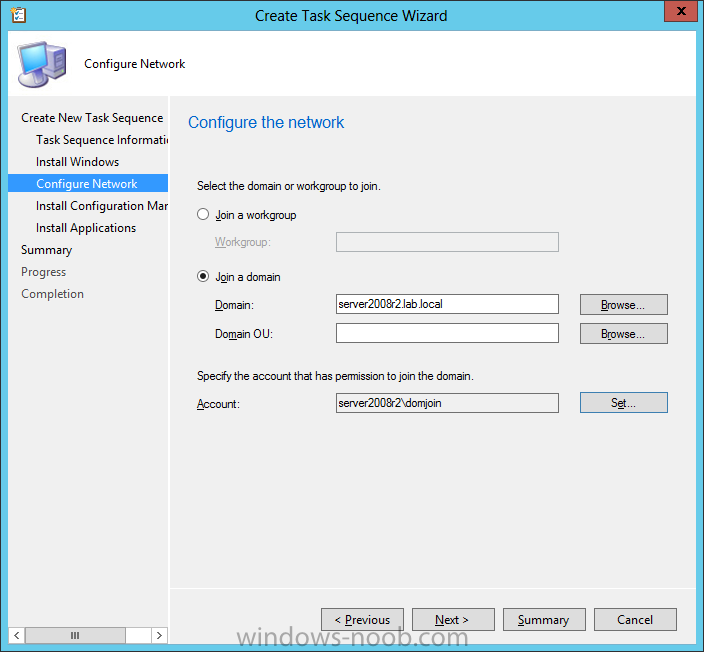
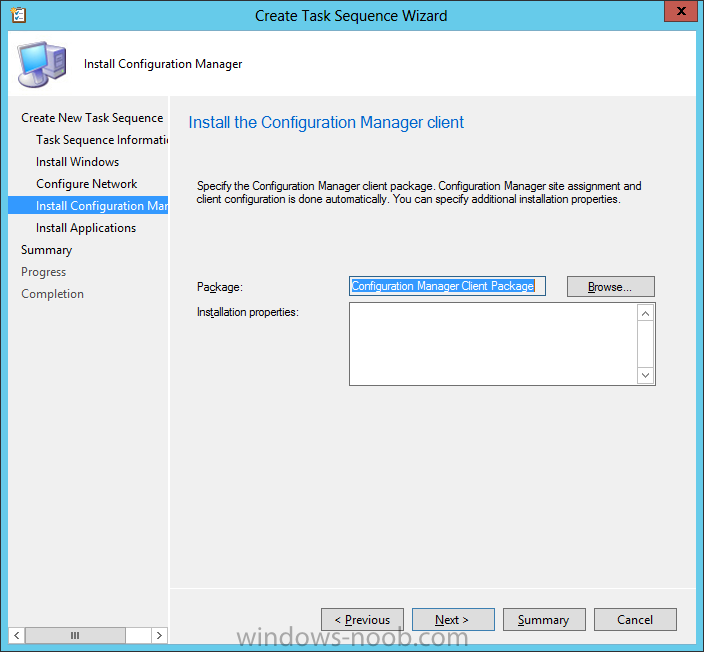
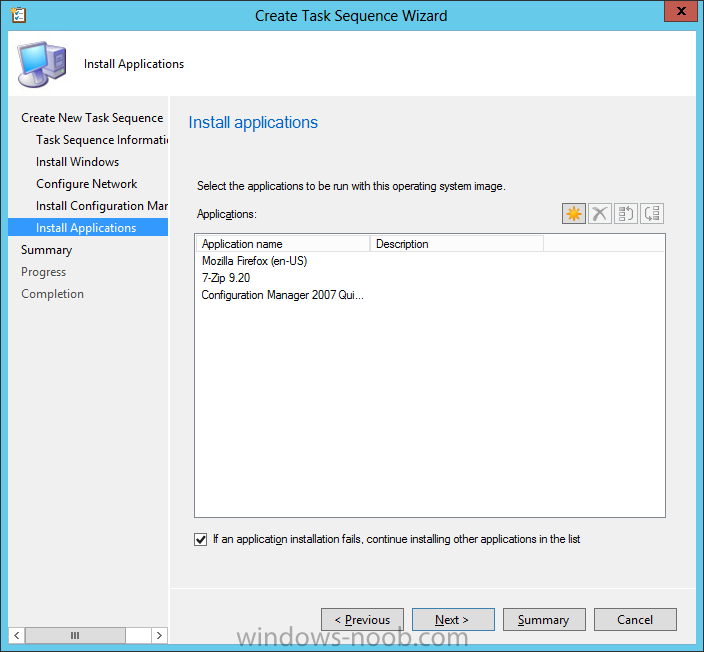
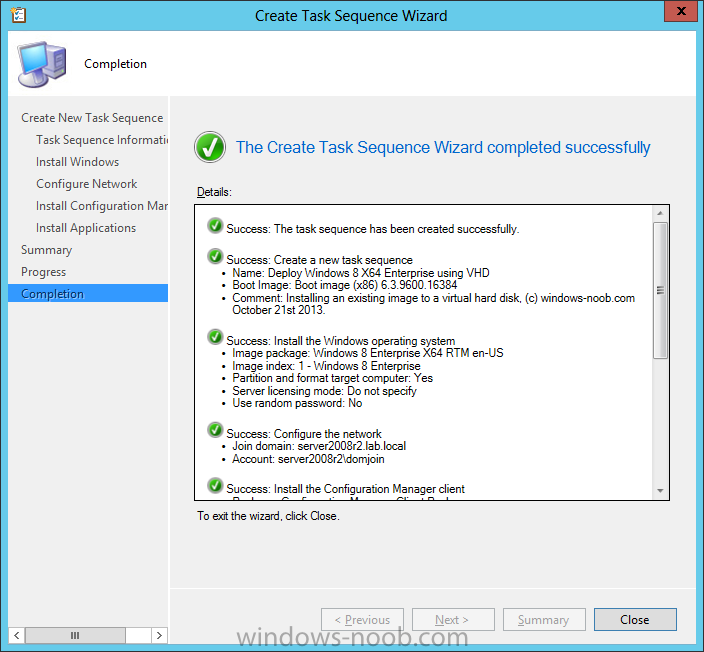
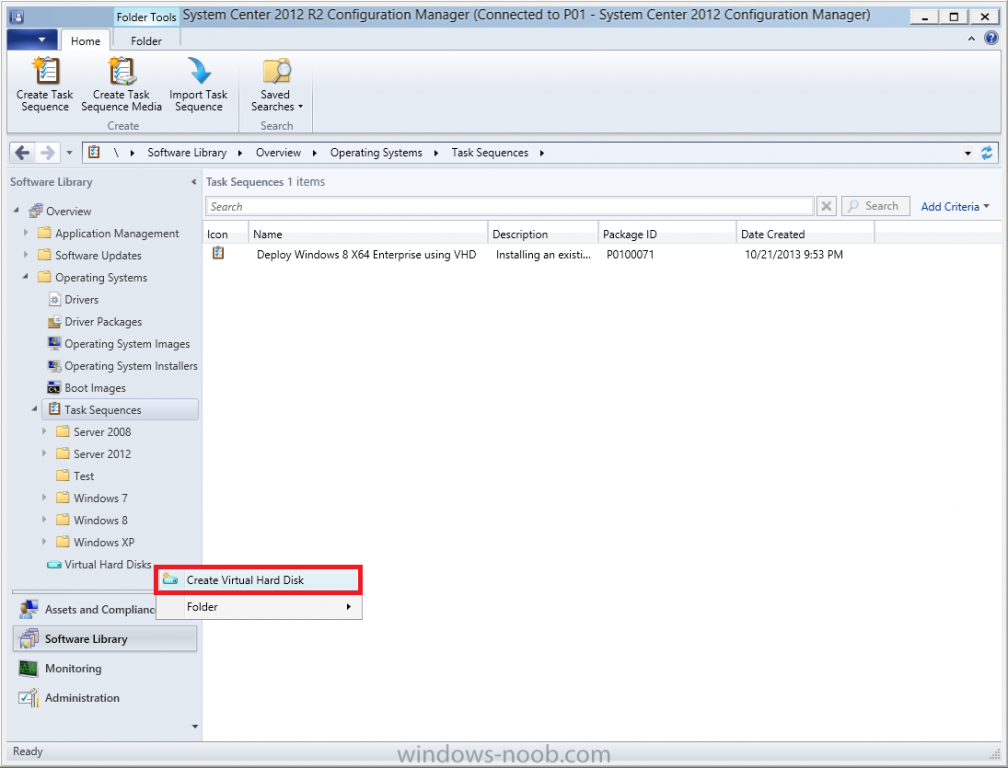
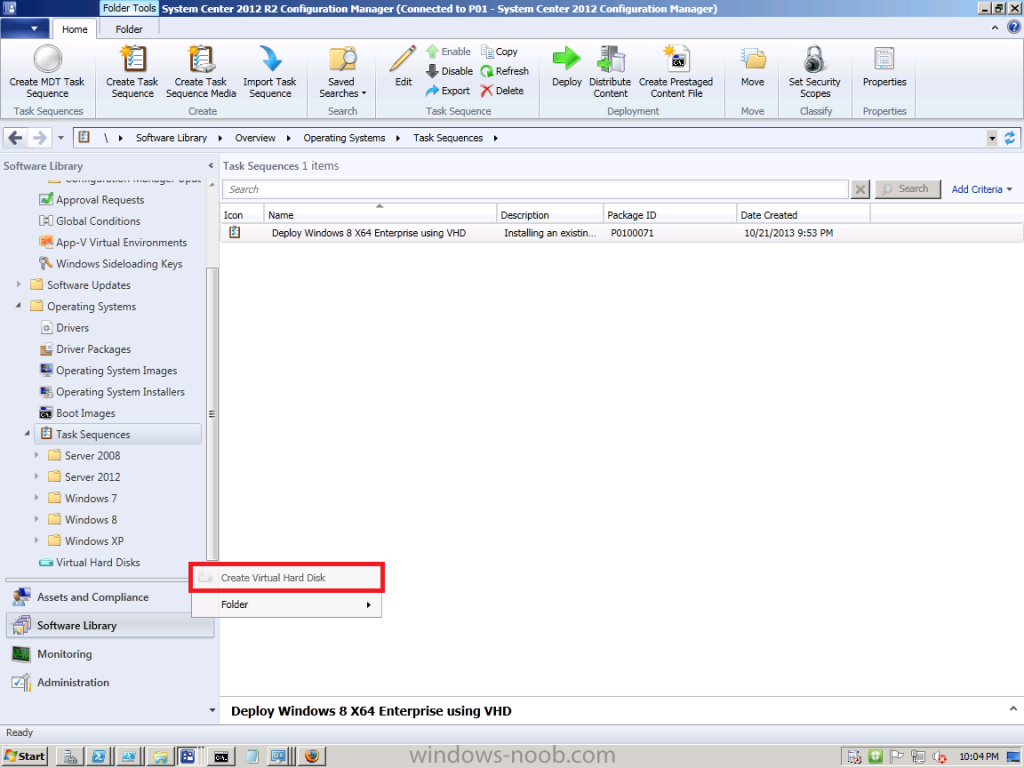
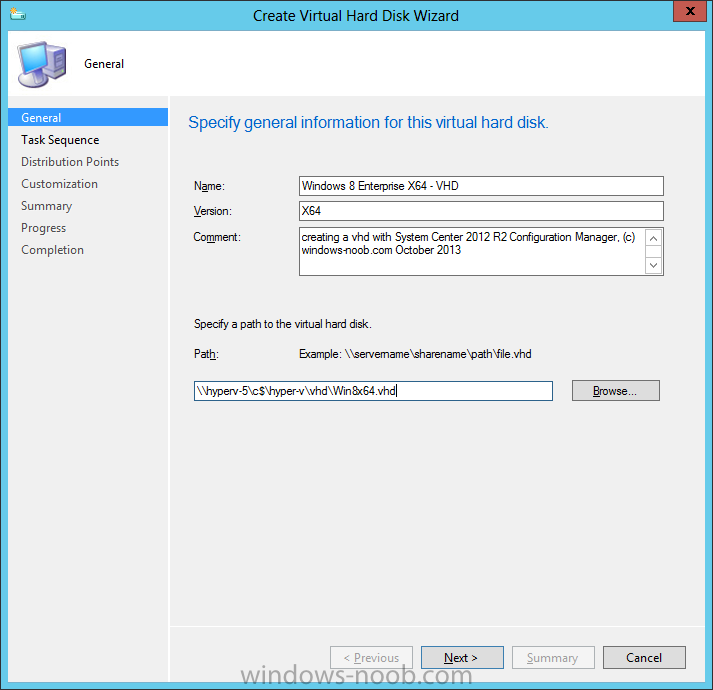
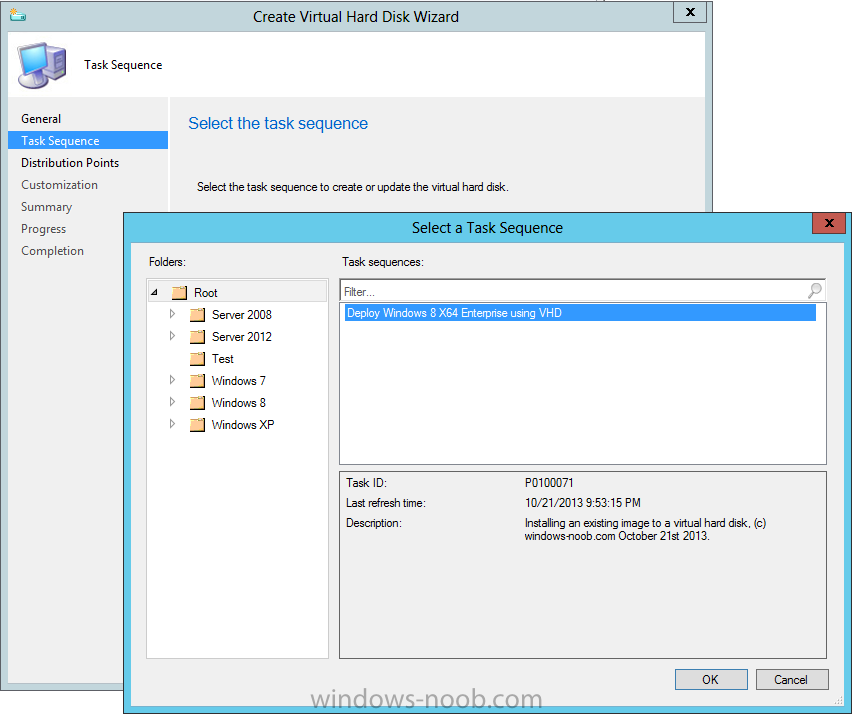
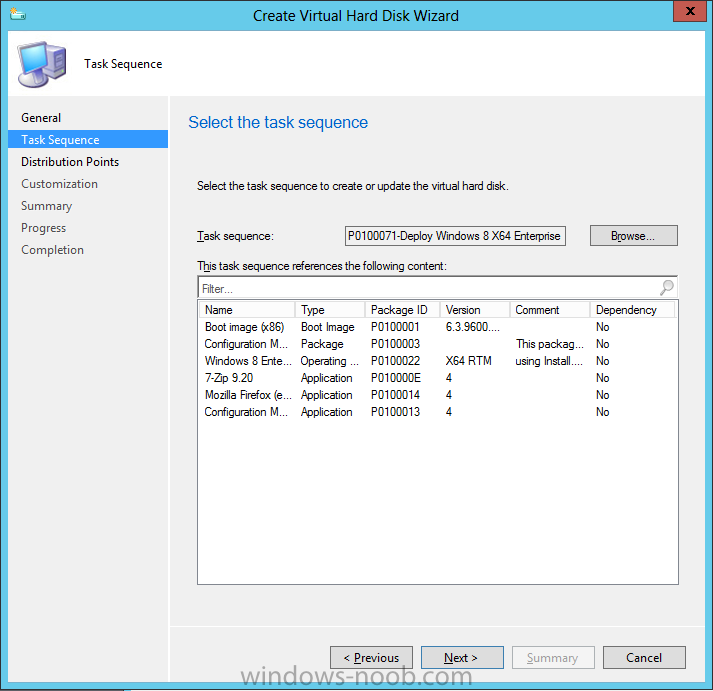
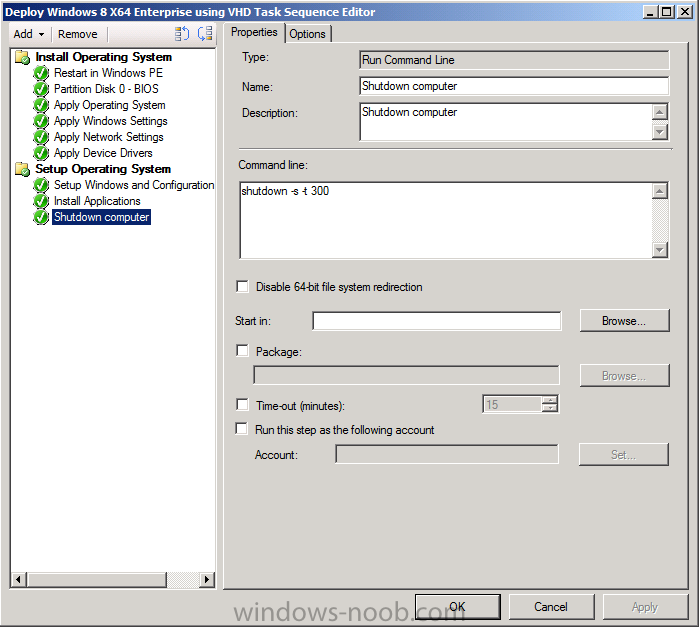
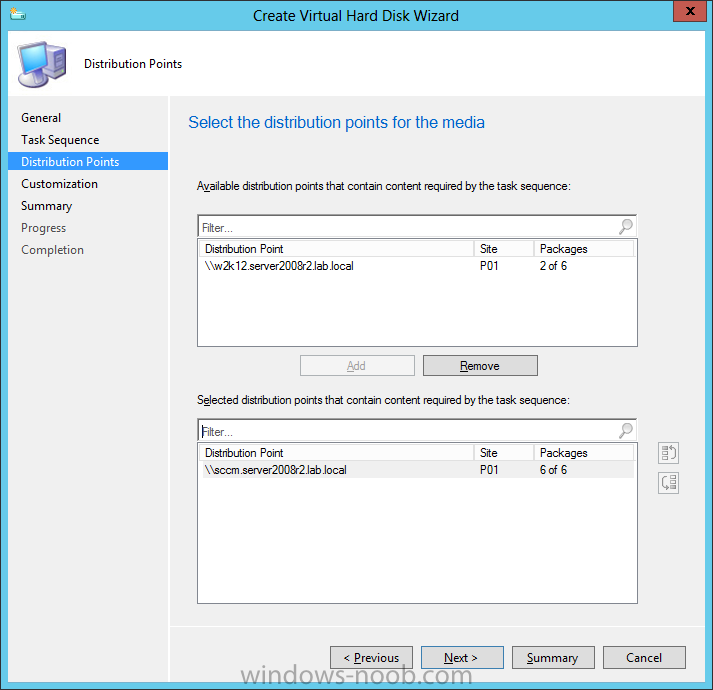
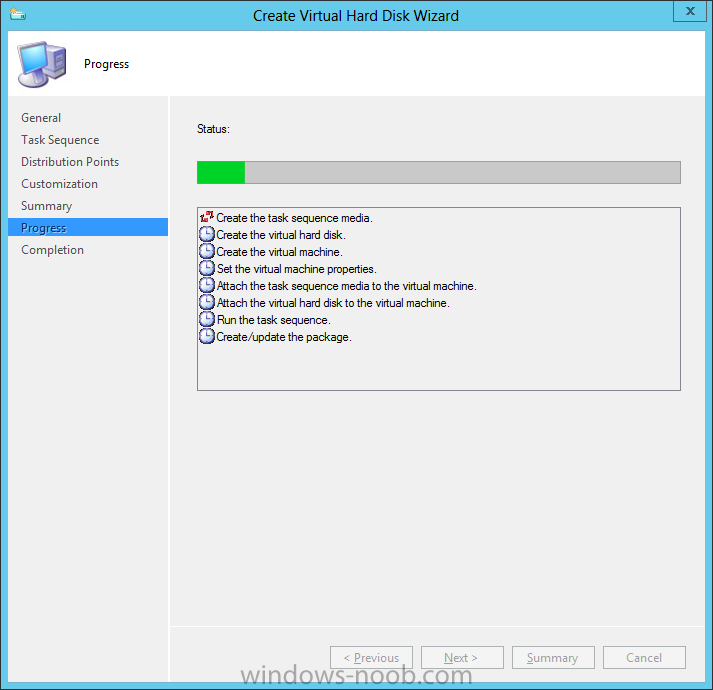
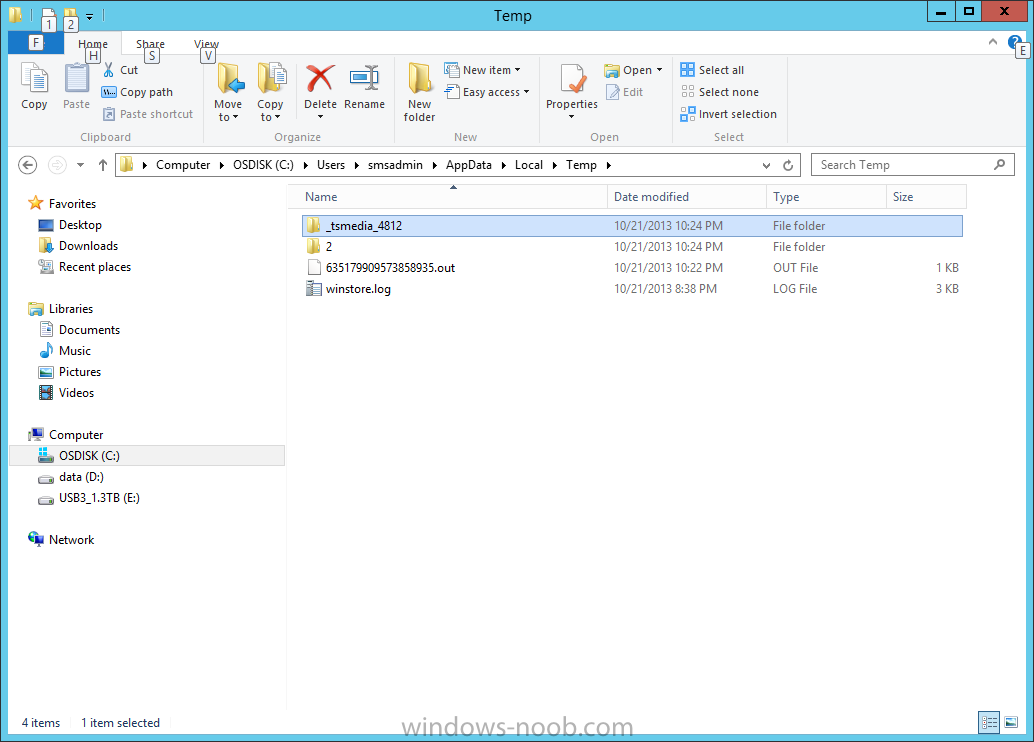
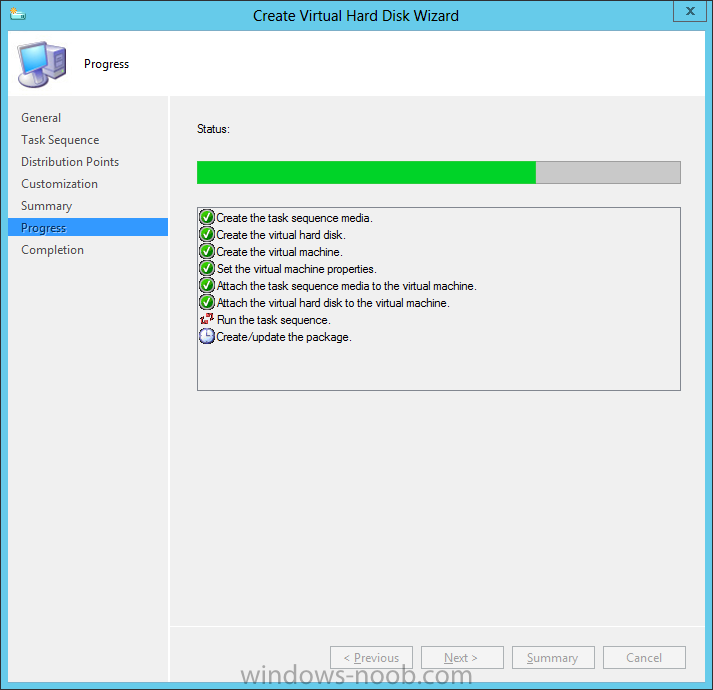
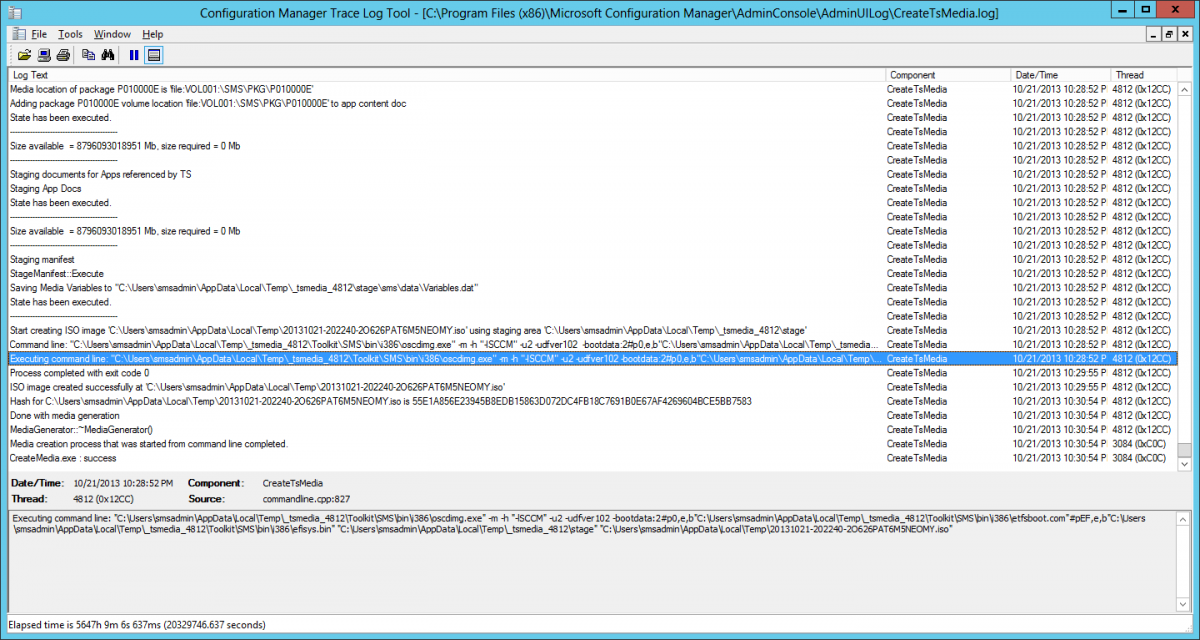
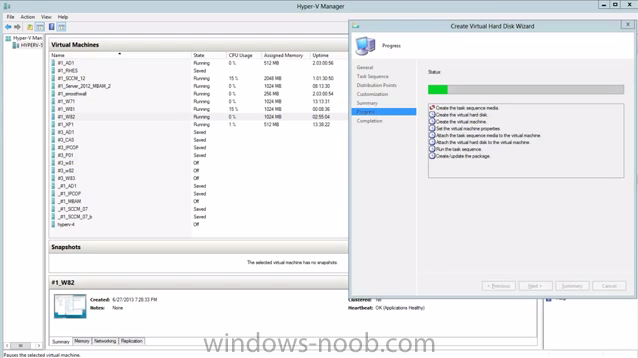
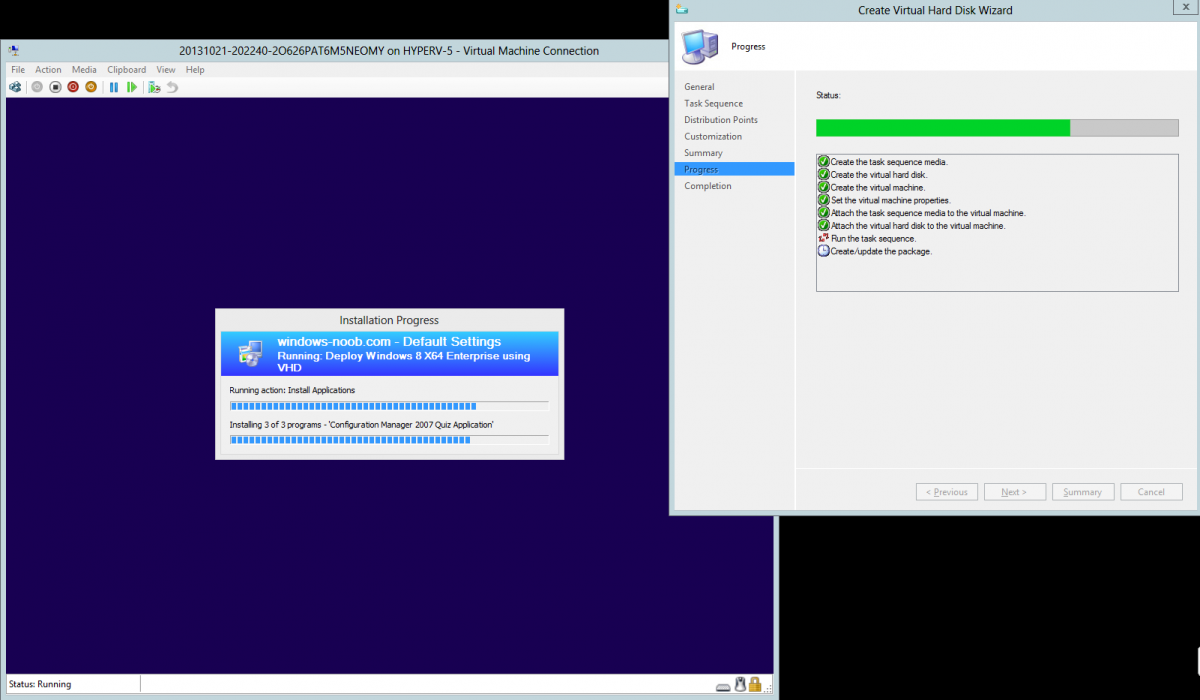
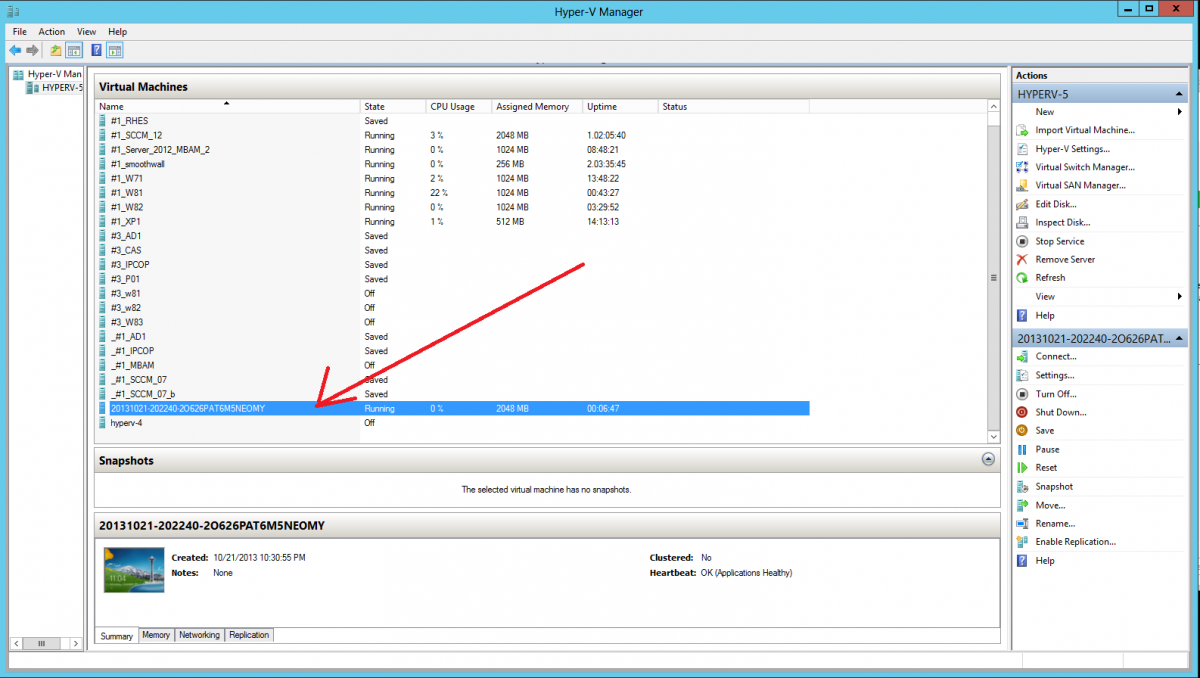
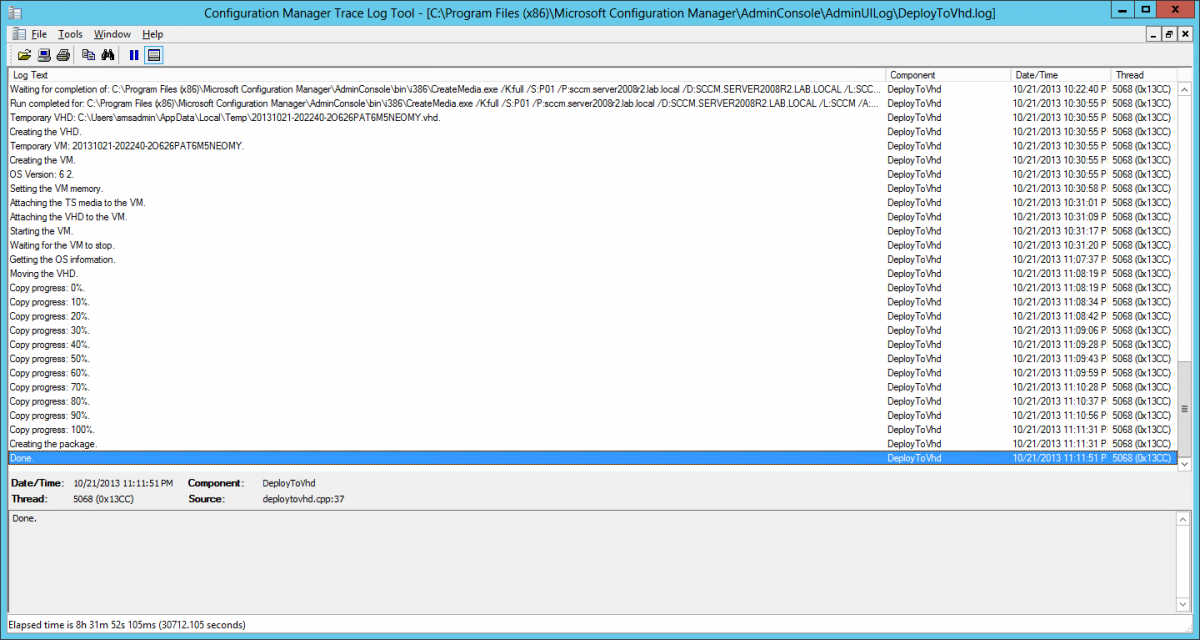
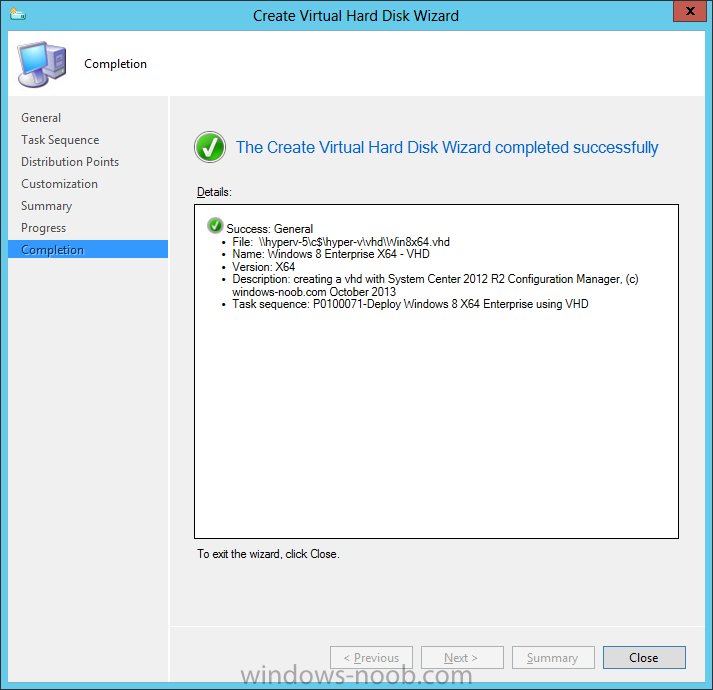
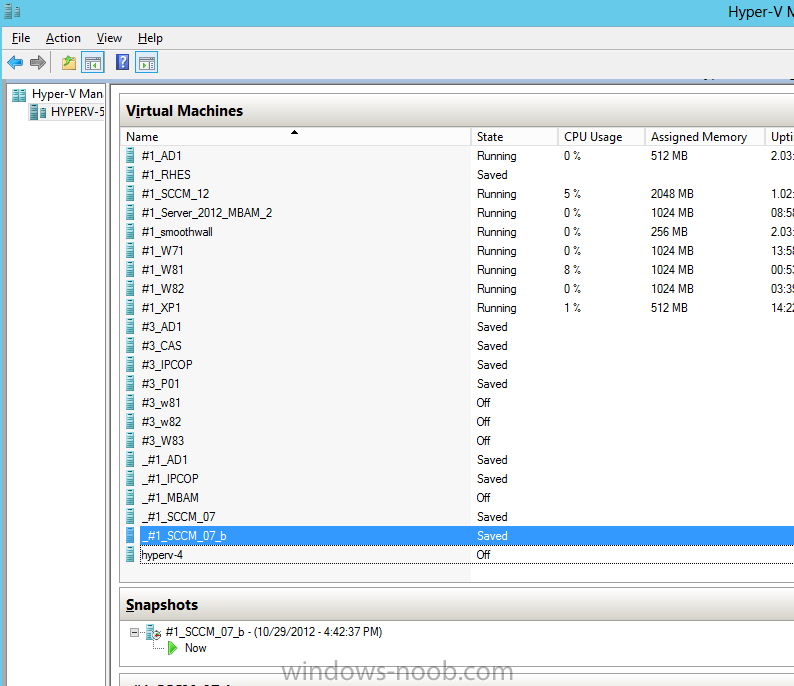
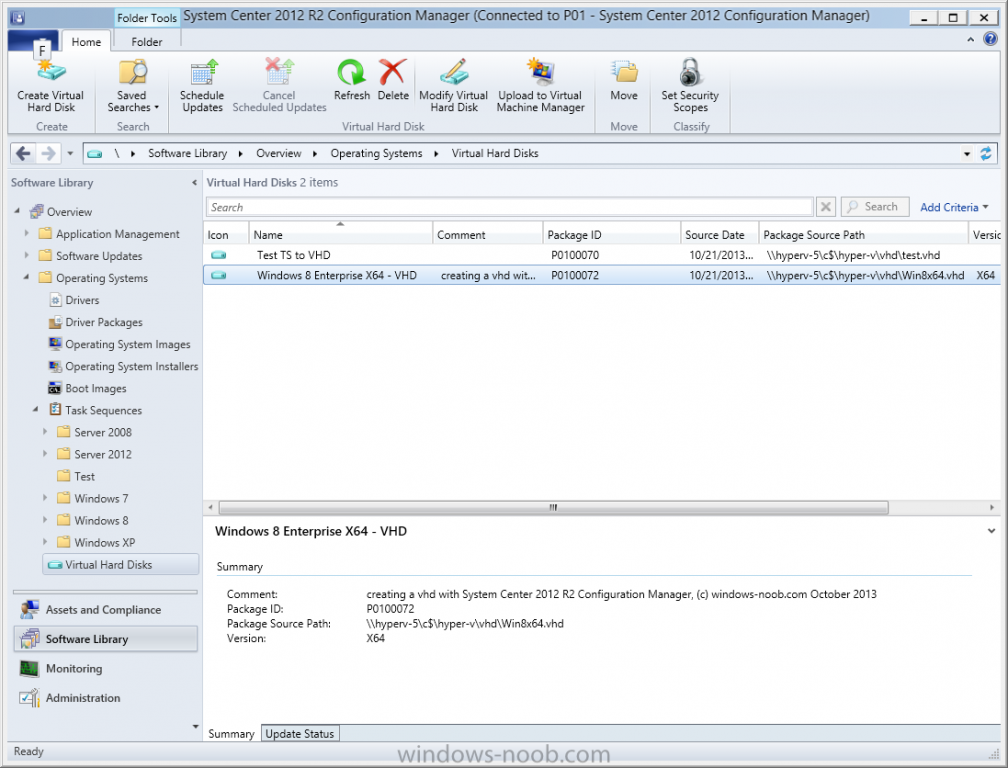
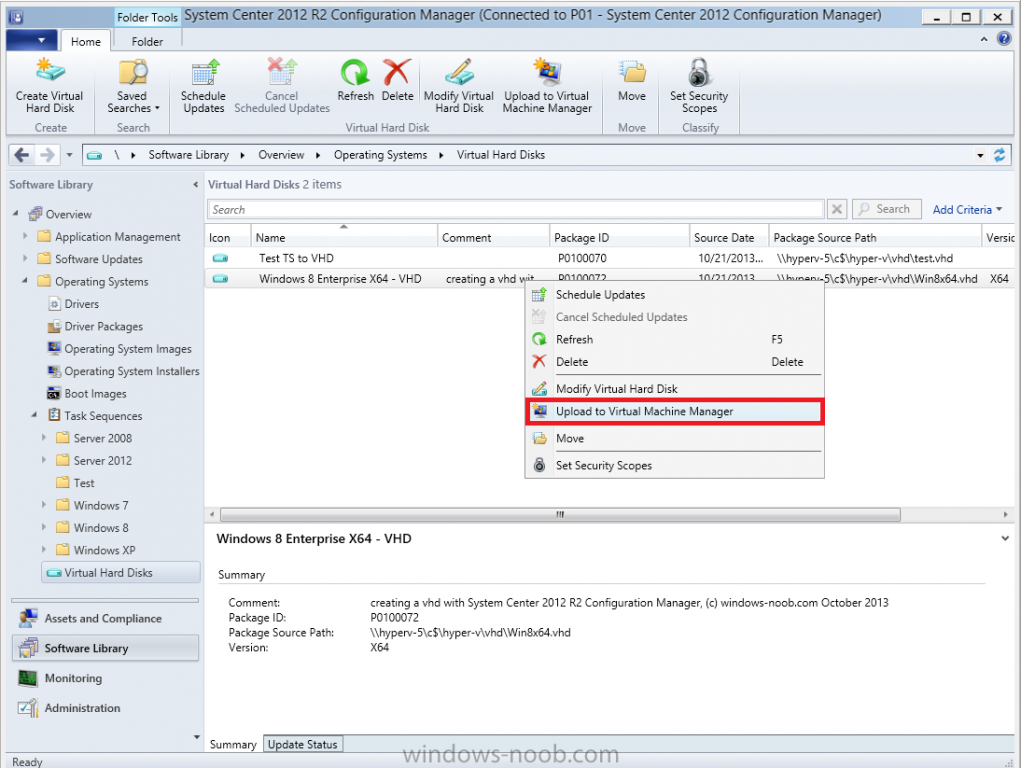
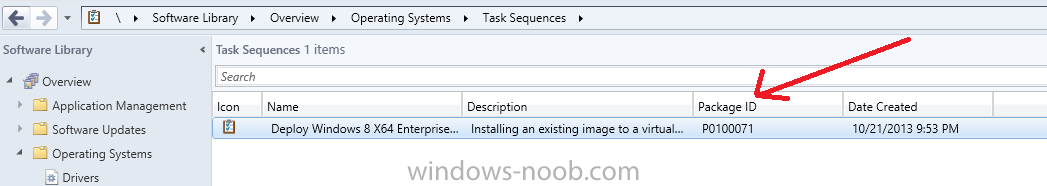
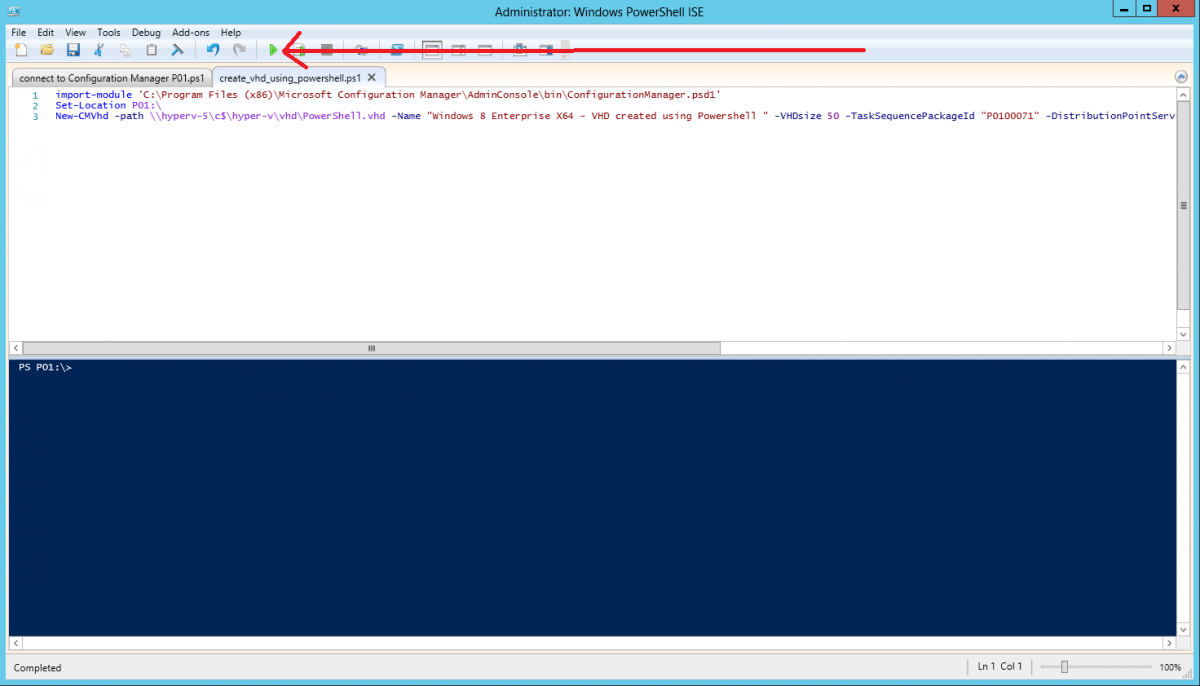
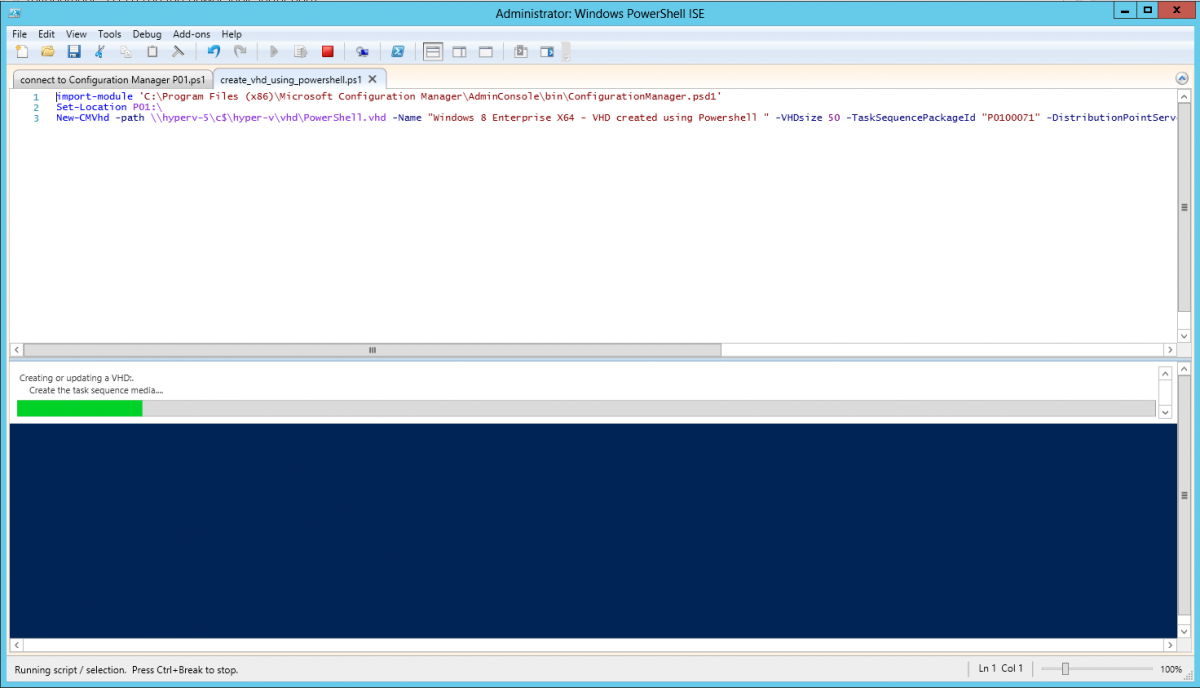
