-
Posts
9251 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
369
Everything posted by anyweb
-
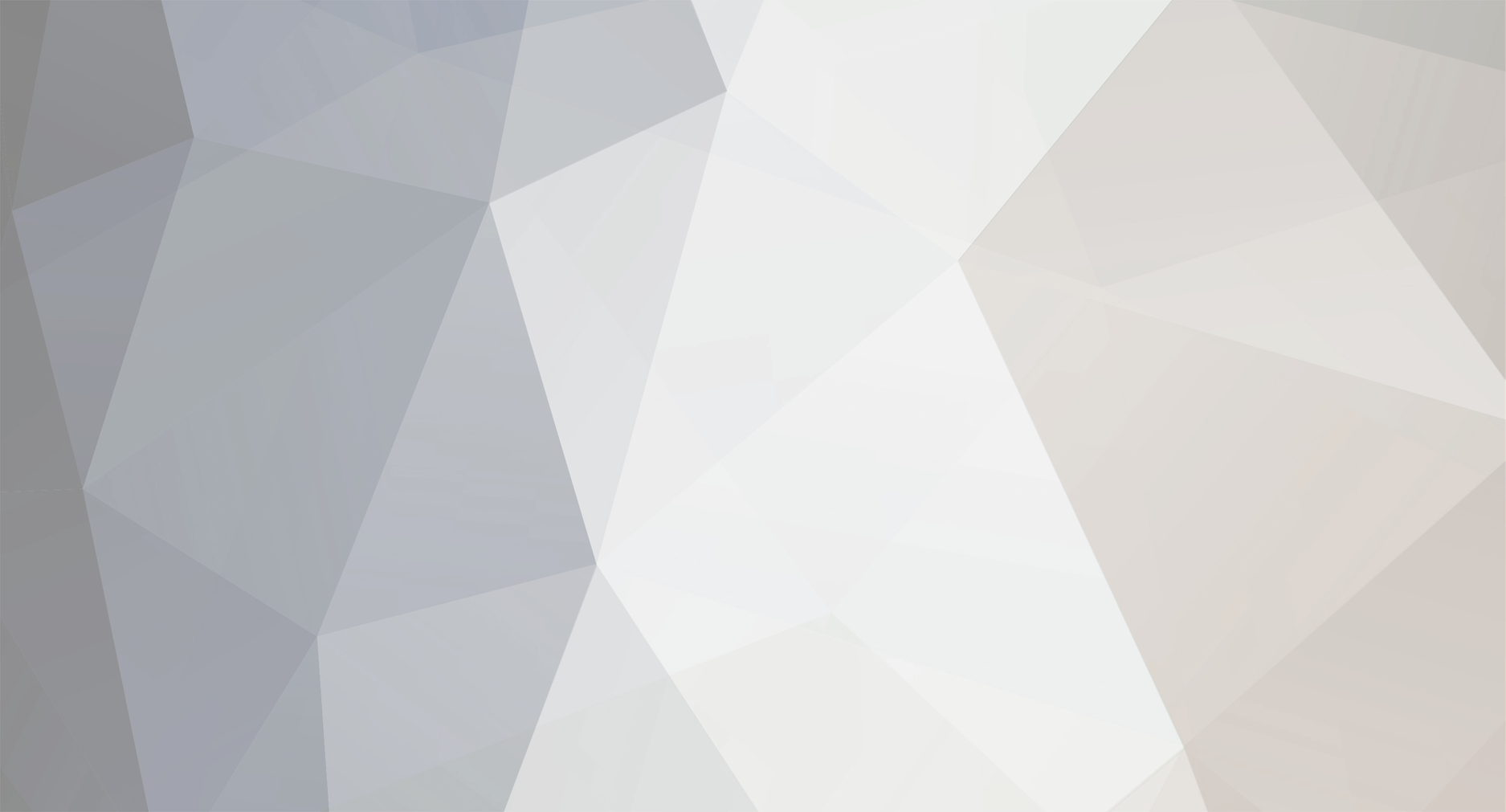
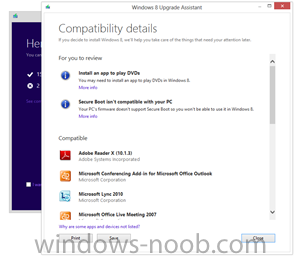
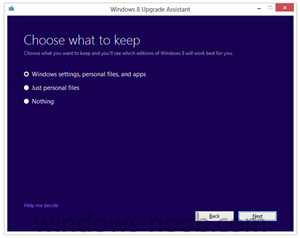
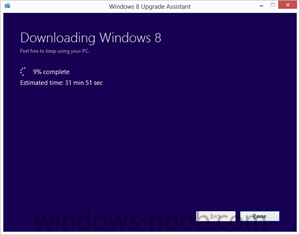
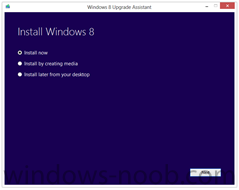
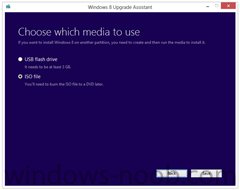
We set out to make it as easy as possible for everyone to upgrade to Windows 8. Starting at general availability, if your PC is running Windows XP, Windows Vista, or Windows 7 you will qualify to download an upgrade to Windows 8 Pro for just $39.99 in 131 markets. And if you want, you can add Windows Media Center for free through the “add features” option within Windows 8 Pro after your upgrade. When you use Windows.com to purchase an upgrade to Windows 8 Pro, the Windows 8 Upgrade Assistant makes upgrading simple by walking you through the upgrade process step-by-step from purchase to download and then of course installation. The Windows 8 Upgrade Assistant will check to make sure your PC is ready for Windows 8. It will provide a detailed compatibility report that lets you know of anything you may have to address before or after the upgrade and outlines actions to take. It will also inform you of any application or device compatibility issues. It will ask you what you want to keep from your current Windows installation. You will be able to upgrade from any consumer edition of Windows 7 to Windows 8 Pro and bring everything along which includes your Windows settings, personal files, and apps. If you are upgrading from Windows Vista, you will be able to bring along your Windows settings and personal files, and if you are upgrading from Windows XP you will only be able to bring along your personal files. Of course, if you want to start fresh, you can choose to bring nothing along. Or if you prefer to format your hard drive as part of your upgrade experience, you can do so as long as you boot from media and then format your hard drive from within the setup experience for installing Windows 8, not prior to it. Once you purchase your upgrade, the Windows 8 Upgrade Assistant kicks off your download. It has a built-in download manager that allows you to pause and continue your download at any time as well as a check to ensure your download completes successfully. After your download