Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'Hyper-V Host'.
-
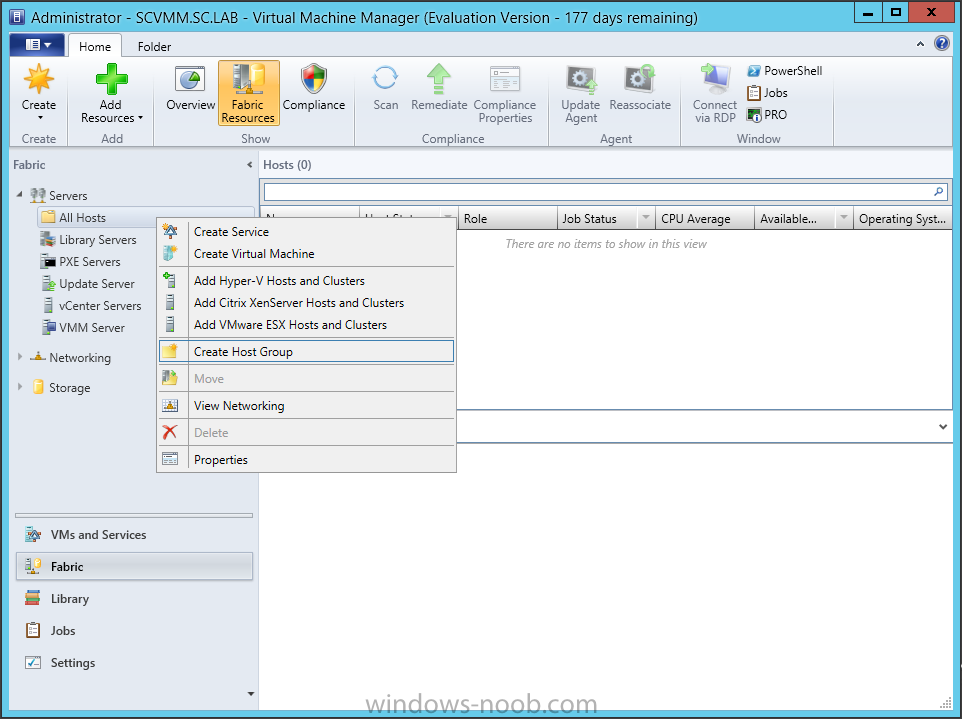
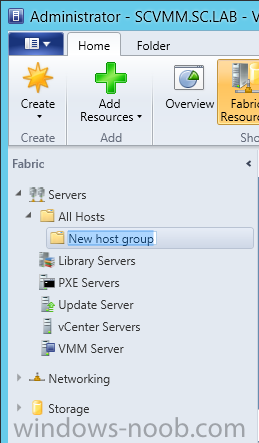
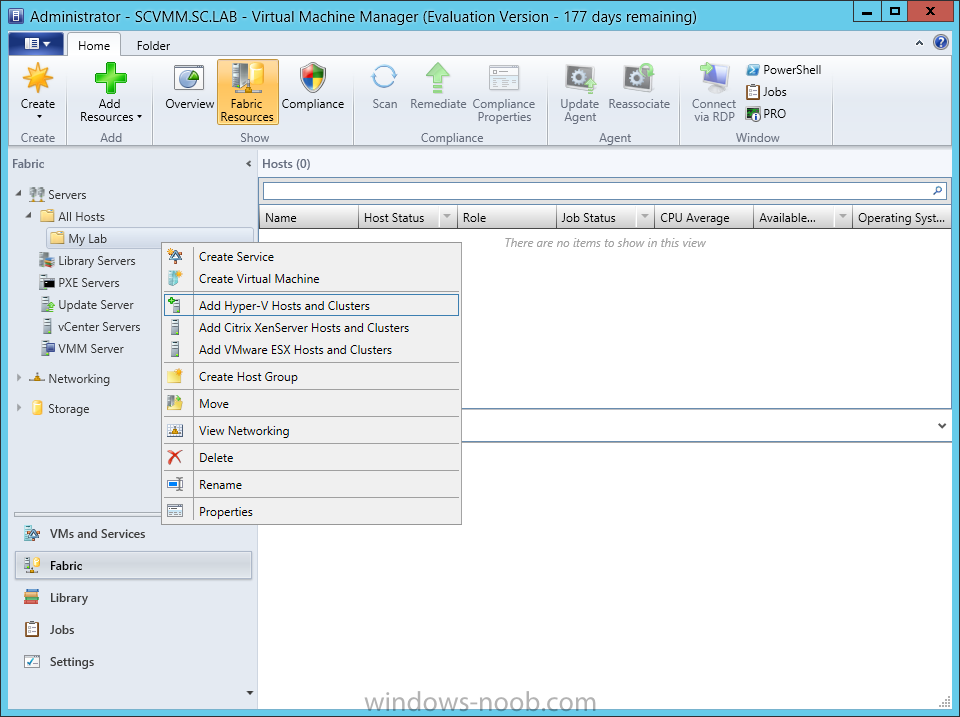
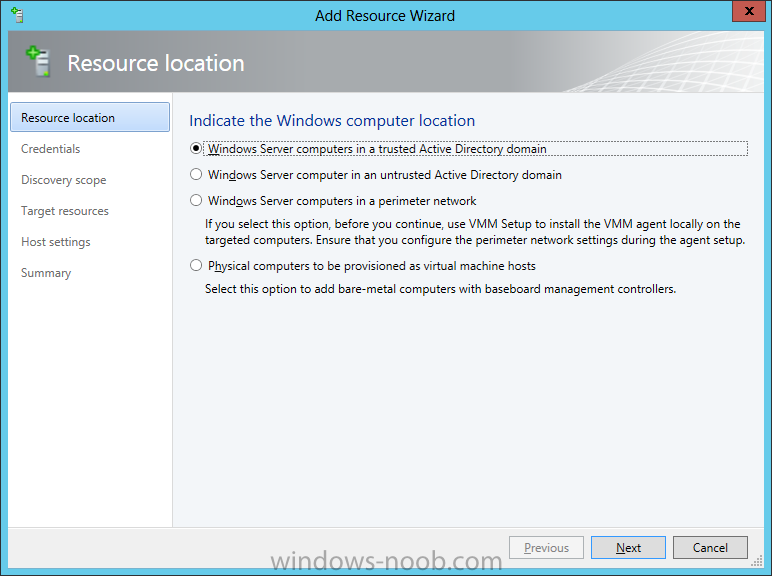
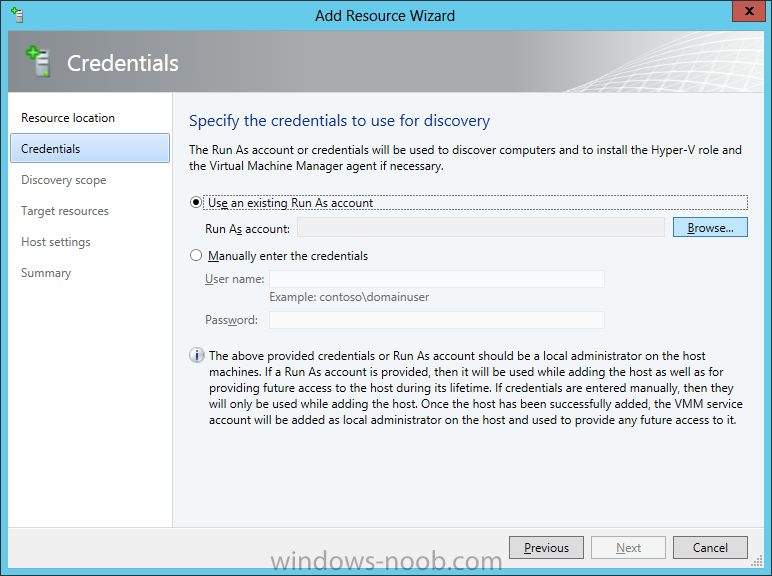
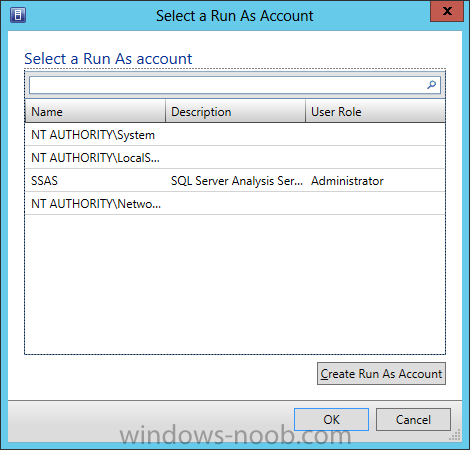
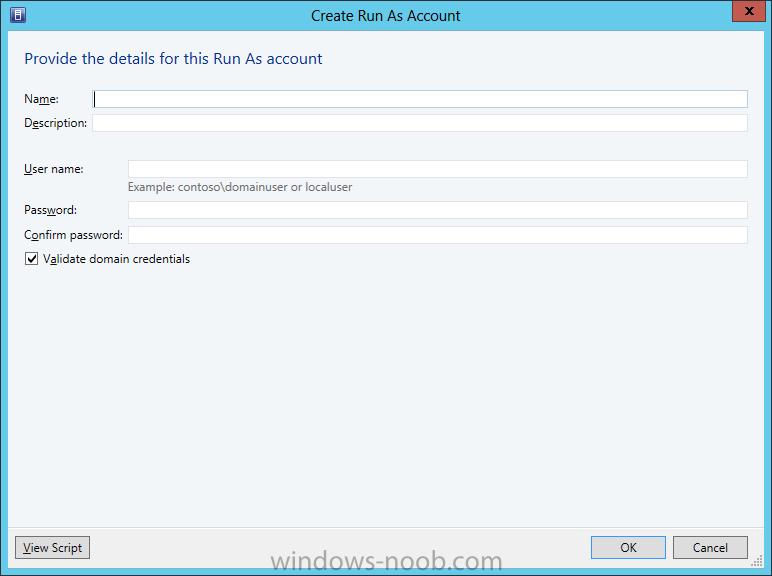
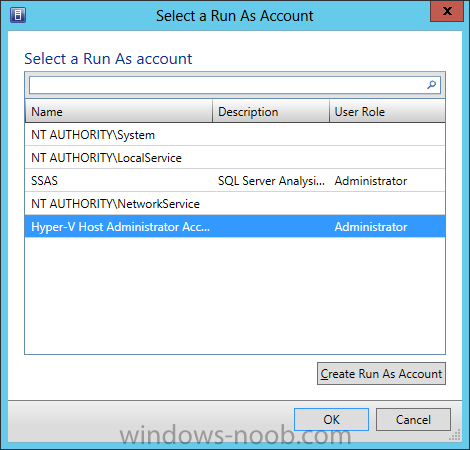
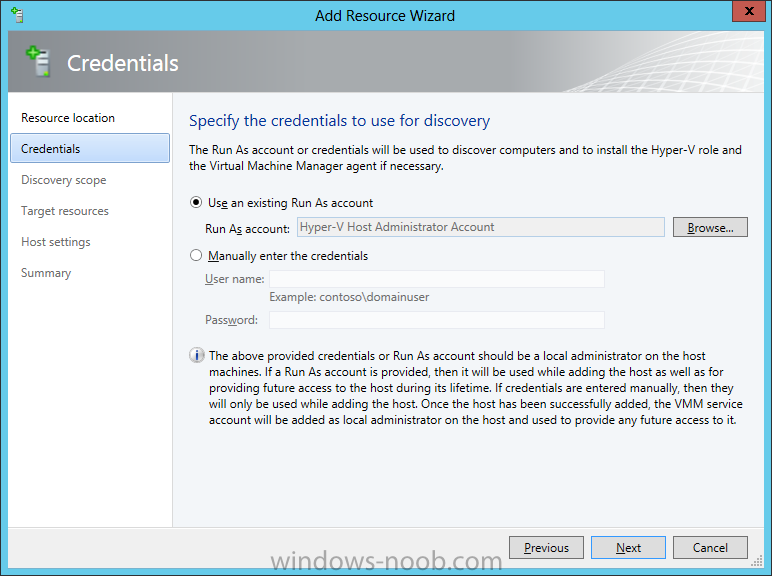
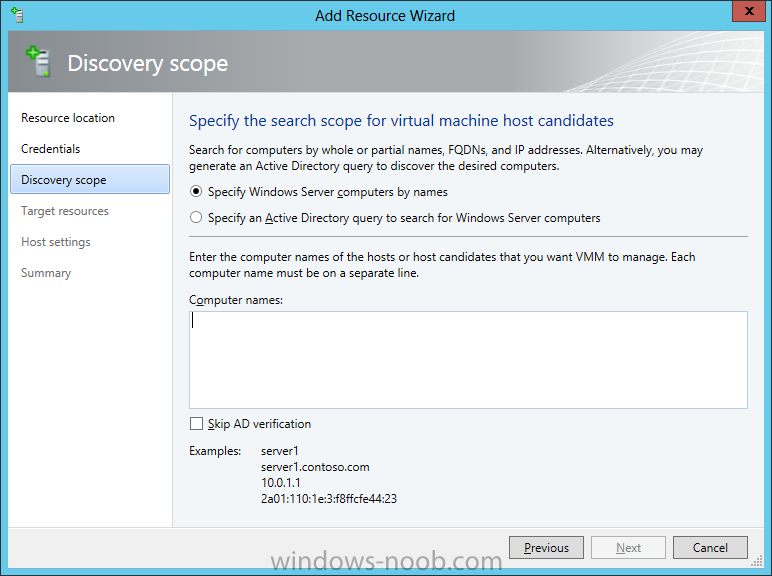
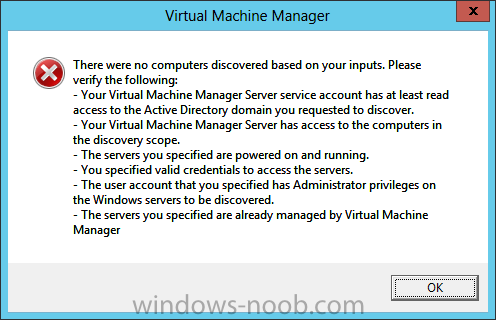
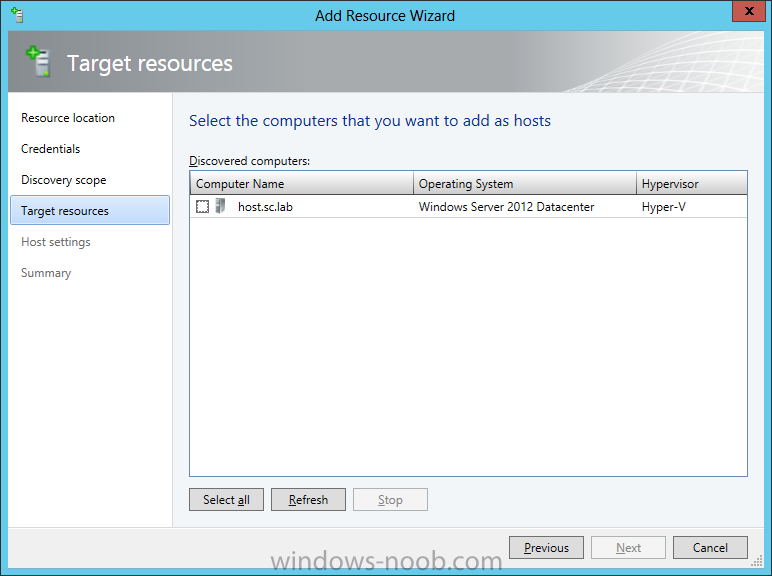
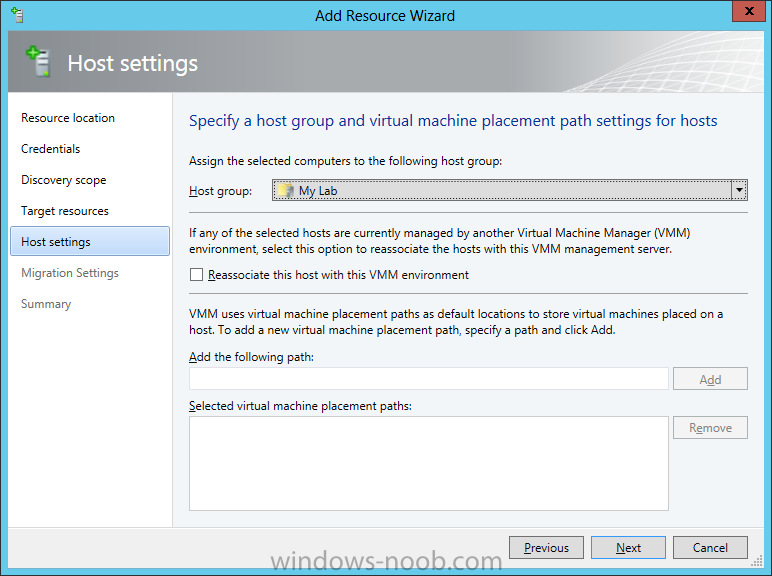
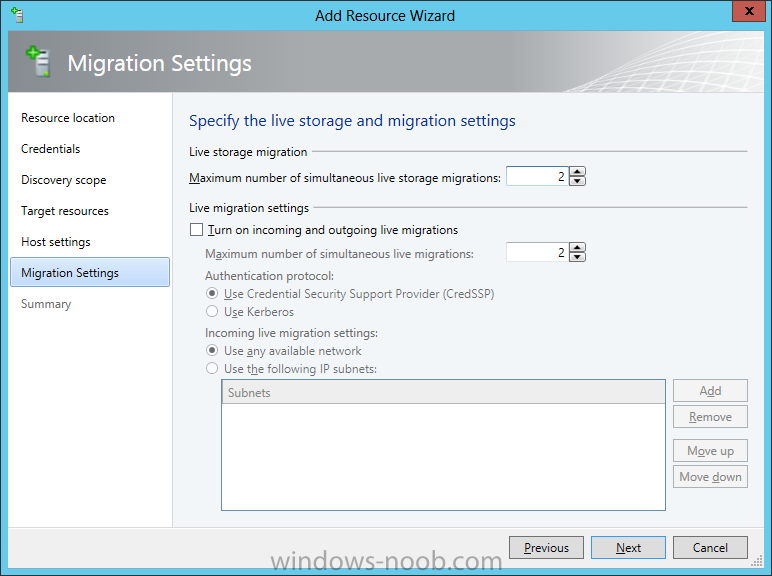
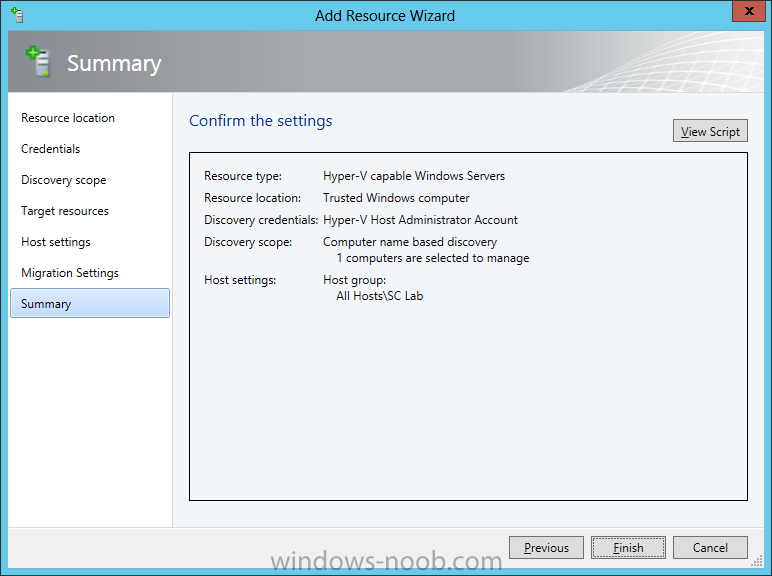
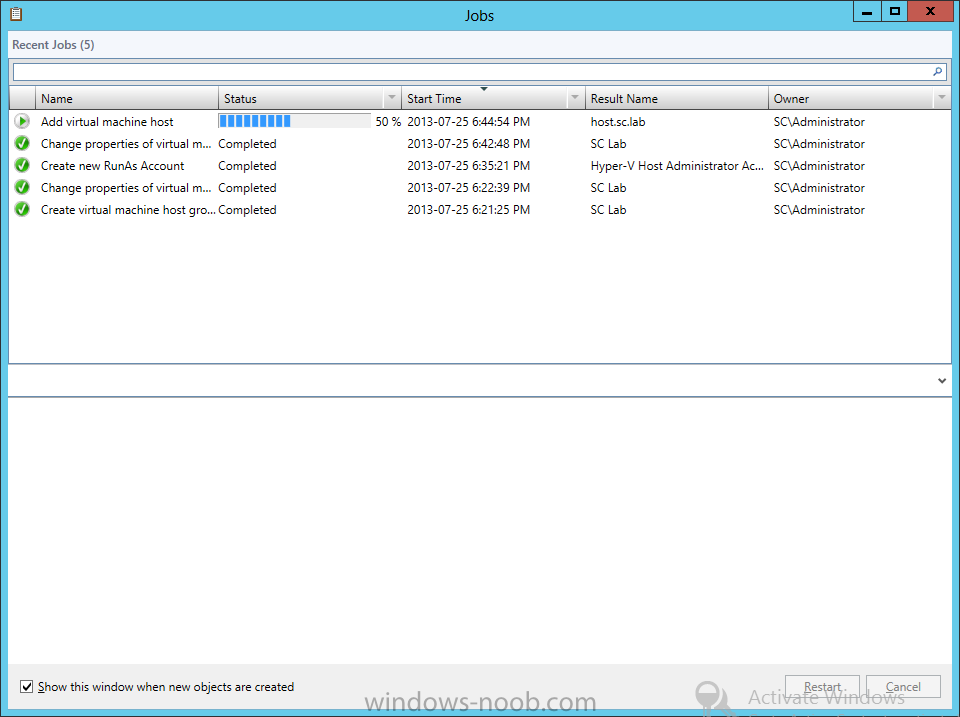
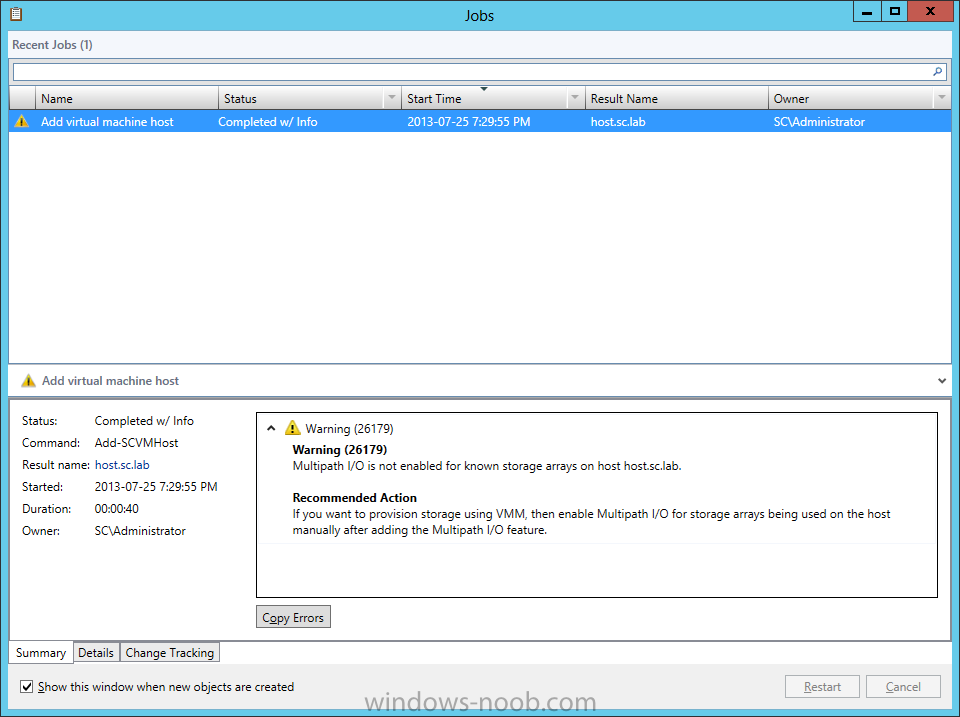
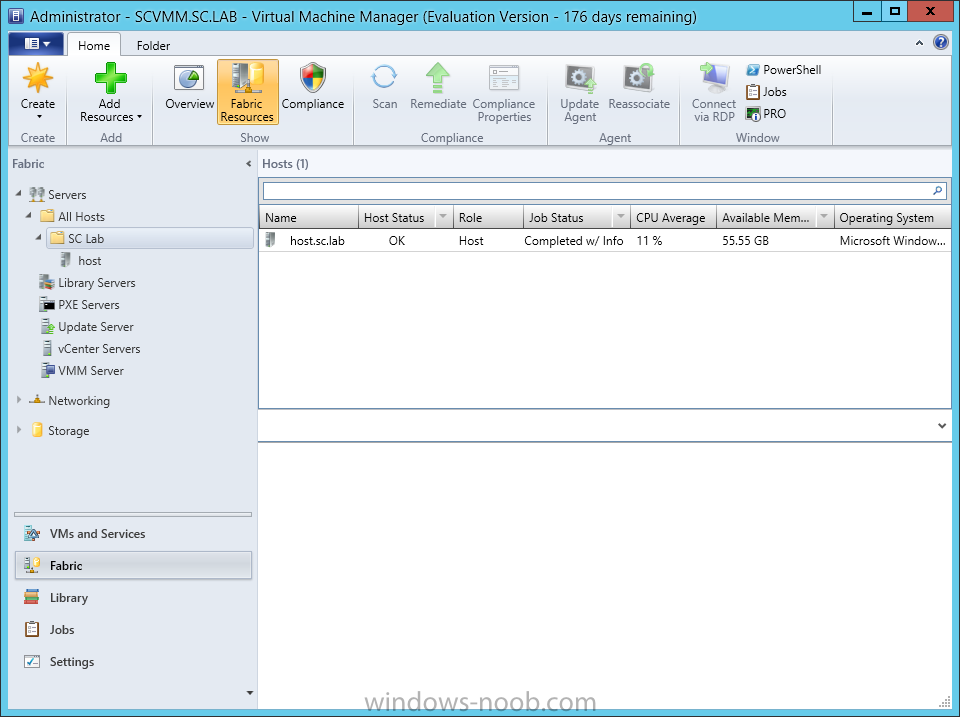
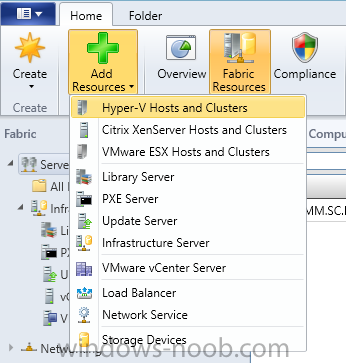
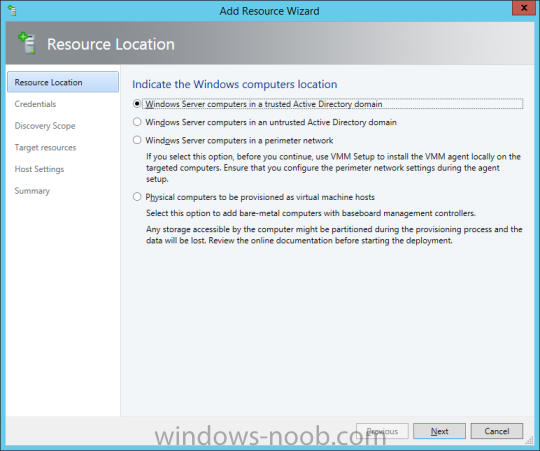
In our last post we finished installing Forecast Analysis Reporting. Now we will start on the configuration. Hello everyone, if you have been following along with my guides, you should now have SCVMM installed. But SCVMM won’t do you any good if it doesn’t know about any Hypervisor/virtualization hosts or VMs, so that’s where we will start as part of these Configuration guides. First, start by launching the SCVMM console. Click on Fabric in the lower left. Now expand the ‘Servers’ directory. From there, right-click on ‘All Hosts’ and choose ‘Create Host Group’. Name your custom Host Group whatever you want. Note, you can rename it at any time if you need to. Now right-click on your new Host Group and choose ‘Add Hyper-V Hosts and Clusters’. On the Resource Location screen of the Add Resource Wizard, make