Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'cdp'.
-
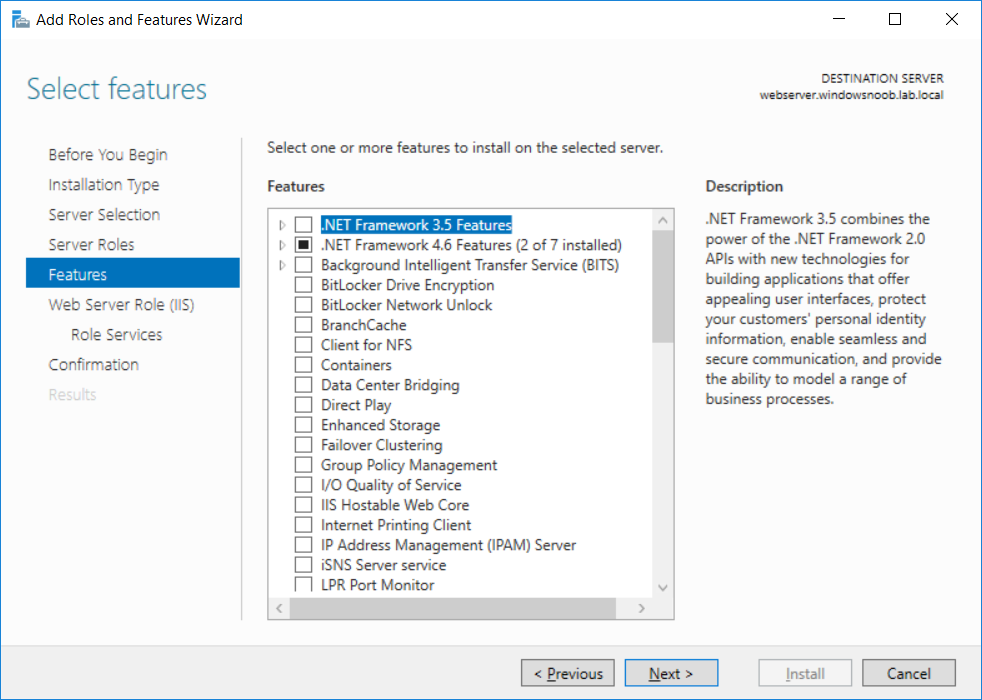
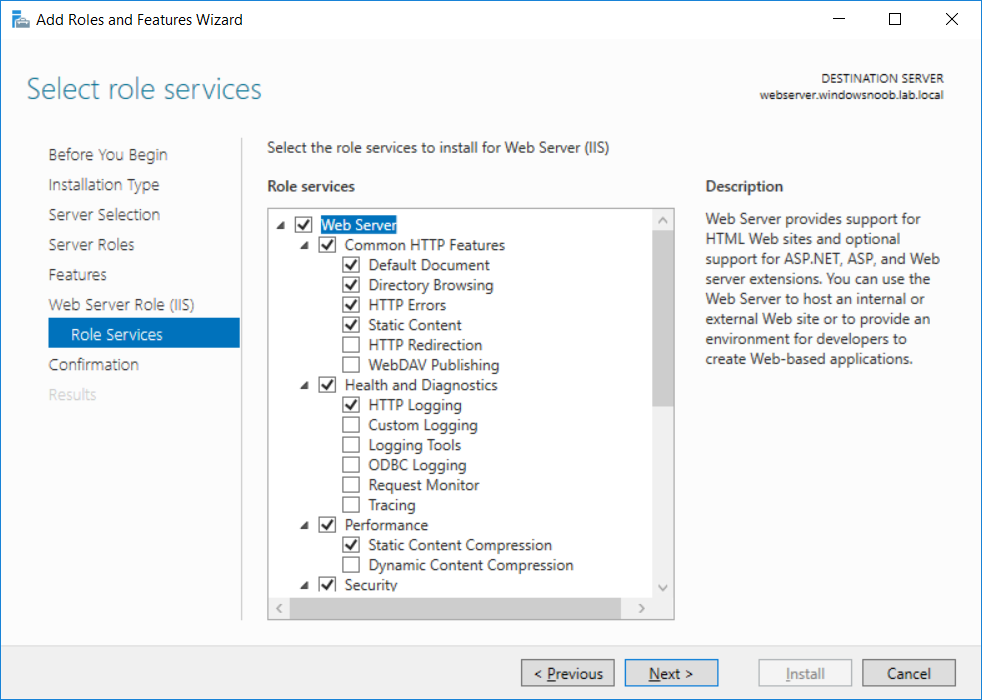
