-
Posts
9202 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
367
Everything posted by anyweb
-
enable F8 support and post the log here, i'm sure its a network related problem
-

Deploying software that have custom configurations
anyweb replied to Matt's question in Deploy software, applications and drivers
sorry it's not my area i'd suggest you ask the Gurus on myitforum.com cheers anyweb -

Software Distribution
anyweb replied to Dave Valcourt's question in Troubleshooting, Tools, Hints and Tips
you can set the type of advertisement to be mandatory and set it to 'reinstall if failed' keep that test collection as a place for testing new packages until you get them right then use another collection for package deployment cheers anyweb -
well to rule out any boot.wim related problems, please use either the Windows Server 2008 DVD OR use the Windows Vista SP1 dvd, if your 'ultimate' dvd is not sp1 then DONT use it cheers anyweb
-

Deploying software that have custom configurations
anyweb replied to Matt's question in Deploy software, applications and drivers
you should probably be creating msi packages then cheers anyweb -
are you using the windows vista SP1 dvd to get the boot.wim or some other dvd...
-
did you follow ALL of the steps outlined here ?
-
Several Microsoft watchers have speculated that Microsoft may release the Windows 7 beta to Microsoft Action Pack subscribers on or before the 5th January. Microsoft posted a note to its partner site regarding the latest Microsoft Action Pack Subscription quarterly update kit. In the update Windows 7 is included as "download only". The packs content is due to start shipping on "January 5, 2009, depending on region, and continues with the first month of each subsequent quarter (January, April, July, and October). Allow 15 to 30 business days to receive your kit." Despite the rumours we still believe that little will occur over the holiday season and Microsoft will make Windows 7 beta 1 available at Steve Ballmer's CES keynote on January 7th. Microsoft recently sent beta invites to potential testers and Microsoft employee Scott Wylie revealed build 7004 in a blog posting last week. According to sources, Microsoft has finished the Beta 1 bits and they have been signed off as build 7000. Build 7001 and 7002 have been reserved (skipped) and 7003 onwards marks the new RC branch. Ballmer is widely expected to announce the beta to a packed hall full off CES attendees on January 7th 2009. via neowin.net
-
Windows Vista has been out and about for a while now, and it has already been updated with a service pack, with a second service pack on its way. Vista's successor, Windows 7, is also getting closer and closer to release, but despite all that, Windows XP is still going strong, and demand for the operating system remains high. Because of that, Microsoft has yet again extended Windows XP's lifetime for OEMs and resellers. via osnews.com
-
if you havn't created the two SMS groups in AD like you are supposed to then how can I help ? or can you please explain what you think you are missing here as I'm out of ideas
-
what hardware are these systems, could be that the bios has a SATA mode for hard discs which needs 1. a SATA driver or 2. set from SATA to Compatible in the bios cheers anyweb
-
read this post then scroll down for the solution cheers anyweb
-
everyone=all users so not likely, can you open Windows Explorer and browse to the same folder and WRITE a file to it ? cheers anyweb
-

Updates for Workstation with SCCM 2007 ?!?!?
anyweb replied to TronixS's question in Software Update Point
i've tested this and it works fine with lots of updates in the update list have a look at my software update point howto maybe you've missed some steps ? in your WUAhandler.log file I see this so, do you have a group policy setup pointing to the WSUS server ? if so that is not correct and needs to be disabled. SCCM must handle all the updates itself not wsus cheers anyweb -
give Everyone full access to the share and try again, does it work then ?
-

MSCCM 2007, trying to create a new collection but cannot...
anyweb replied to togeoff's question in Collections
you can of course link collections to AD Security Groups for example by using queries select SMS_R_SYSTEM.ResourceID,SMS_R_SYSTEM.ResourceType,SMS_R_SYSTEM.Name,SMS_R_SYSTEM .SMSUniqueIdentifier,SMS_R_SYSTEM.ResourceDomainORWorkgroup,SMS_R_SYSTEM.Client from SMS_R_System where SMS_R_System.SystemGroupName = "w2k8\\Microsoft Office 2007" or even link to AD Organisational units Query for a single organizational unit: select * from SMS_R_System where SystemOUName = "ABC1.ABC.YOURDOMAIN.COM/ OUNAME / OUNAME / OUNAME /WORKSTATIONS/STANDARD" Query for multiple organizational units: select * from SMS_R_System where SystemOUName in ( "ABC1.ABC. YOURDOMAIN.COM/OUNAME/OUNAME/OUNAME/OUNAME/WORKSTATIONS", "XX.XX. YOURDOMAIN.COM/NAME/OUNAME/OUNAME/WORKSTATIONS" ) Query for a single Active Directory Site: select * from SMS_R_System where ADSiteName = "Default-First-Site-Name" Query for a multiple Active Directory Sites: select * from SMS_R_System where ADSiteName in ( "Default-First-Site-Name", "Site-XXX" ) you can see how to change rules for collections in this post cheers anyweb -
what OS are you trying to add the install.wim file from ? and how was that copied to the share it is in now
-