the appropriate selection for the Windows Computer Location, and then click Next. Note that you can even choose ‘Physical computers to be provisioned as virtual machine hosts’, which would allow you to provision bare-metal systems! For our lab example, since we have an Active Directory domain that the SCVMM server is a member of, we will choose the first option. On the Credentials screen, click Browse so that we can add an existing account as the Run As account. Note the information at the bottom of this screen, which reminds us that the Run As account needs to be a Local Administrator on the host machines you want to manage. On the Select a Run As Account, click the ‘Create Run As Account’ button, since we don’t have an account already within SCVMM to use. On this screen you need to provide the details about the account. You can give it a name (Note that this is NOT the actual username used for the account, but an identifying name), and description. You will need to provide the actual username and password for the account. In my lab example I created an account called SCVMMAdmin, and used that on this screen. Enter an applicable account on this screen and then click OK. Now our newly added account is available to be selected. You will notice in my example that I named the account “Hyper-V Host Administrator Account”. Select your account and then click OK. Now the Credentials screen will show the account that we have selected. Now click Next. On the Discovery Scope screen, choose the appropriate the scope option. You can use an Active Directory query, or type the names to search for. In my lab example, I just typed the names. Make your appropriate choice and then click Next. NOTE: You can opt to ‘Skip AD Verification’ however it is best to perform AD verification to ensure the system can be communicated with. If there are issues with the wizard not being able to communicate with the Host(s), you may encounter this error. Read the message displayed and then click OK. Perform whatever actions are required to resolve the communication issues, and then re-attempt to add a host system. On the Target Resources screen, if the host system(s) are able to be contacted, they will appear here. Select the system(s) that you want to add as hosts, and then click Next. On the Host Settings screen, you can assign the selected computers to a specific Host Group (i.e. the one we originally created). You could use the Host Groups to organize hosts based on area/zone (i.e. PROD, UAT, TST, DEV, etc.). For our lab example, just click Next. On the Migration Settings screen you can specify how many live migrations (for both storage, and VMs) can be performed simultaneously. For this example in my lab, since I don’t have a second physical host to use for live migrations, I won’t turn this feature on. At this point, just click Next. Review the information on the Summary screen and then click Finish. This will open the Jobs screen, and show the progress of adding the host. If there are any issues, you will be alerted to them here. Correct any issues, and re-attempt to add the host. Once it has been added successfully, you can close the Jobs window. You will notice in my lab example, that adding my host completed but with a Warning. This is because my physical host does not have Multipath I/O. This is used in reference to SAN storage, which I don’t have. Back in the main SCVMM console your Host will now be present. Congratulations, you now have SCVMM installed, along with adding a Host hypervisor (in our case, Hyper-V) system to be managed. Next we will create host groups and clouds.