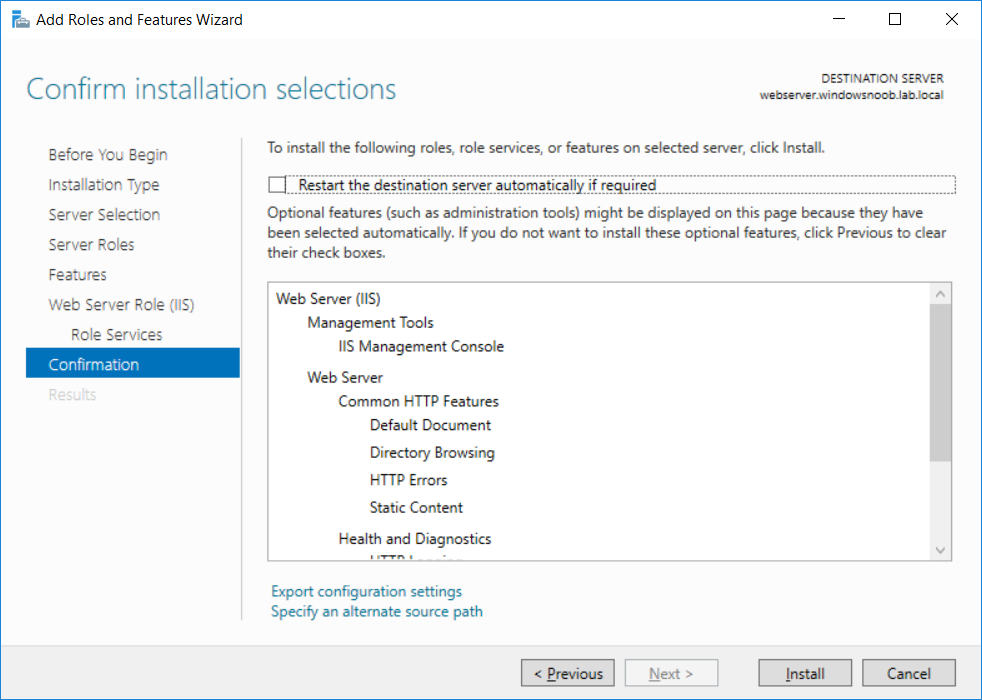
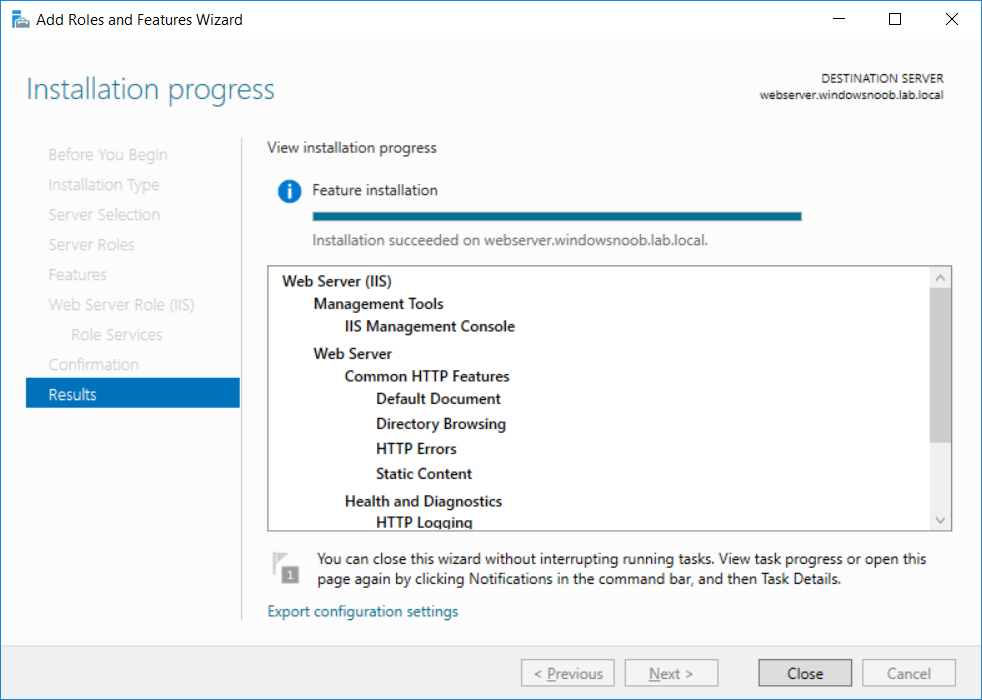
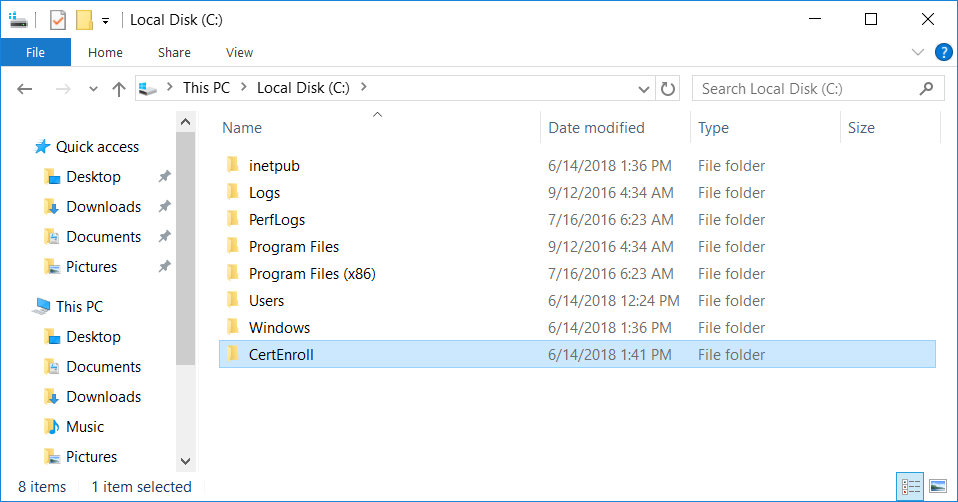