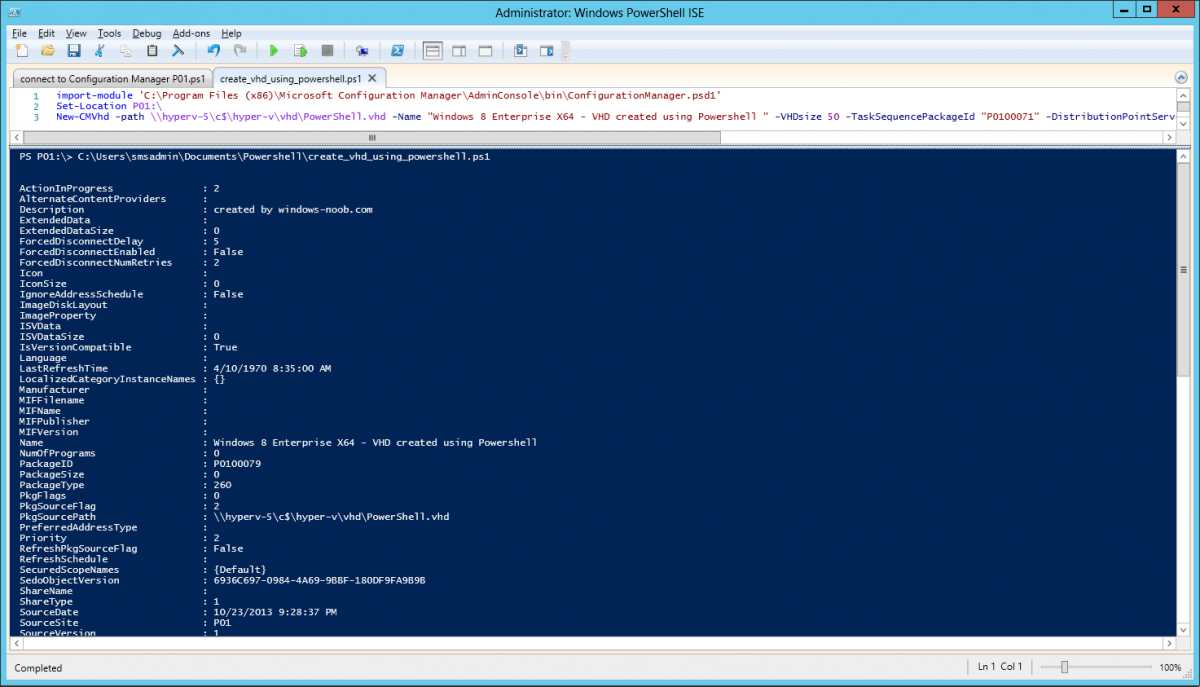
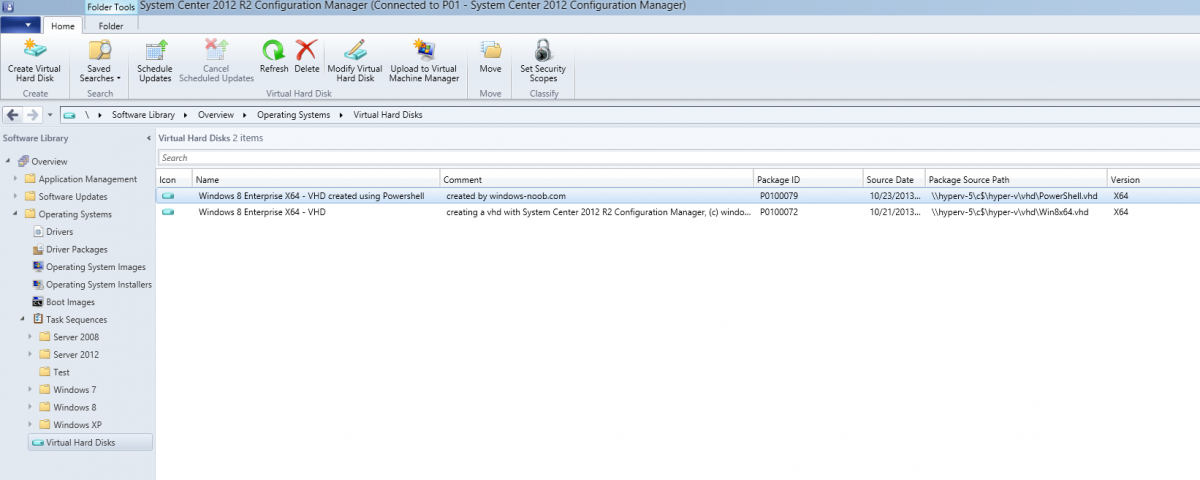
Introduction Microsoft released System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager on October 18th, 2013 as planned (General Availability) and now we all have the ability to test the new features in the finished product. I've installed it in my lab and wanted to test the New operating system deployment features, one of which is the ability to create a VHD from a task sequence right from the Configuration Manager console. Before getting started however you'll need to have at least one host capable of running HyperV (such as Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012R2) with the System Center 2012 Configuration Manager console installed. Tip: You'll need System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager installed, here's a step by step guide to get your started. Step 1. Create a new task sequence Note: Perform the following on any computer with the System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager AdminConsole