finishes, you can choose to proceed with the upgrade (“Install now”) or install later either from your desktop or by creating your own media. If you choose to create your own media, you will be able to create your own bootable USB or .ISO file which can be burned onto a DVD for upgrade and backup purposes. If you prefer, you also have the option of purchasing a backup DVD for $15 plus shipping and handling. We believe that your upgrade experience in Windows 8 will be a breeze by offering a faster experience, a single upgrade path, and compatibility from prior versions of Windows. We’ve continued to listen to our customers and have expanded the ability to download to over 100 countries and 37 languages. We have simplified the Windows upgrade experience with the Windows 8 Upgrade Assistant which supports you during your upgrade with everything from selecting your language to pausing your download to built-in compatibility checks - it’s seamless. And if you’re an enthusiast you will have the flexibility to download and control how you upgrade. If you prefer to shop at a local store, a packaged DVD version of the upgrade to Windows 8 Pro will be available for $69.99 during this promotion. This upgrade promotion for Windows 8 Pro both online and at retail runs through January 31st, 2013. We wanted to share information about this upgrade promotion with you as we continue to drive toward the RTM milestone for Windows 8. We will of course have more to say and more details to provide closer to general availability. Oh, and by the way - if you’re not upgrading from a prior version of Windows and are building your own PC or installing Windows 8 in a virtual machine or a separate partition, you will be able to purchase and install the Windows 8 and Windows 8 Pro System Builder product. via > windowsteamblog
-
best practise would entail separating the different programs (OS, Configuration Manager, SQL Server 2008) to different physical disks and to use RAID 10, for example OS on C:\, Configmgr on D:\ SQL on E:\ and so on.. but as this is only a lab i've just installed Configuration Manager and SQL Server 2008 R2 on D:\. The reason you'd keep them on different physical discs is all about IOPS (input output per second). If you want more info on that see here and refer to the advice from Technet here, from which I've pasted some info below..
-