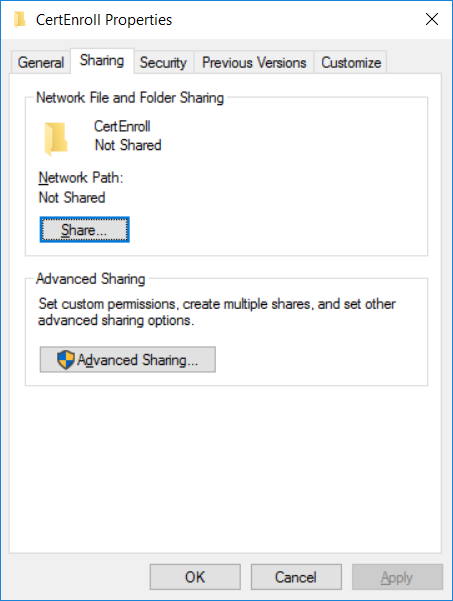
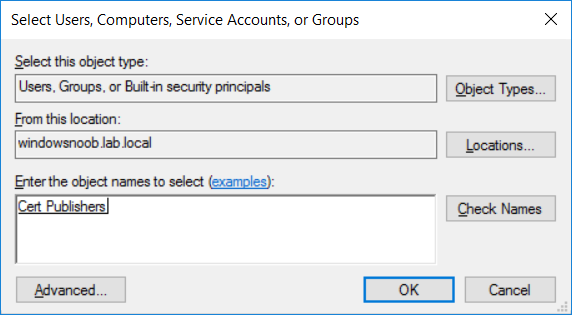
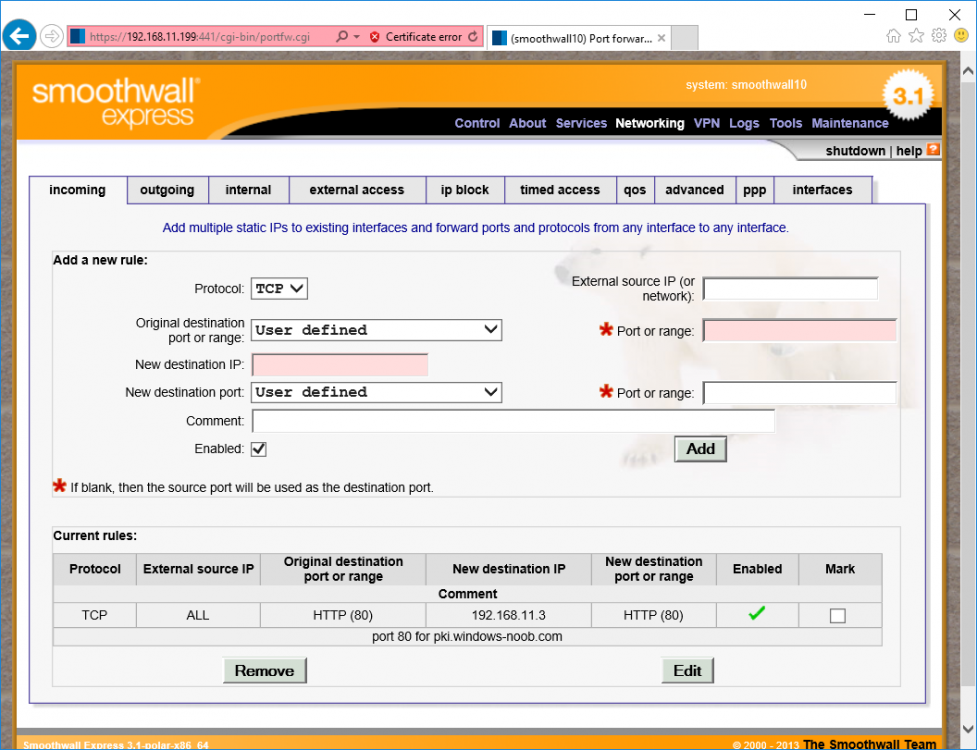
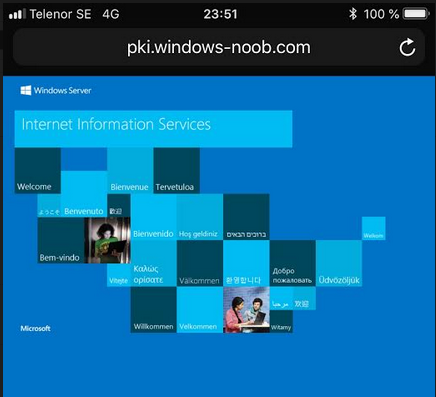
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup (this part) Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post config...