installed as SMSAdmin. Open the Admin console, expand Software Library, Operating System Deployment and right click on Task Sequences, choose Create Task Sequence. choose the third option, install an existing image to a virtual hard disk choose a suitable name for your task sequence and select a boot image In this task sequence I am deploying Windows 8 X64 Enterprise using the Install.wim file from the DVD, I also select to enable the Administrator account and I specify a password select to Join a domain and fill in appropriate domain join credentials and install the configuration manager client, you can add switches here if needed and select to install some applications if you wish click next through to the completion message You can now edit the task sequence if you wish and add/remove steps, note the last step is a shutdown command, this is a special step and is 'looked for' by the wizard later on so that it knows the task sequence is complete and to generate the VHD. Step 2. Create a Virtual Hard Disk Note: Perform the following on a HyperV host computer with the System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager AdminConsole installed as SMSAdmin. Method #1 - Do it using the AdminConsole In the Admin console Expand the Task Sequences node in Operating System Deployment and right click on Virtual Hard Disks. If this is greyed out it's because you are not running the console on a Hyperv Enabled host (I've tested it on Server 2012 running Hyperv with the R2 admin console installed). To make it clear, i'm including two screenshots of the same action, one on a hyperV host, the other is an adminconsole with no hyperV hosts locally installed. Note: the below screenshot is on a host without hyperv installed or enabled. Note how the Create Virtual Hard Disk action is greyed out. Note: the below screenshot is on a hyperv host Now that we've started the create virtual hard disk wizard, fill in some details about our virtual hard disk. next select our task sequence that we created in Step 1 and depending on how complicated the task sequence was it will take some time to generate