Config Manager 2012 install issue
anyweb replied to jldeanley77's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
are you logged in as the SMSadmin user ? -

SCCM 2007 Deploying Windows 7 with Boot Media
anyweb replied to randy21m's topic in Configuration Manager 2007
press F8 at the start of the apply operating system step, does that work ? that way you can capture the log...- 2 replies
-
- 0x80070002
- SCCM 2007
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with:
-
and that link (amongst others) is already included in Part 1 of my new series underneath Technet Recommended Reading, f.y.i cheers niall
-

Password Protect a Task Sequence?
anyweb replied to thadkew's question in Frontends, HTA's and Web Services
then your abortscript will simply do as follows replace c: with a variable like OSdisk, you can create the OSDISK variable using a script to check for the presence of c:\windows\explorer.exe -
you didnt post any errors ?
-

The Unknown Computer (x64) Account was accidentally deleted
anyweb replied to akirk06's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
what about this ? http://www.niallbrady.com/2012/05/24/oops-you-deleted-the-unknown-computers-collection-in-configuration-manager-2012/ -
Summary: Microsoft’s new Surface tablets are exquisitely engineered, and no one can accuse them of being me-too products. Yesterday’s launch was impressive, but it also left many questions unanswered. Monday, at an invitation-only media event in Los Angeles, Microsoft got the tech press to do something almost unprecedented: wait with eager anticipation for a Microsoft product announcement. Even more astonishing is that the reveal lived up to the hype. They are exquisitely engineered. From a distance, the magnesium cases and ClearType displays are drop-dead gorgeous. The impression of world-class design and engineering is even more striking when you actually pick one up and play with it, as I was able to do (albeit briefly) following the press event. The ARM-powered Windows RT model is one-tenth of a millimeter thinner than the latest iPad. It has a 10.6-inch screen with a 16:9 HD resolution, compared to the iPad’s 9.5-inch screen with a 4:3 aspect ratio. The larger display on the Surface means more weight—24 grams extra, to be precise, or just under an ounce more than its rival from Cupertino. A second model, built around an Intel Ivy Bridge CPU, runs Windows 8 Professional. Compared to its Windows RT cousin it’s slightly less thin (13.5 mm instead of 9.4 mm) and heavier (903 g, or a sliver over 2 pounds, compared to 1-1/2 pounds). This is no “me too” product. Both Surface models are unapologetically unlike anything you’ve ever seen before. The signature feature—one that probably has some Apple product designers wondering “Why didn’t we think of that?”—is the magnetic cover that snaps firmly into place and doubles as a keyboard. The Touch Cover (3 mm thin) comes in an assortment of bold colors and includes a full-size keyboard with slightly raised keys and a trackpad. The Type Cover, at 5mm, uses the same layout, but with keys that have the travel you would expect from a conventional keyboard. To appreciate the clever design and solid working of the magnetic latch, you really have to try it. There’s also a kickstand integrated into the case itself. Snap it open to rest the tablet open at a 22-degree angle, which is ideal for watching a movie, chatting via webcam, or typing. Both covers offer some of the power-saving features of the iPad Smart Cover, but the integrated keyboard and kickstand are a genuine improvement. You can turn a Surface tablet into the functional equivalent of a notebook without third-party add-ons. And the snug-fitting, rigid cover makes it possible to use the device in this configuration even on a lap. Oh, and both models have full-size USB ports (USB 2.0 for the Windows RT model, USB 3.0 for the