- 3 replies
-
- SCVMM
- Virtual Machine Manager
- (and 5 more)
-
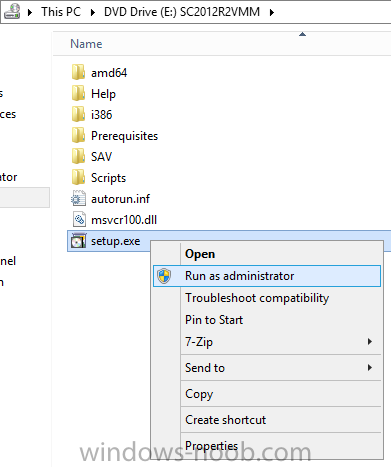
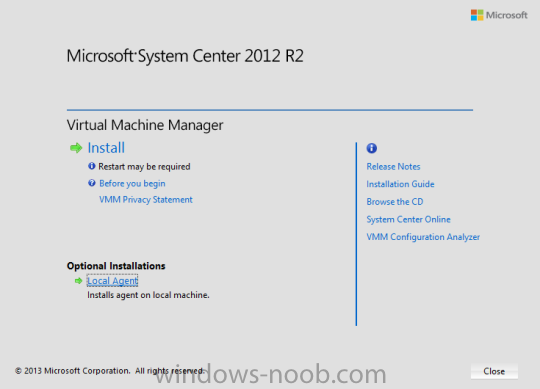
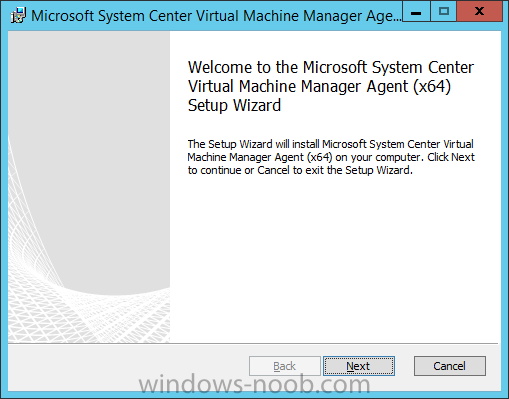
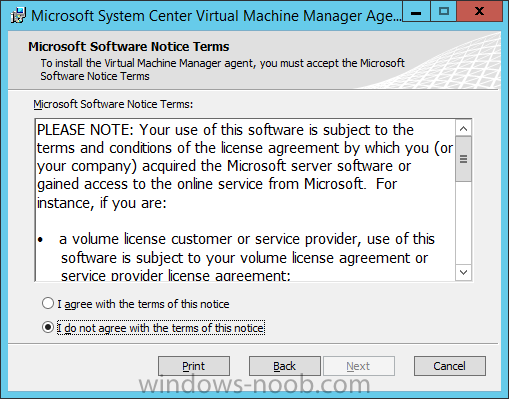
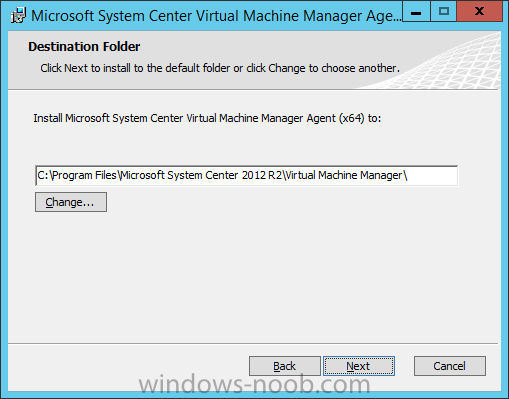
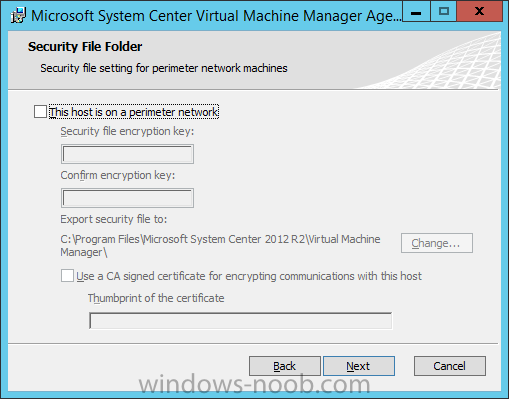
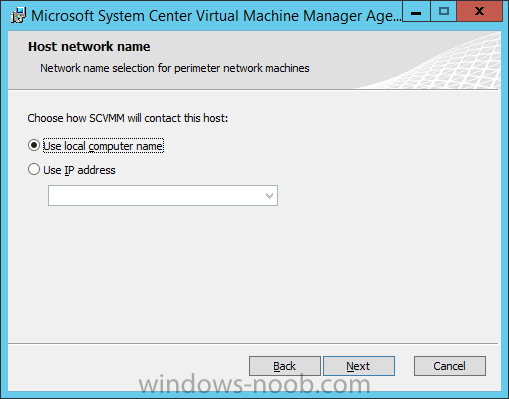
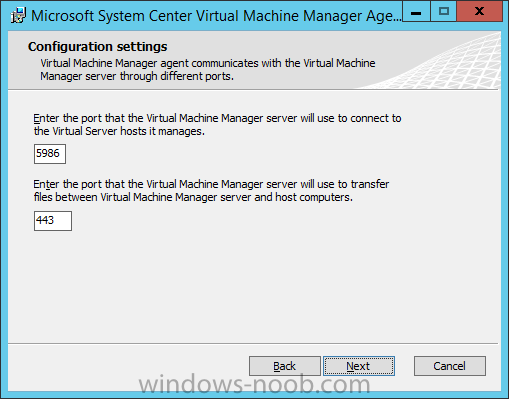
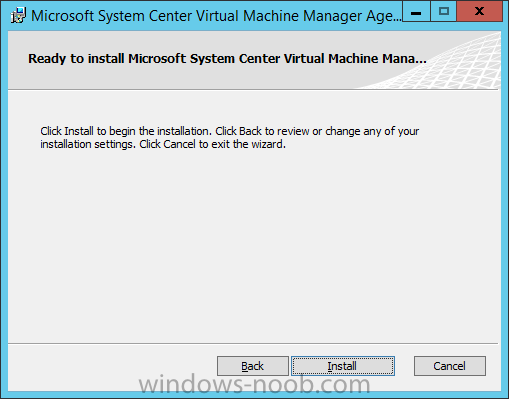
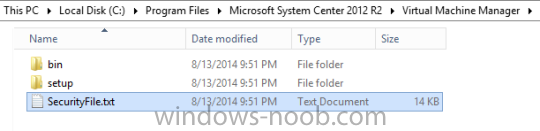
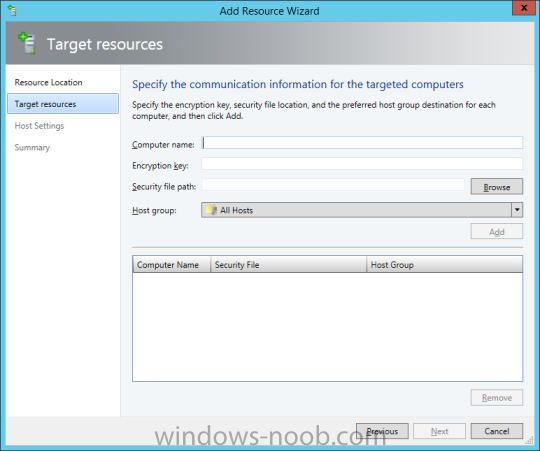
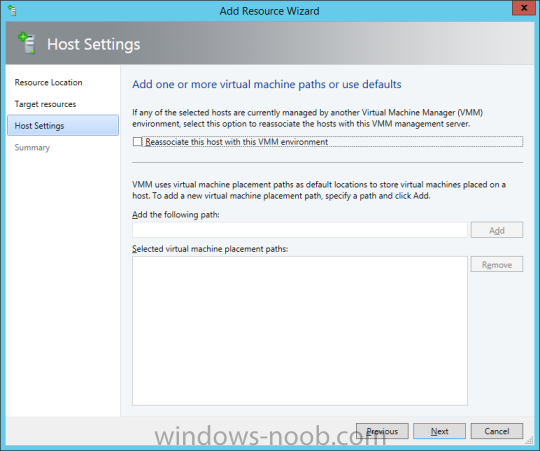
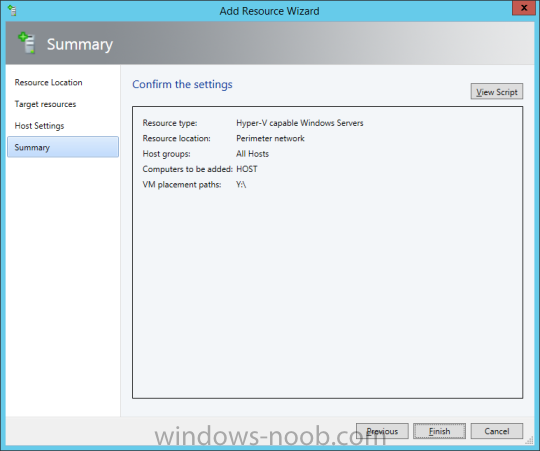
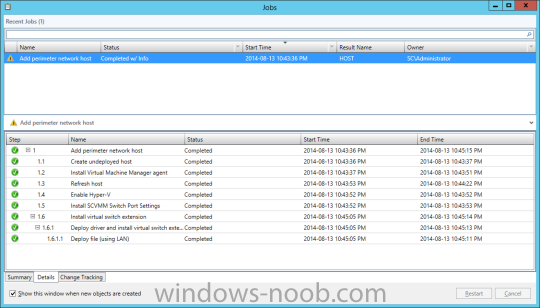
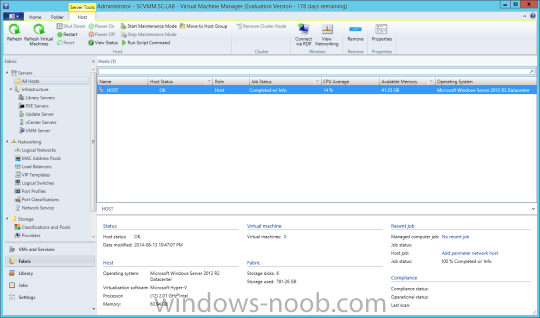
In my home lab environment, I have a single host, which is NOT a member of my lab’s domain. This is due to the fact that I am constantly re-building my lab environment, which includes my Active Directory Domain Controllers. Therefore, I don’t want to add my host to the domain, and then potentially loose access to it when rebuilding (although I could still use the Local Administrator account). With that being said, I want to add my Host to SCVMM (which is running in a VM on the Host itself). Therefore, I need to be able to add a Host that is not a domain member (aka. a Workgroup host). So, I will be following this TechNet article (http://technet.microsoft.com/en-ca/library/gg610642.aspx), which walks through the process. I will add screenshots to make it easier to follow. You can use the following