Configuring Software Update Point within SCCM
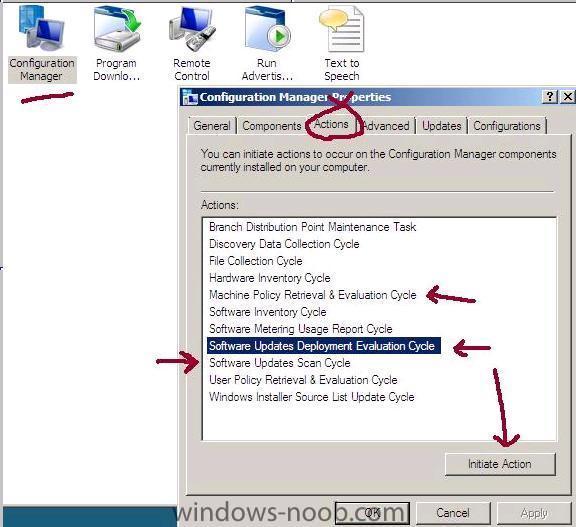
anyweb replied to anyweb's question in Software Update Point
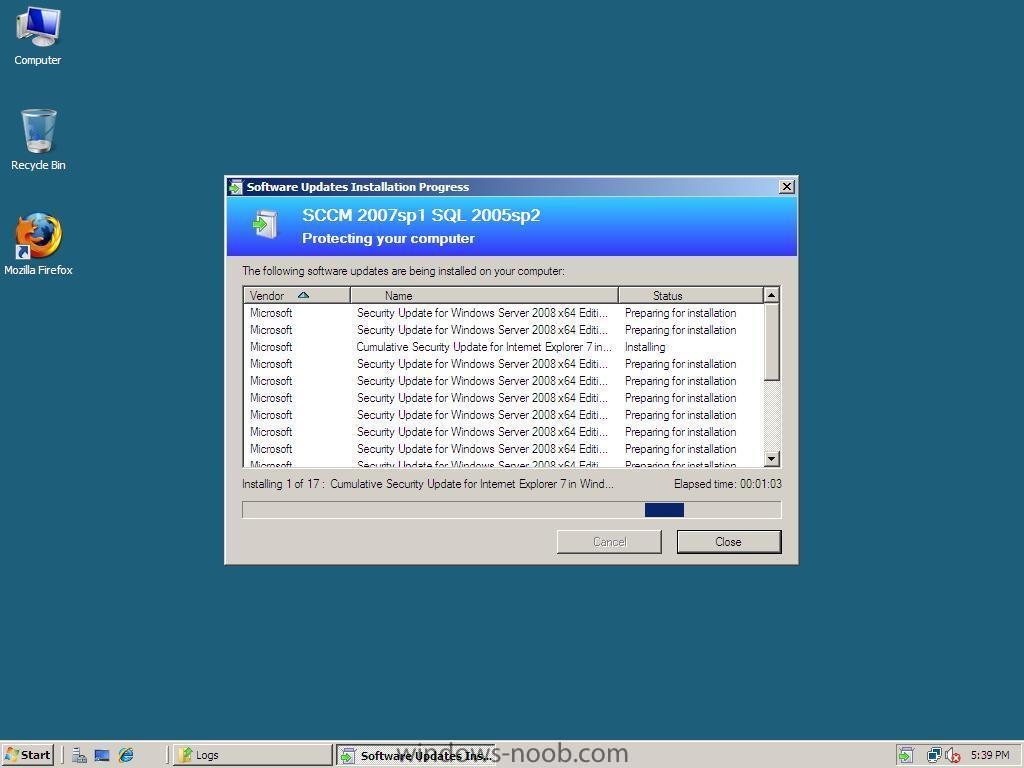
Verify On a client, open up control panel and the Configuration Manager client agent, click on the actions tab and Initiate the Following actions to trigger a check for any changes in Client Policy. Machine Policy Retrieval & Evaluation Cycle Software Updates Deployment Evaluation Cycle Software Updates Scan Cycle More info about the above Actions on Technet > http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb632393.aspx Machine Policy Retrieval & Evaluation Cycle: Bypasses the automatic policy polling interval on clients to get the machine policy as soon as possible. Software Updates Deployment Evaluation Cycle: Evaluates the state of new and existing deployments and their associated software updates. This includes scanning for software updates compliance, but may not always catch scan results for the latest updates. This is a forced online scan and requires that the WSUS server is available for this action to succeed. Software Updates Scan Cycle: Scans for software updates compliance for updates that are new since the last scan. This action does not evaluate deployment policies as the Software Updates Deployment Evaluation Cycle does. This is a forced online scan and requires that the WSUS server is available for this action to succeed. If you don't see any updates coming then read the WUAHandler log for details to see what is happening.... the log is located in C:\windows\system32\ccm\logs (x86) or c:\windows\syswow64\ccm\logs you can also browse the c:\windows\syswow64\ccm\cache folder to see if any updates have started to download yet be patient, even if you set the deadline for 10:10 it might take time to get them transferred over. Tip: To troubleshoot scan errors, you can run the Troubleshooting 1 - Scan errors report which will return a count of computers for each error that occurred during the last scan for software update compliance on client computers. You can then drill down to the Troubleshooting 3 / Computers Failing with a specific scan error report to view a list of computers that returned that specific scan error. here's what your desktop will look like when the software updates are being pushed out, you can click on the update icon to get details of the updates themselves after they are applied the update icon will change colour and here is my WUAhandler.log file (of a successful update) compare it to your own if you are experiencing problems to see what is different... WUAHandler.log -
starting over is sometimes a good idea but only if you plan how to install the next one and follow the plan cheers
-
are there any errors in your event viewer ? have you tried rebooting the server ? can you give me more info....
-
ok well have you configured any 'helpers' for options on the dhcp server ?
-
is your WDS server running on the same server as the SCCM one ? is the SCCM server also hosting the DHCP server ? do the files mentioned below actually exist `? (tried updating the distribution points) it looks like your server is trying to download 64 bit boot files and is only getting 32bit ones (x86) so check the properties of the boot files in WDS cheers
-
anything in between your client and the server ? is your SCCM server also your domain controller and dhcp server ?