Windows 8 Professional version). That’s a key differentiator from the iPad. It’s a bold break from Microsoft’s classic business model. For years, Microsoft has been telling OEMs to pay attention to user experience, stop loading machines with crapware, and concentrate on a few great models instead of a full line of dozens of mediocre offerings. This introduction is the same message, delivered with genuine emotion and the equivalent of a punch in the gut: “OEMs, please pay attention. This is how you build a PC.” In the press release announcing the new tablets, Microsoft says, “OEMs will have cost and feature parity on Windows 8 and Windows RT.” But it’s safe to say that Steve Ballmer’s voicemail box is overflowing with colorful messages, delivered at full volume, by the heads of the OEMs who will have to compete with these new designs. Microsoft kept this project secret, with not a single leak. One executive told me that the team working on Surface started its work three years ago, at the same time that development began on Windows 8. Using the trademark of an already-established product helped, as did a windowless lab protected by the kind of security normally reserved for government agencies with three-letter acronyms. So how many other, similarly well kept secrets are in the pipeline? The room full of reporters and analysts who watched the unveiling were generally approving and occasionally wowed by the spectacle. But the launch left many unanswered questions, a few genuine uncertainties, and a slight bit of disappointment. How much will these gizmos cost? Microsoft isn’t talking details. The official line is relatively vague: Suggested retail pricing will be announced closer to availability and is expected to be competitive with a comparable ARM tablet or Intel Ultrabook-class PC. If one assumes that “comparable ARM tablet” means an iPad equipped with 32 or 64 GB of memory, then the equivalent Windows RT Surface models should cost $600 and $700, respectively. Of course, that price will presumably include the keyboard cover (available as extra-cost add-ons from Apple and third parties). It will also include Microsoft Office. (In my hands-on tests, I was able to try out the Microsoft Office 2013 apps on a Windows RT Surface.) As for the Windows 8 Professional Surface, the current crop of Ultrabooks runs $999, give or take a couple hundred dollars. That is, not coincidentally, the starting price of a MacBook Air. Of course, one could make the case that a single Surface device is actually two devices in one—a tablet and a keyboard-equipped notebook. If prospective buyers accept that proposition, then a “competitive” price will seem like a bargain. When can you buy one? Put your credit card back in your wallet: Surface for Windows RT will release with the general availability [GA] of Windows and the Windows 8 Pro model will be available about 90 days later. Both will be sold in the Microsoft Stores in the US and available through select online Microsoft Stores. The smart money expects Windows 8 GA in October, which means a four-month wait for ARM-powered Surface tablets. And you’ll have to wait till early 2013 to get your hands on an Intel-powered Surface. That’s disappointing. As I wrote yesterday, “Whatever Microsoft unveils tomorrow, I hope it’s not another big announcement of an exciting future product that won’t reach customers for 4-6 months or maybe even until next year.” Oops. One possible reason for the long wait is competitive pressure. If other OEMs will be releasing their own devices to compete with Microsoft’s designs, it would be unsporting—and attract the attention of antitrust regulators—for Microsoft to beat them to market. Detailed specs are sketchy. In the private demo area after the event, Joshua Topolsky of The Verge and I peppered Microsoft reps for details on specs like screen resolution, but we got no definitive