procedure to add Hyper-V hosts that are in a perimeter network (also known as DMZ, demilitarized zone, and screened subnet) as managed Hyper-V hosts in Virtual Machine Manager. You can only add stand-alone hosts that are in a perimeter network. VMM does not support managing a host cluster in a perimeter network. NOTE: You can also use this procedure to add a stand-alone Hyper-V host that is in a workgroup and not part of a domain. Before you can add a host that is on a perimeter network to VMM, you must install an agent locally on the server that you want to add. TO INSTALL THE VMM AGENT ON THE TARGET HOST On the VMM product media or network share, right-click Setup.exe, and then click Run as administrator. On the Setup menu, under Optional Installations, click Local Agent. On the Welcome page, click Next. Review and accept the software license terms, and then click Next. On the Destination Folder page, accept the default location or click Change to specify a different location, and then click Next. On the Security File Folder page, do the following: Select the This host is on a perimeter network check box. In the Security file encryption key box, enter an encryption key, and then enter it again in the Confirm encryption key box. Security Note: The encryption key is a value that you choose. We recommend that you enter an encryption key that contains a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers and symbols. Important: Make note of the encryption key that you use to create the security file. You must enter this same key again when you add the host in the VMM console. Either accept the default location where the encrypted security file will be stored, or click Change