a list of task sequence referenced content select a distribution point that has all the packages on it (XX of XX) and click your way through the wizard, at this point you'll see be prompted to allow access to your host computer (to create the file) and shortly after the magic begins The task sequence media creation is logged in the CreateTSMedia.log file located on the hyperv host running the adminconsole (Typically C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Configuration Manager\AdminConsole\AdminUILog) The user you are logged in as will have it's AppData\Local\Temp dir used as a temporary scratch space, so make sure you have lots of space if needed or use the link at the bottom of this page to change your TMP environment variables to point to a drive with more free space. and off it goes creating the virtual hard disk (look at this video to see the process in more detail, watch above the hyperv4 vm to see the new virtual machine being created, this video has no audio yet, it's coming hopefully if i get time...) This involves, automatically creating a temporary virtual machine in hyperV, starting it automatically, starting the task sequence automatically and finally sealing the VHD file which can then be seen in the configuration manager console. Below you can see the temporary virtual machine in hyperv shortly before the VHD is created (task sequence is complete) The temporary virtual machine continues to run the task sequence, eventually installing our applications once complete the Virtual machine shutsdown and the VHD copying starts, you can now monitor the DeploytoVHD.log file (in C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Configuration Manager\AdminConsole\AdminUILog) When the logfile confirms the process is done then you can assume that the wizard is also complete...and it is... :-) and you'll notice that the temporary virtual machine is gone and clicking on Virtual Hard Disks in the Admin console will list our newly created VHD file, success ! at which point you can modify the VHD (by choosing that action in the ribbon or via right click) or just upload it