answers. The press release says the Windows RT model has a “ClearType HD display,” while the Pro model has a “ClearType Full HD display.” In his onstage introduction of the Pro model, Microsoft’s Mike Angiulo noted its “1080 resolution,” which would explain the “Full HD” label. Based on my inspection of the Windows RT version, I suspect it’s a 1366×768 device, which can handle 720p HD content. Still, we shouldn’t need to ask for basic specs like this. Battery life? No comment. It’s reasonable to expect that the two devices will be able to match Apple’s specs for the equivalent devices, but we won’t know until we can test shipping hardware. This announcement was unprecedented both in its form and in its substance, and it will take some time to digest the impact of it all. Will these new, unquestionably impressive designs put to rest the doubts that some critics have expressed about the Metro user experience? Will consumers be confused by the differences between two similarly named devices with very different capabilities? A TV reporter I spoke with struggled with what should be a simple question: Do both these devices run Windows 8? How will Android device makers react? The current crop of Android-powered tablets is incredibly weak compared to the iPad. The new Surface designs offer another point of comparison where Android falls far short. How will Apple respond? Tim Cook’s dismissive remarks about Windows 8 tablets—“You can converge a toaster and a refrigerator…”—might ring a little hollow now that the real thing is available for comparison. We’ll learn the answers to those questions over time. Meanwhile, I can’t wait to get my hands on one of these sleek new devices for more than 10 minutes. via Zdnet > http://www.zdnet.com/blog/bott/microsofts-new-surface-tablets-make-a-solid-first-impression/5142?tag=main;carousel
-
i believe TrueSec sell an application to manage small deployments of Endpoint Protection here is their website explaining it, there's a trial download too http://lms.truesec.se/ alternatively there is Windows Intune which can install and manage (via the cloud) the Windows Intune version of Endpoint Protection, it's not free either but it works very well indeed
-
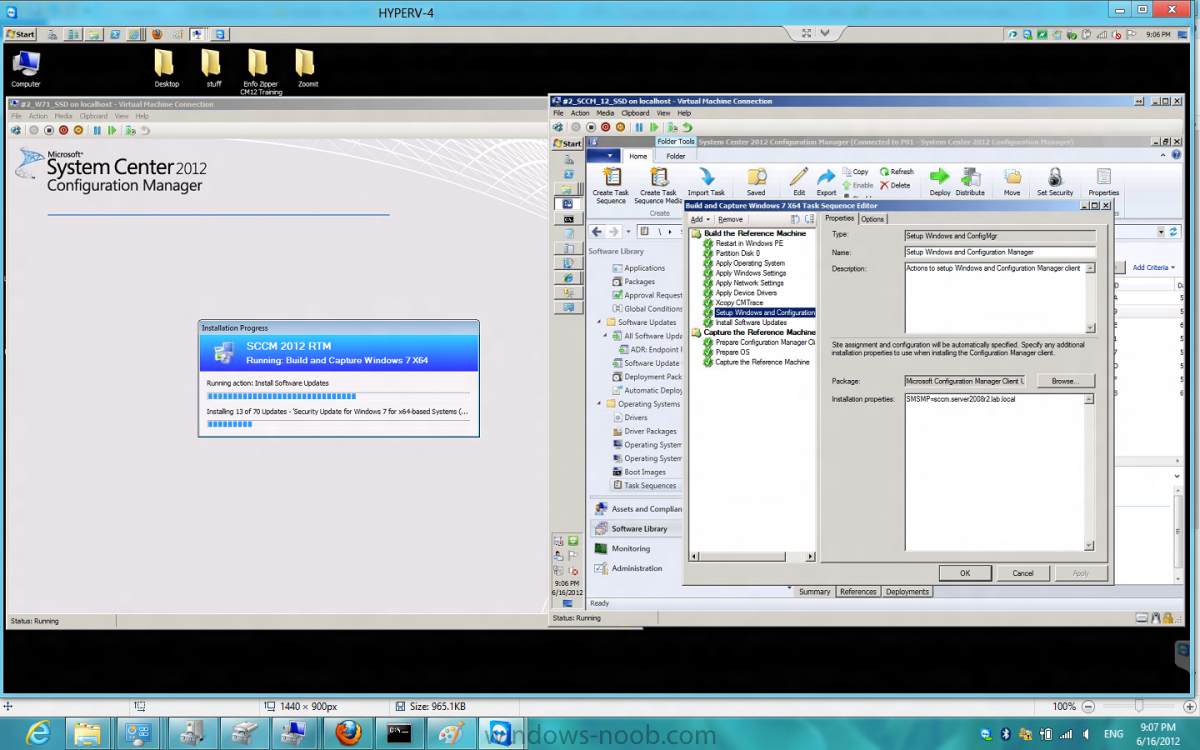
i tested it today and it works just fine (see screenshot), i booted from a boot media iso created the same way as you, for your info i'm showing you what my task sequence looks like and particularly the setup windows and configmgr step are you sure you have targetted updates (deployed a Software udpate group) to the build and capture collection ?
-

using SCCM 2012 in a LAB - Part 1. Installation
anyweb replied to anyweb's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
you do realise that Configuration Manager 2012 has RTM'd already and that the RC is therefore redundant ? -
I think the best place to get that answer is from your Microsoft representative, if you have the Core or Enterprise CAL you should be ok to install Configuration Manager, do you ?
-

SCEP 2010 Clients not updating
anyweb replied to flannelfriday's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
check the policy applied on the client, is it the antimalware policy you applied to the collection that this computer is a member of ? also verify that it is getting the correct Client Device settings for that collection -

using SCCM 2012 in a LAB - Part 1. Installation
anyweb replied to anyweb's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
are you logged in with a domain user account when running the check (or just as a local account) -

SCCM 2012 RTM - Reports give no results for HDD space
anyweb replied to dverbern's question in System Center Service Manager
nicely done -

How can I import computers into SCCM 2012 using a file ?
anyweb replied to anyweb's topic in Configuration Manager 2012
sorry, where are there contrary reports ?