- 2 replies
-
- 2
-

-
- co-mangement
- ca
-
(and 12 more)
Tagged with:
-
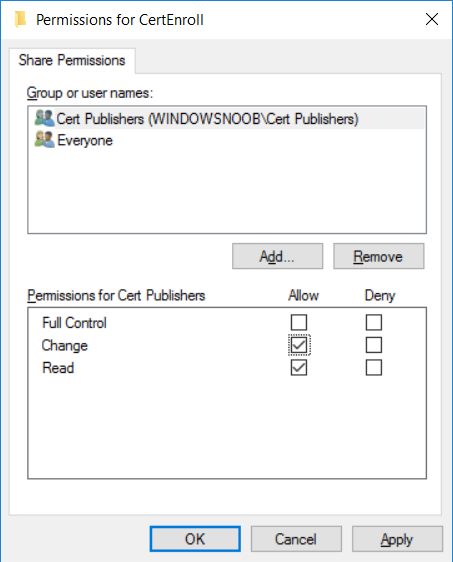
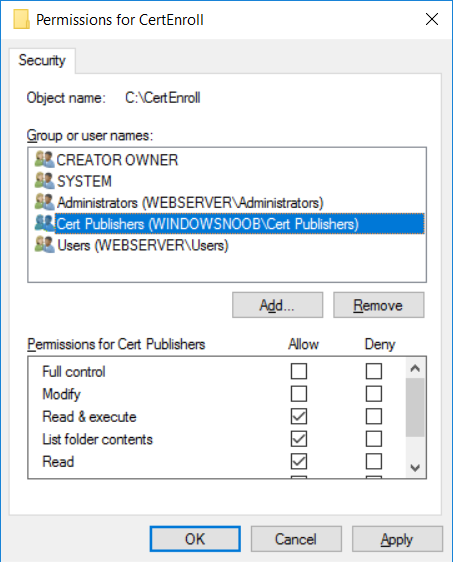
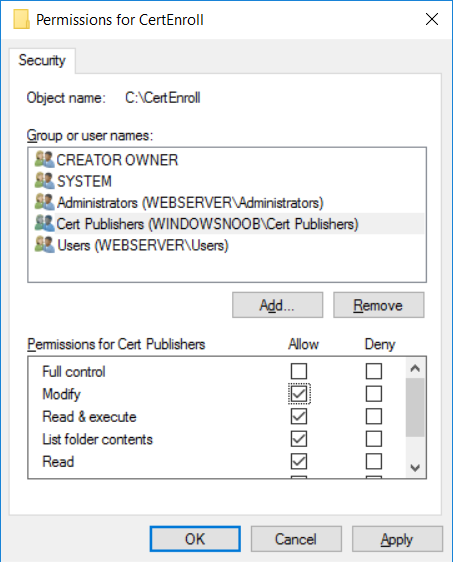
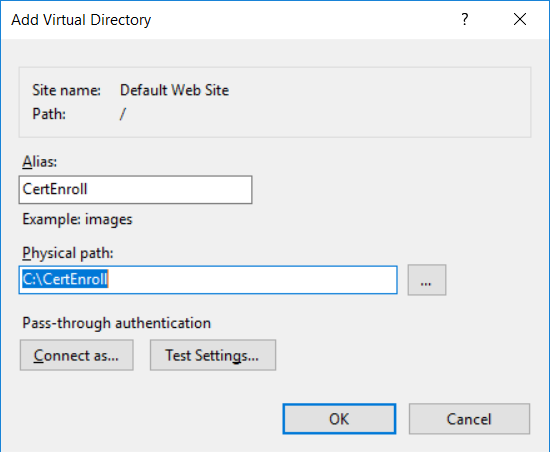
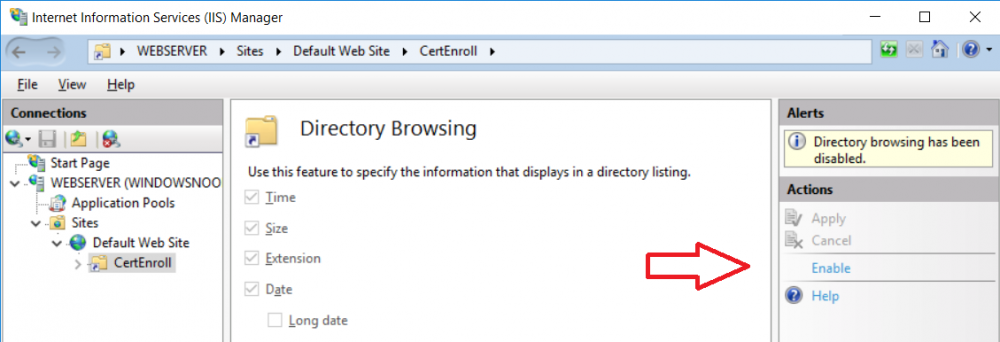
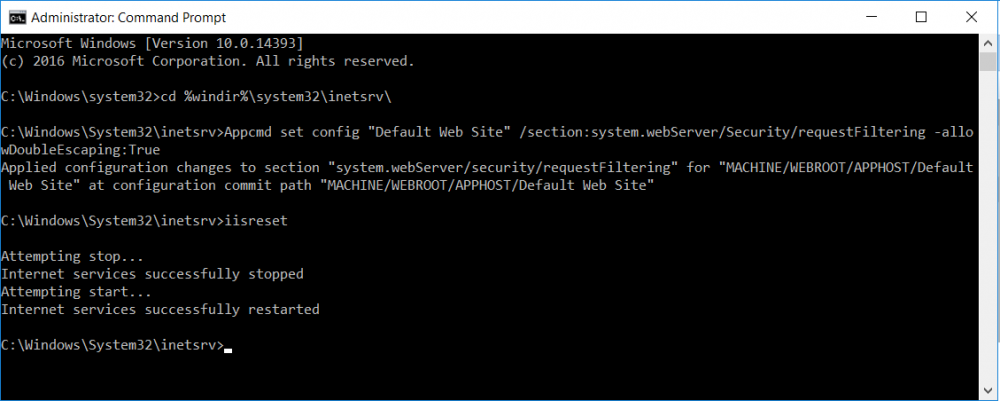
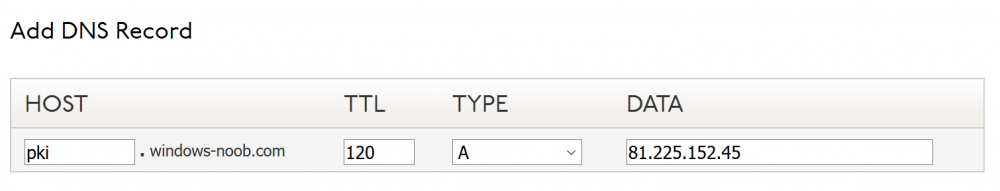
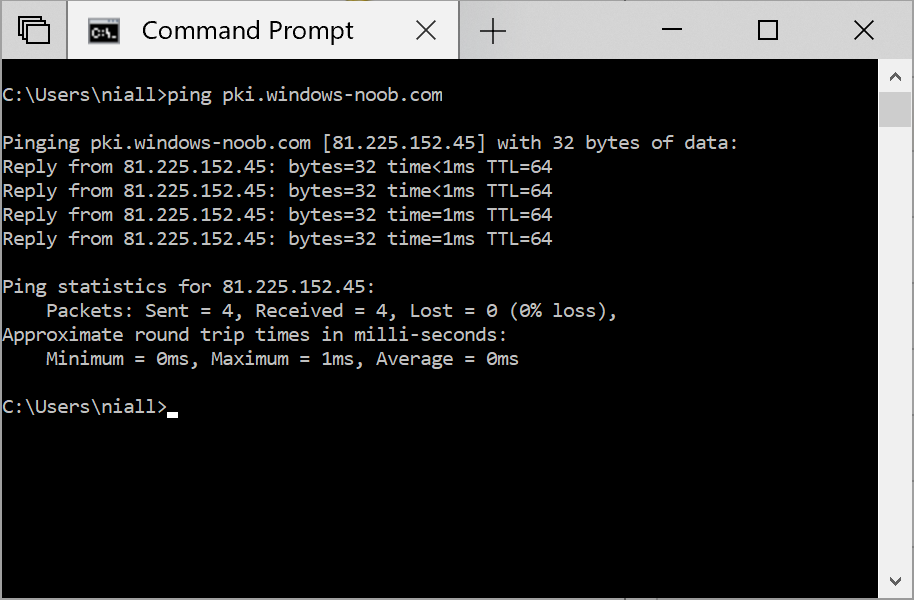
This series is comprised of different parts, listed below. Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication (this part) Part 4 - Post config...