to Virtual Machine Manager. Method #2 - Do it using PowerShell Start PowerShell ISE (PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment) as Administrator and paste in the following code import-module 'C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Configuration Manager\AdminConsole\bin\ConfigurationManager.psd1' Set-Location P01:\ New-CMVhd -path \\hyperv-5\c$\hyper-v\vhd\PowerShell.vhd -Name "Windows 8 Enterprise X64 - VHD created using Powershell " -VHDsize 50 -TaskSequencePackageId "P0100071" -DistributionPointServerNames SCCM.server2008r2.lab.local -Version "X64" -Description "created by windows-noob.com" The first two lines simply import the configuration manager powershell module and then set your path to your primary server P01. The New-CMvhd cmdlet is a new cmdlet in R2 and it is used to create the VHD using powershell. In the above, the -TaskSequencePackageId value is the PackageID of your task sequence, make sure to set the appropriate values in the New-CMvhd command to suit your environment (for example your server share). Click on the Green arrow to run your powershell script and off it goes ! and after some VHD creation...............job done ! and our VHD appears in the console not too bad eh ? cheers niall Related reading What’s New in System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager - http://technet.microsoft.com/library/dn236351.aspx How an I install System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager - How can I install System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager ? Changing the TMP variable for OSD media creation - http://blogs.technet.com/b/configmgrteam/archive/2013/07/16/customizing-the-temporary-location-for-osd-media-creation.aspx Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) - http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd819514.aspx using System Center 2012 Configuration Manager - Part 12. Connecting PowerShell and Building a reference image of Windows 8 with .Net 3.5 Configuration Manager SP1 Cmdlet Reference - http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj821831.aspx