to specify a different location to store the encrypted security file. Important: Make note of the location where you stored the security file. In the “To ensure that the Security.txt file is available to VMM” procedure, you must transfer the security file to a location that is accessible to the computer on which a VMM console is installed. To use a certificate to encrypt communications between the VMM management server and the host, select the Use a CA signed certificate for encrypting communications with this host check box. In the Thumbprint of the certificate box, enter the thumbprint of the certificate. Note: To obtain the thumbprint of a certificate, open the Certificates snap-in, and then select Computer account. In the Certificates snap-in, locate and then double-click the certificate that you want to use. On the Details tab, select theThumbprint field. In the lower pane, highlight the thumbprint value, and then press Ctrl+C to copy the value to the clipboard. When you are finished, click Next. On the Host network name page, specify how the VMM management server will contact the host, and then click Next. You can select either of the following options: Use local computer name Use IP address If you select Use IP address, click an IP address in the list. Important: Make note of the computer name or IP address of the host. You must enter this same information again when you add the host in the VMM console. On the Configuration settings page, accept the default port settings, or specify different ports, and then click Next. Important: We recommend that you do not change the default port 5986 for agent communication. The port settings that you assign for the agent must identically match the port setting that the VMM management server uses. By default, the VMM management server uses port 5986 for agent communication with hosts in a perimeter network, and port 443 for file transfers. On the Ready to install page, click Install. TO ENSURE THAT THE SECURITYFILE.TXT FILE IS AVAILABLE TO VMM On the target host, navigate to the folder where the security file is stored. By default, the location is C:\Program Files\Microsoft System Center 2012\Virtual Machine Manager. The name of the security file is SecurityFile.txt. Transfer the security file to a location that is accessible to the computer on which a VMM console is installed. For example, transfer the file to the computer where the VMM console is installed, to an internal file share, or to a USB flash drive. TO ADD THE HYPER-V HOST IN THE PERIMETER NETWORK In the VMM console, open the Fabric workspace. In the Fabric pane, click Servers. On the Home tab, in the Add group, click Add Resources, and then clickHyper-V Hosts and Clusters.The Add Resource Wizard starts. On the Resource location page, click Windows Server computers in a perimeter network, and then click Next. On the Target resources page, do the following: In the Computer name box, enter the NetBIOS name or the IP address of the host in the perimeter network. In the Encryption key box, enter the encryption key that you created when you installed the agent on the target host. In the Security file path box, enter the path of the SecurityFile.txt file, or clickBrowse to locate the file. In the Host group list, click the host group where you want to add the host.For example, click the Seattle\Tier2_SEA host group. Click Add.The computer is listed under Computer Name in the lower pane. Repeat this step to add other hosts in the perimeter network. When you are finished, click Next. On the Host settings page, in the Add the following path box, enter the path on the host where you want to store the files for virtual machines that are deployed on hosts, and then click Add. If you leave the box empty, the default path of %SystemDrive%\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Hyper-V is used. Be aware that it is a best practice not to add default paths that are on the same drive as the operating system files. Repeat this step if you want to add more than one path. When you are finished, click Next. Note: You can ignore the Reassociate this host with this Virtual Machine Manager environment check box. This setting does not apply to hosts in a perimeter network. On the Summary page, confirm the settings, and then click Finish. The Jobs dialog box appears to show the job status. Make sure that the job has a status of Completed, and then close the dialog box. To verify that the host was successfully added, in the Fabric pane, expandServers, expand All Hosts, expand the host group where you added the host, and then click the host. In the Hosts pane, verify that the host status is OK. Tip: To view detailed information about host status, right-click the host in the VMM console, and then click Properties. On the Status tab you can view the health status for different areas such as overall health, host agent health, and Hyper-V role health. If there is an issue, you can click Repair all. VMM will to try to automatically fix the issue.
-
- Hyper-V Host
- SCVMM
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with: