Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'https'.
-
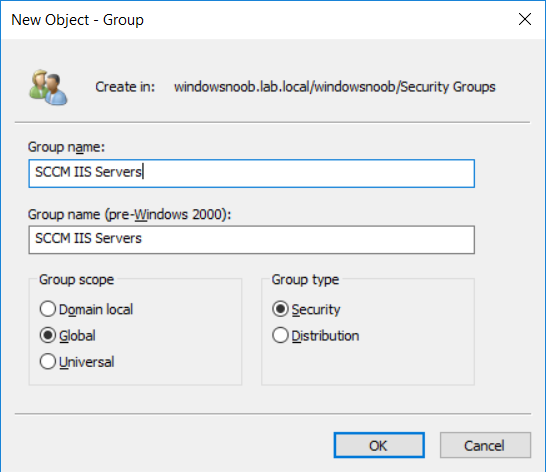
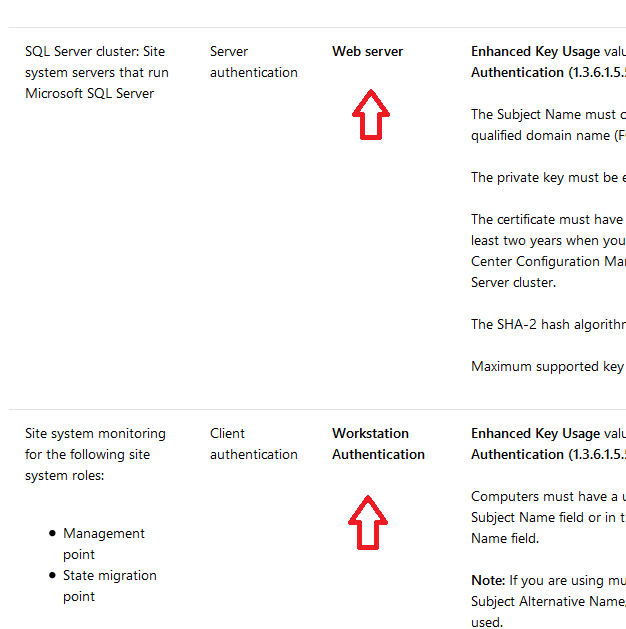
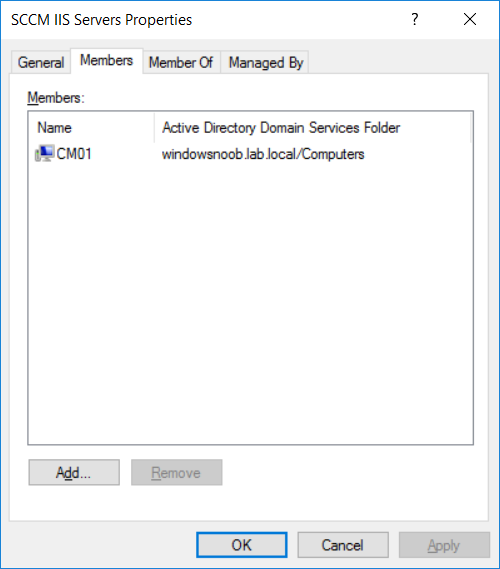
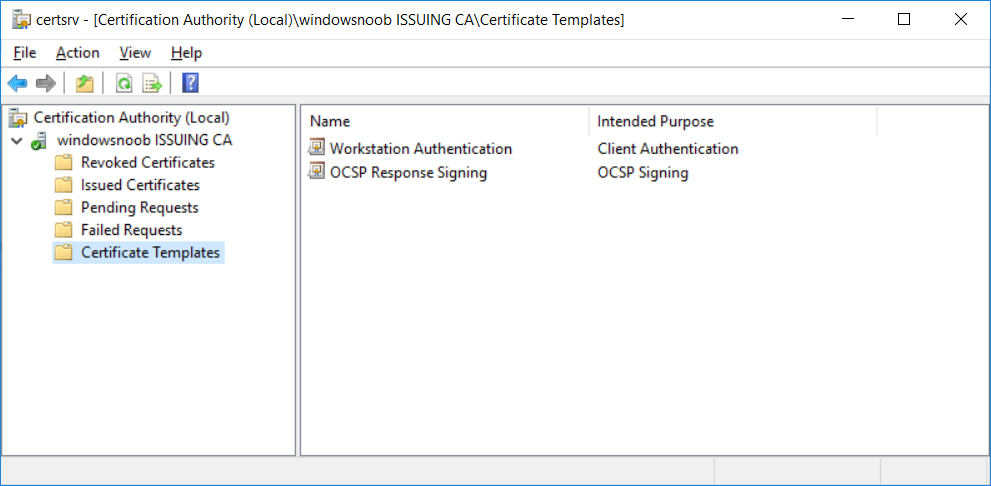
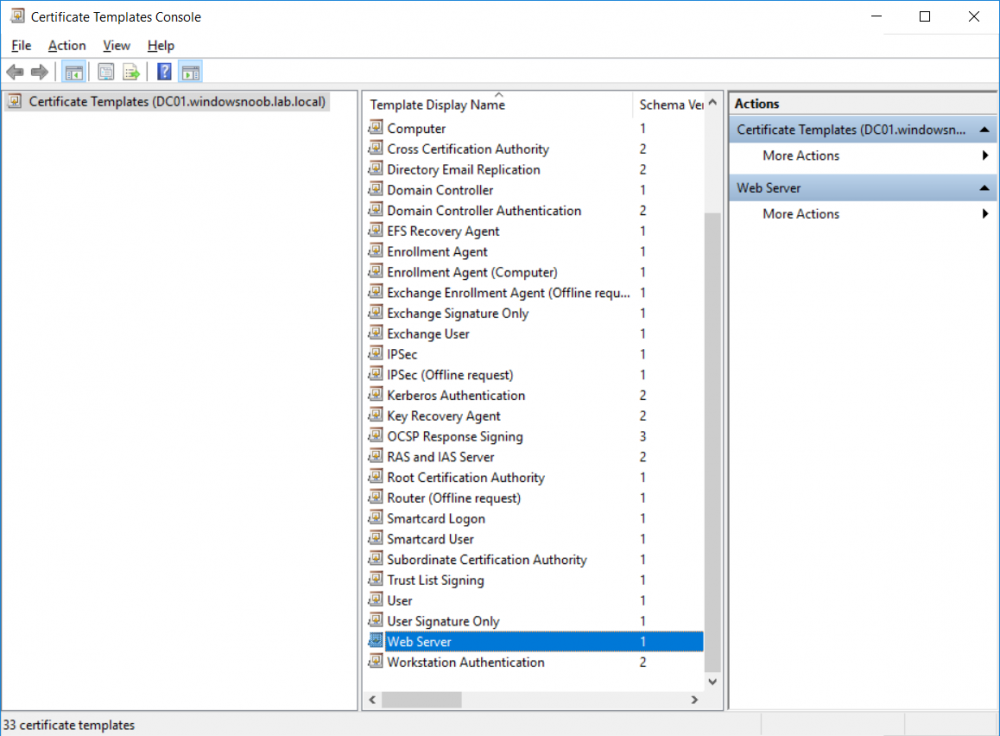
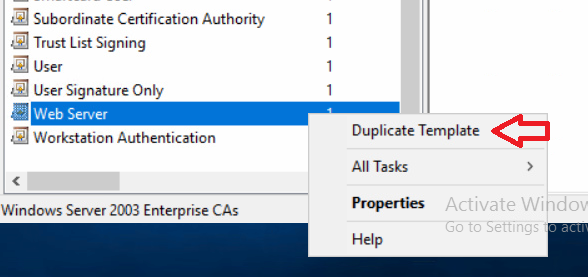
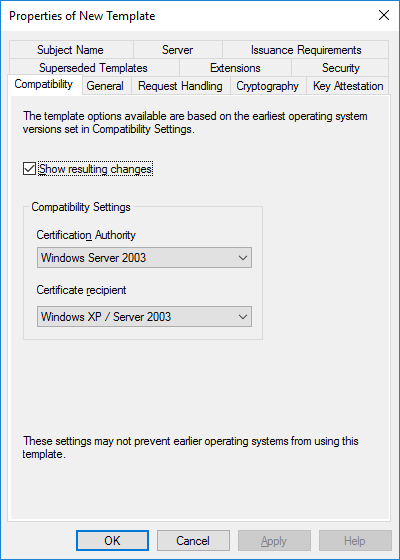
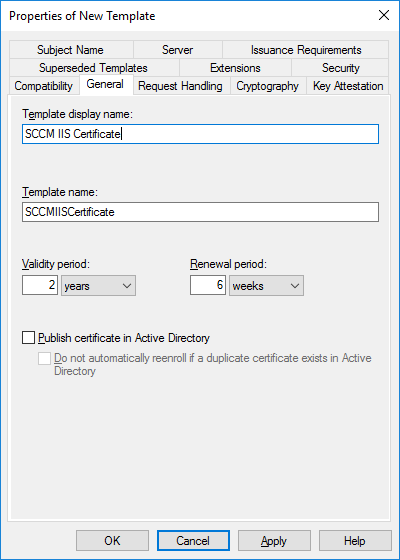
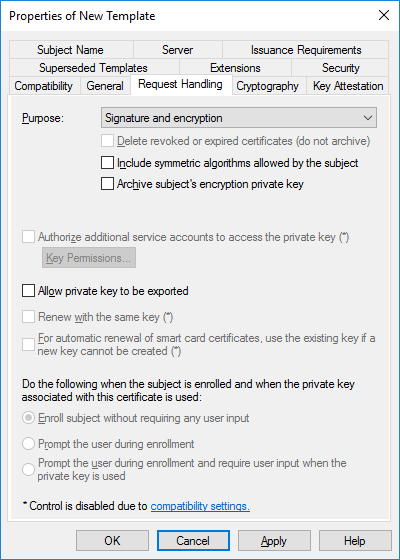
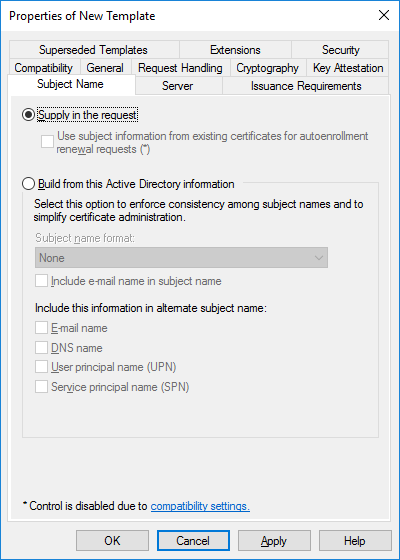
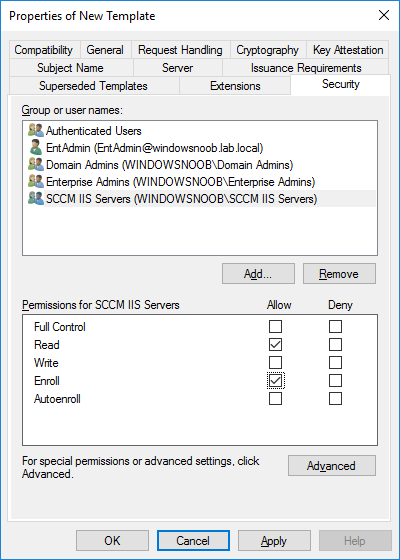
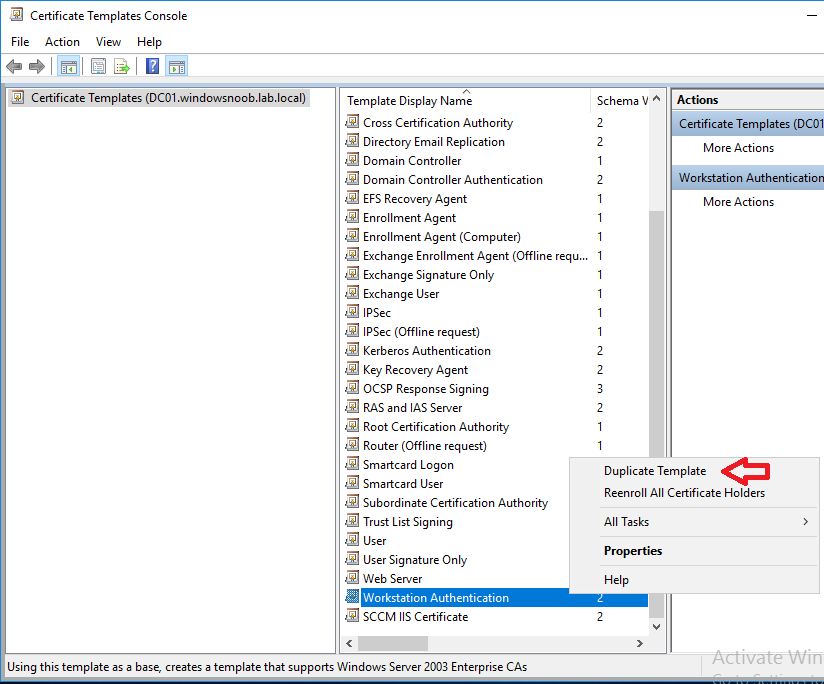
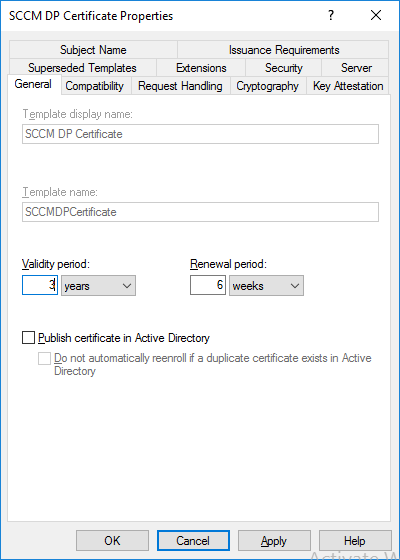
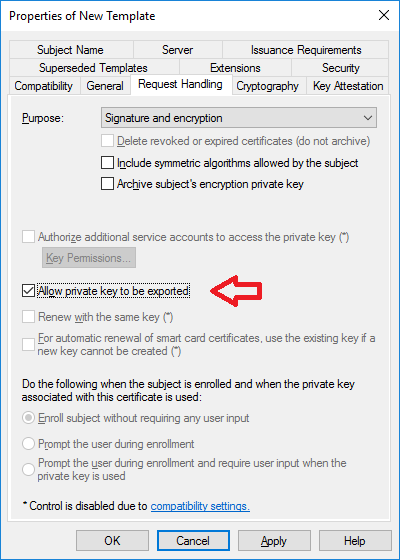
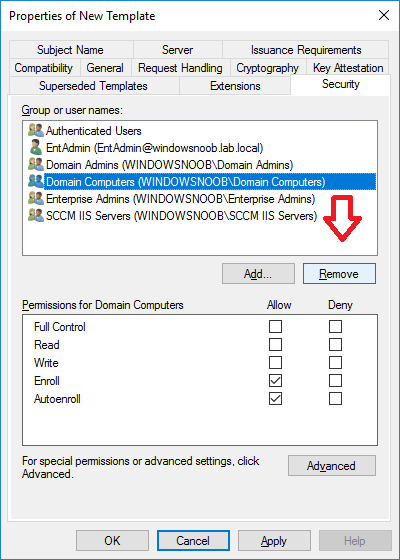
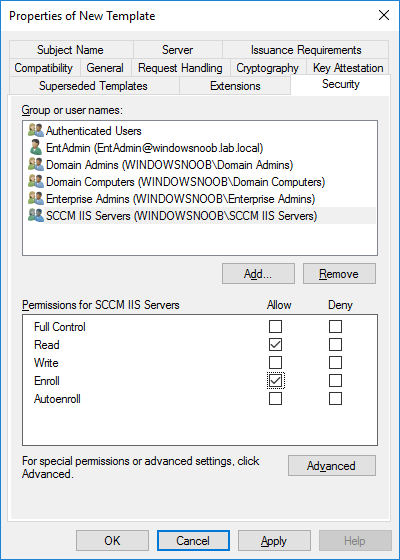
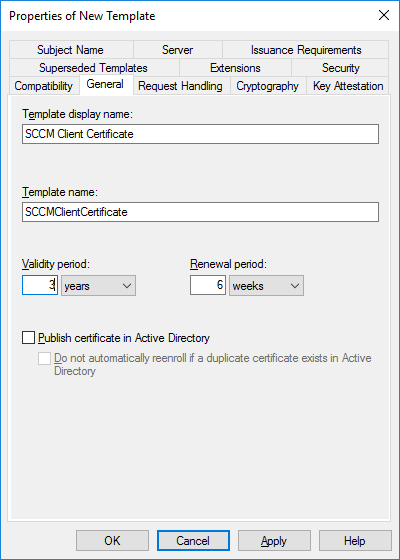
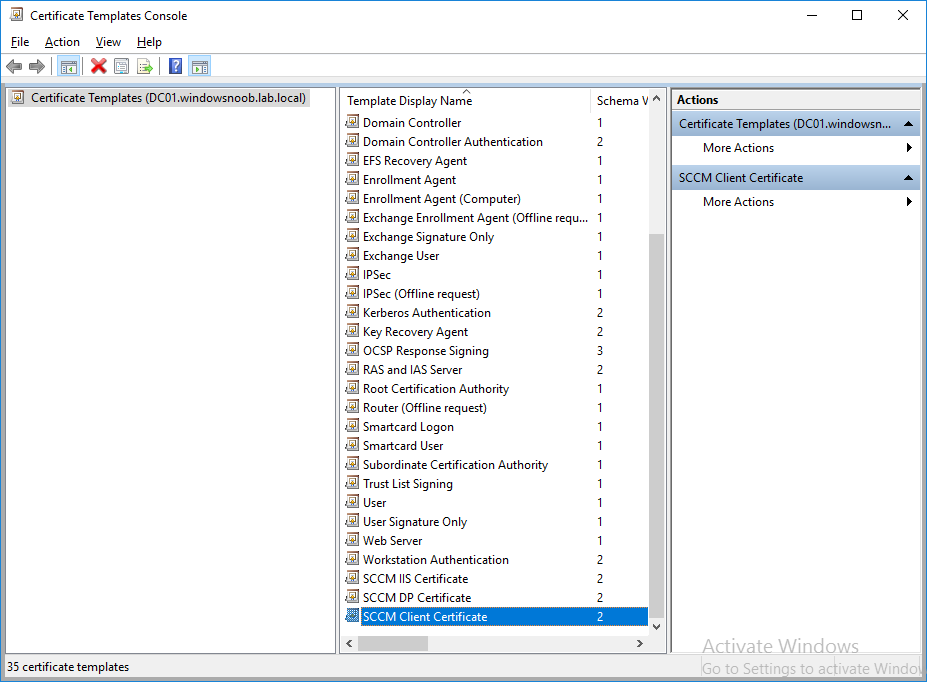
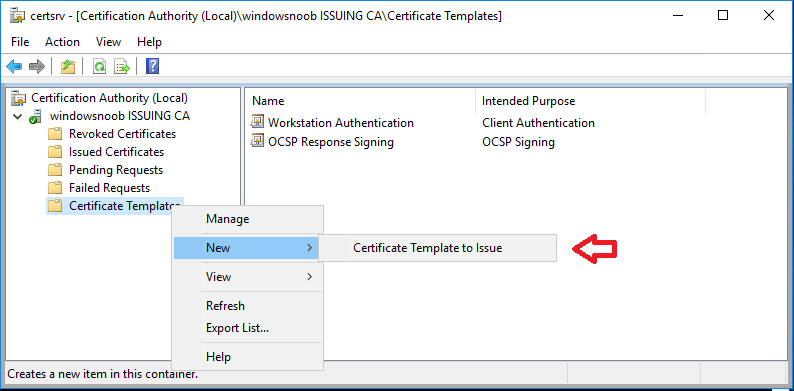
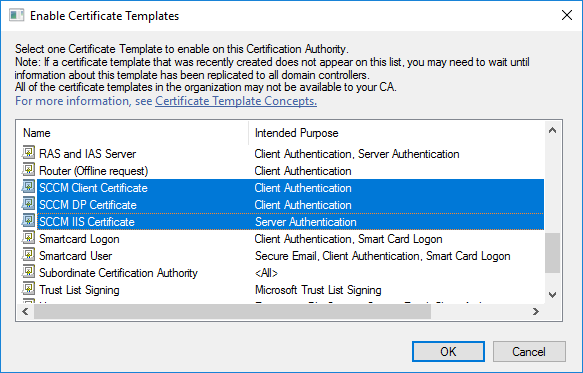
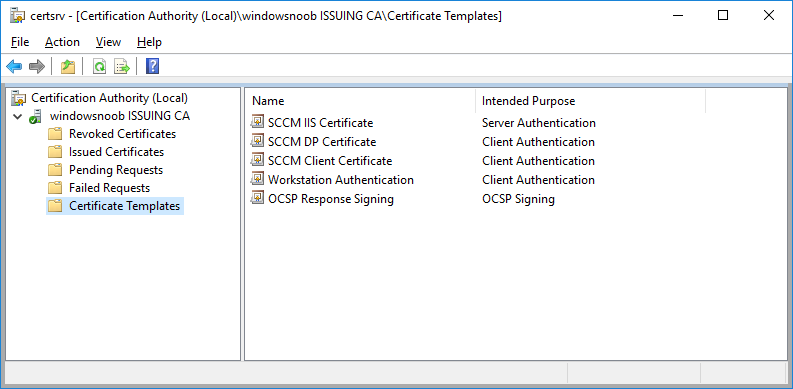
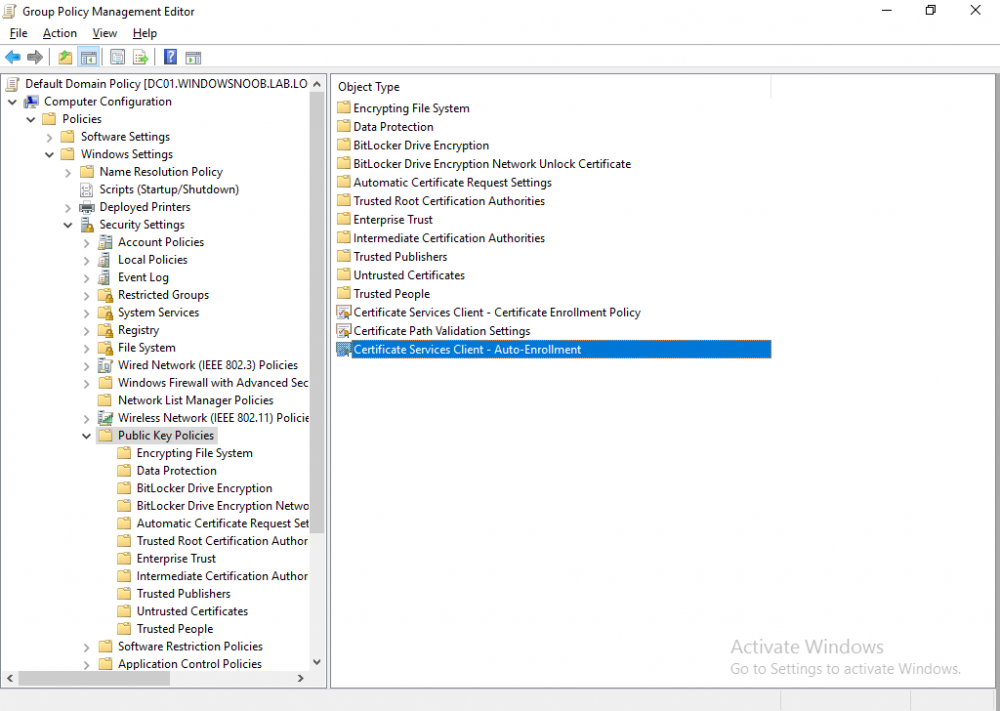
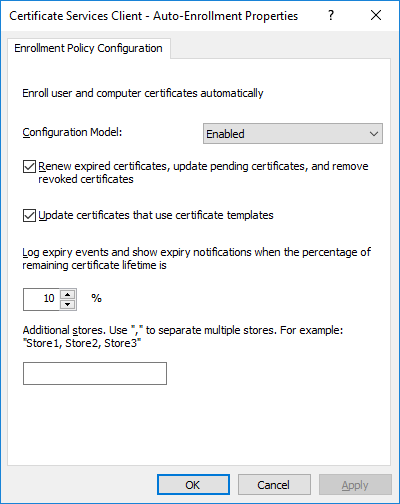
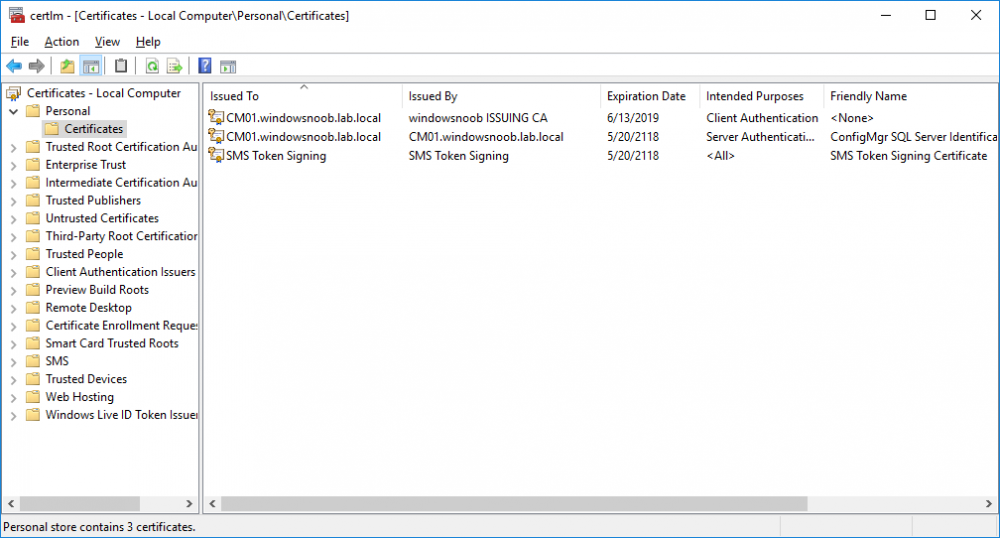
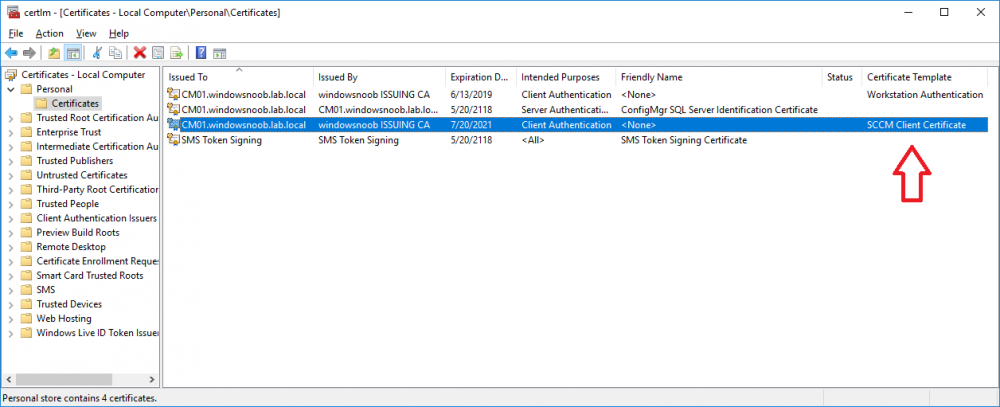
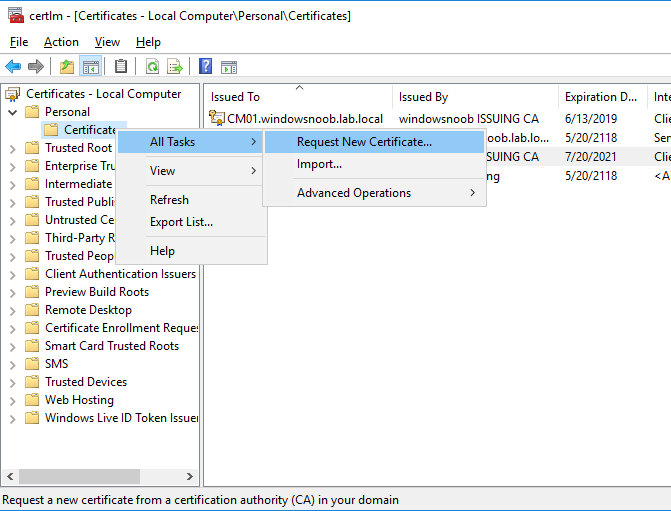
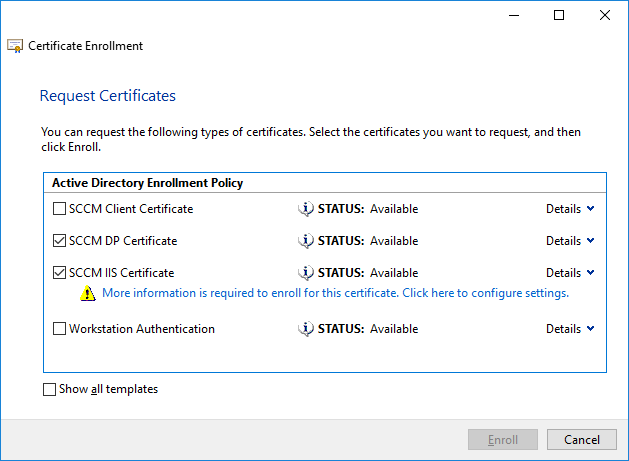
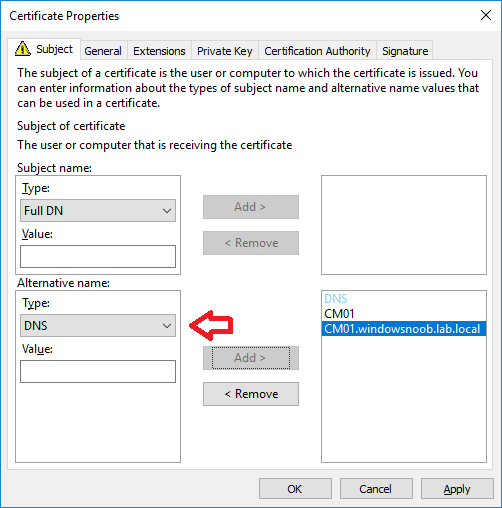
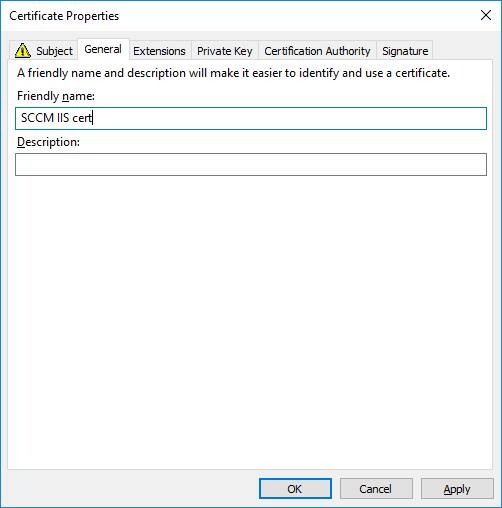
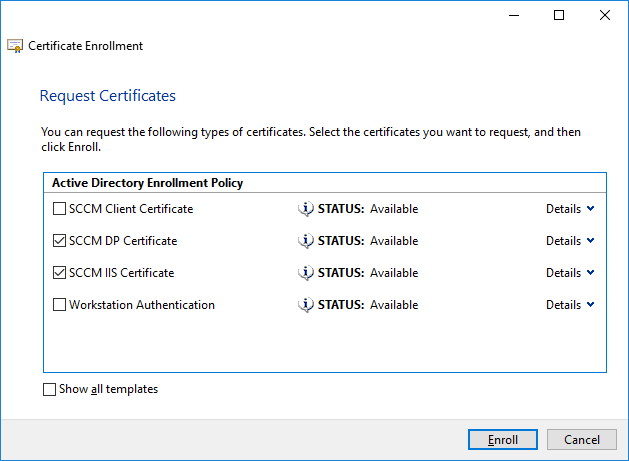
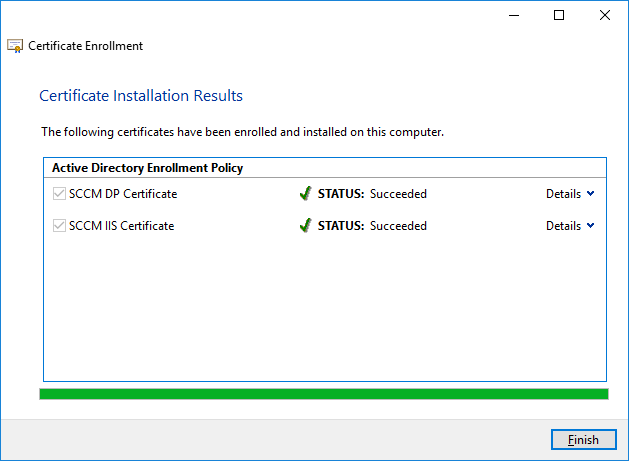
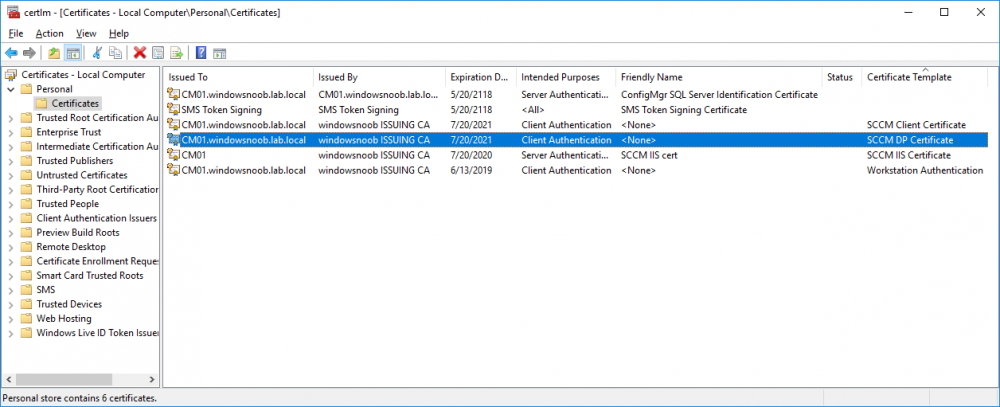
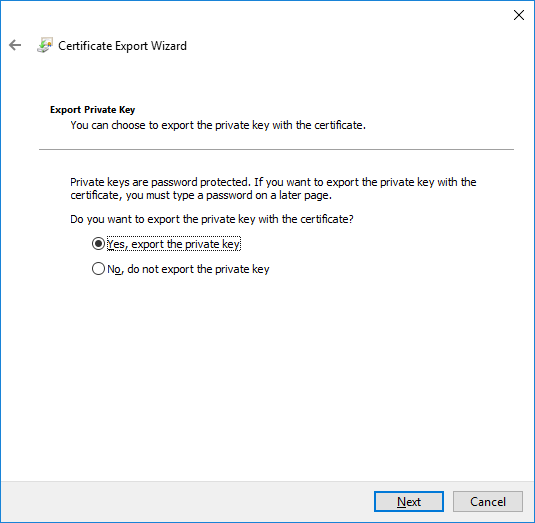
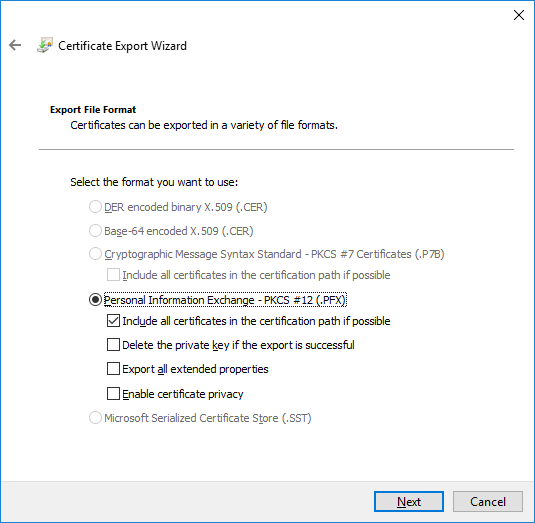
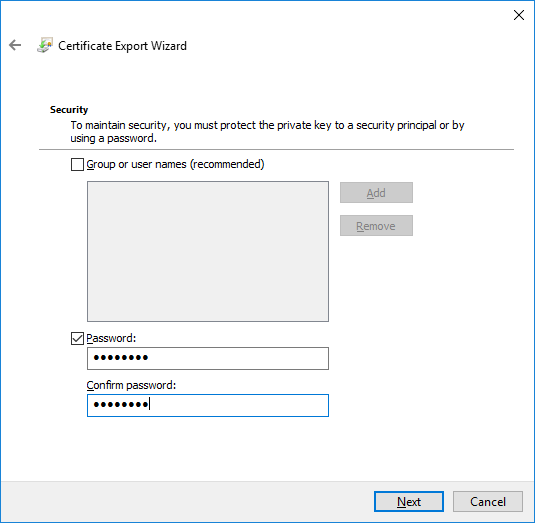
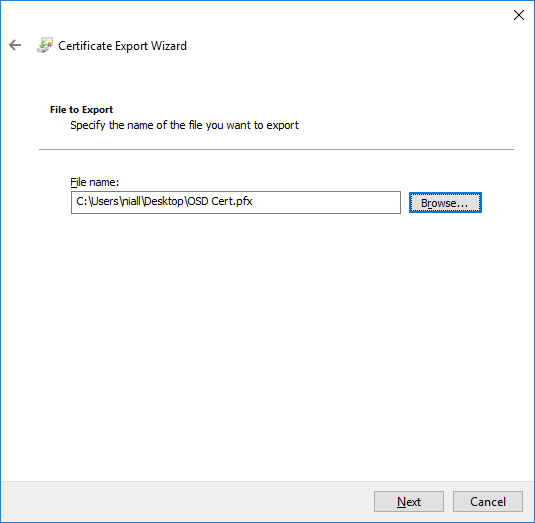
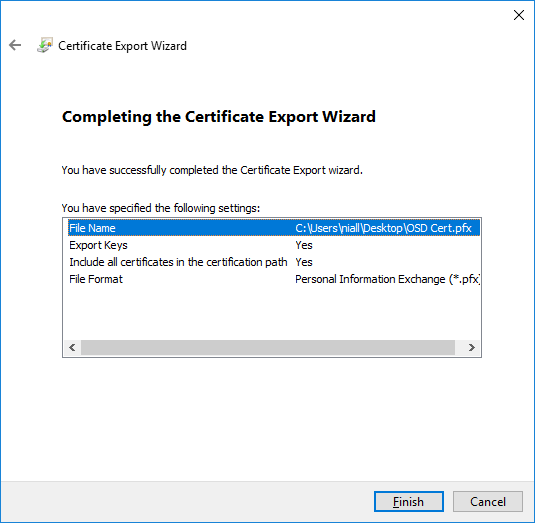
In a previous series of guides I showed you how to configure PKI in a lab on Windows Server 2016. In another series, I also showed you how to install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1802 on Windows Server 2016 with SQL Server 2017. In this lab, I will show you how to configure SCCM to utilize that PKI environment. This series is based upon an excellent video by the talented former Microsoft Premier Field Engineer Justin Chalfant here. If you haven't seen it yet, do check it out. The intention here is that after you've completed this PKI enabled SCCM lab you can then use this in future guides, and to dig deeper into new technologies from Microsoft, for example enabling a Cloud Management Gateway and/or Cloud Distribution Point and using later on, using Co-Management. Note: To complete this lab you must first complete the PKI Lab series (8 parts) and then install a new virtual machine within that PKI lab running System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1902 utilizing this series, that installation of Configuration Manager will be in HTTP mode. In addition, you must configure the Software Update Point role (in HTTP mode) on CM01 See this guide (step 2 onward) for details. For details how to configure that, see this post. It will take some time to setup but you'll be glad you did. Also, don't do this in production without consulting with a PKI Expert. I don't claim to be one, I'm just helping you get it up and running in a lab. This is intended for use in a lab only. Step 1 - Create an Active Directory Security Group In this step you'll create an active directory group which will contain all your site systems that use Configuration Manager server roles which utilize IIS (Internet Information Systems) such as the below (1): Management point Distribution point Software update point State migration point Enrollment point Enrollment proxy point Application Catalog web service point Application Catalog website point A certificate registration point On the Active Directory domain controller (DC01), open Active Directory Users and Computers, and expand the windowsnoob organisational unit (OU) created in this Step 1, part 5 of this blog post. Click on Security Groups, and then right click and choose New, select Group. Give the group a name, SCCM IIS Servers. Once done, right click on the SCCM IIS Servers Active Directory Security Group, choose Properties and click on the Members tab, click on Add, for Object Types make sure Computers are selected. Add the Configuration Manager server (CM01) to that group. Once done, reboot the Configuration Manager server (CM01) using the following command otherwise you might get access denied when trying to request a certificate. shutdown /r Step 2. Create certificate templates on the Issuing CA In this step you will create three new certificate templates for use within SCCM by duplicating existing templates. Using the windowsnoob\Entadmin credentials, logon to the Issuing CA server (IssuingCA) and launch the certificate authority console (CertSrv.msc). In the three templates below, one uses the Web Server template, and the others use the Workstation Authentication template, you can verify which Microsoft certificate template to use by using the tables on the following blog post, of which i'm showing a screenshot below to make it clear. 1. SCCM IIS Certificate Right click on Certificate Templates and choose Manage. Scroll down to Web Server from the templates listed. Right click on the Web Server template and choose Duplicate Template. The Properties of New Template screen appears. Verify that the Certificate Authority Compatibility settings are set to Windows Server 2003. Note: When you use an enterprise certification authority and certificate templates, do not use the Version 3 templates (well you can but read this first). These certificate templates create certificates that are incompatible with System Center Configuration Manager. Instead, use Version 2 templates by using the following instructions. On the Compatibility tab of the certificate template properties, specify Windows Server 2003 for the Certification Authority option, and Windows XP / Server 2003 for the Certificate recipient option. (1) Click on the General tab and rename it to SCCM IIS Certificate. On the Request Handling tab, verify that Allow private key to be exported is not selected (default). On the Subject Name tab verify that the Supply in the Request is selected (default). On the Security tab, add the previously created Active Directory Security Group called SCCM IIS Servers and give it Read and Enroll access. Optionally you can remove Enroll from the Domain Admin and Enterprise Admins as it is mentioned in the docs. Click Apply to apply the changes and then close the Properties of New Template. 2. SCCM DP Certificate This template is used by the distribution point site system for Operating System Deployment (clients that are not domain joined). Next, right click on Workstation Authentication from the templates listed and choose Duplicate Template. The Properties of New Template screen appears. The Properties of New Template screen appears. Verify that the Certificate Authority Compatibility settings are set to Windows Server 2003. Click on the General tab and rename it to SCCM DP Certificate, change the validity period to something more reasonable, like 3 years. On the Request Handling tab, ensure that Allow private key to be exported is selected to allow us to export the certificate as a pfx file and we need the private key to do so, as we'll import that certificate into our console so that the clients can utilize it during imaging (workgroup members, to authenticate back to your site). On the Security tab, add the previously created Active Directory Security Group called SCCM IIS Servers and give it Read and Enroll access. Next, remove Domain Computers altogether. Click Apply to apply the changes and then close the Properties of New Template. 3. SCCM Client Certificate This template is used by clients to communicate with site systems. Next, right click on Workstation Authentication from the templates listed and choose Duplicate Template. The Properties of New Template screen appears. The Properties of New Template screen appears. Verify that the Certificate Authority Compatibility settings are set to Windows Server 2003. Click on the General tab and rename it to SCCM Client Certificate, change the validity period to something more reasonable, like 3 years. Under Subject Name verify that Build from Active Directory is selected. On the Request Handling tab, verify that Allow private key to be exported is not selected (default). On the Security tab, select Domain Computers and ensure that Read, Enroll and AutoEnroll permisions are selected. Click Apply to apply the changes and then close the Properties of New Template. The three SCCM templates are now shown below. Close the Certificate Templates console. Next you will issue these certificate templates. To do so, in the Certificate Authority (on the IssuingCA), right click on Certificate Templates and choose New, then Certificate Template to Issue. In the Enable Certificate Templates window, select the 3 previously created SCCM templates as shown below and click OK. They will now appear under Certificate Templates. Step 3. Verify Auto-Enrollment GPO is enabled for the Client Certificate In Part 8 of the PKI lab you enabled Auto Enrollment so that clients can request certificates automatically. As it is a lab, the setting is deployed in the default domain GPO. The setting is in Computer Configuration, Policies, Windows Settings, Security Settings, Public Key Policies, and Certificate Services Client - Auto Enrollment. The setting should look like so (Enabled). Step 4. Requesting the IIS and DP/OSD Certificates on the IIS Site System On the SCCM server (CM01), which hosts all those IIS ConfigMgr roles, start certlm.msc from an Administrative command prompt. if you expand Personal, then Certificates, you'll see certificates issued to that computer, there will be a few by default. In the administrative command prompt, run gpupdate /force to pull down group policy changes...and refresh the view in certlm. Below you can see the SCCM Client Certificate template was used to generate this Client Authentication certificate. Requesting New certificates Next, you will request certificates from Active Directory, to do so, right click on Certificates and choose All Tasks then Request New Certificate. click Next at the Before you begin screen, and verify that Active Directory Enrollment Policy is selected before clicking Next. Select the SCCM DP Certificate and SCCM IIS Certificate from those listed (you already have the SCCM Client Certificate from AutoEnrollment). You'll notice that for the SCCM IIS Certificate, more information is required to enroll, Click on the message to enter this info. For Alternative Name, choose the DNS option and then click on Add to add the hostname and fully qualified domain name of your SCCM server (CM01). Note: If you want this server to be available via IBCM you could also add the publicly available FQDN of the site here (eg: cm01.windowsnoob.com) Next Click on General, and give this cert a friendly name so we can distinguish it in IIS later when we bind it. click OK, then click Enroll. It should state a status of Succeeded for both certificates. If not look at the details to find out what went wrong. Click Finish to exit. Step 5. Exporting the Distribution Point certificate Next you need to export the Distribution Point certificate so that during OSD the client can authenticate to the management point in WinPE. To do that, refresh the view in Certificates (certlm.msc) and then select the client authentication certificate created with the SCCM DP Certificate template. Right click and choose All Tasks, then select Export. In the welcome to certificate export wizard click Next and choose to export the private key. stick with the defaults and give it a password that you will use when you import it back into the SCCM Console, I used P@ssw0rd Save the cert to your desktop with a filename of OSD Cert.pfx and continue through that wizard until completion. You should see that the export was successful. That's it for this part, please join me in part 2 where we will complete the configuration of SCCM to HTTPS. cheers niall Recommended reading (1) - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/plan-design/network/pki-certificate-requirements
-
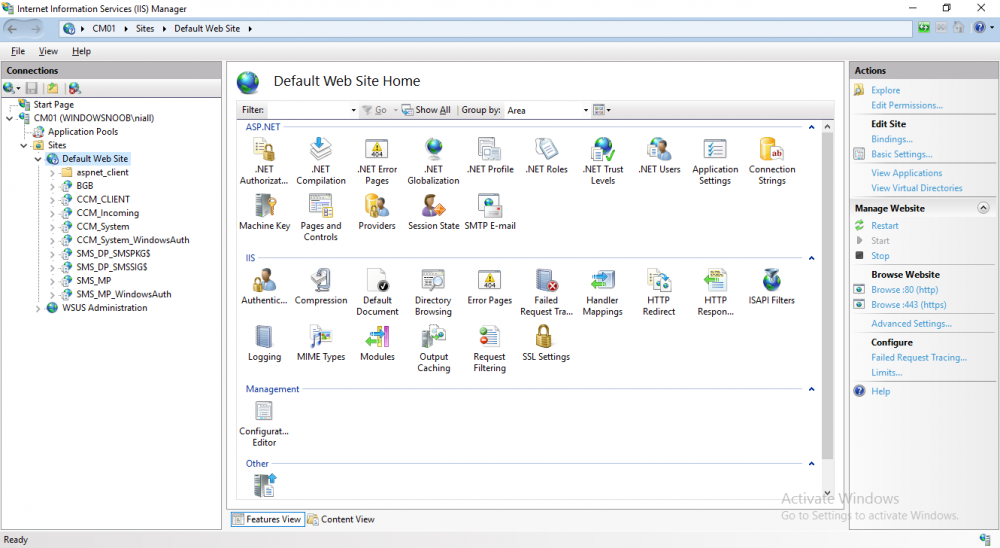
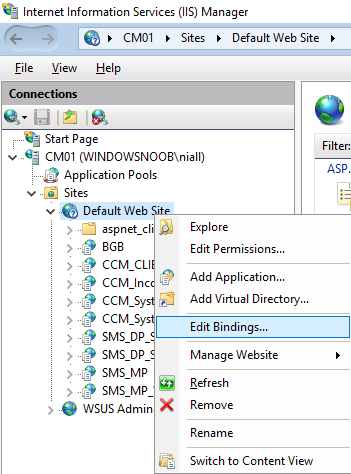
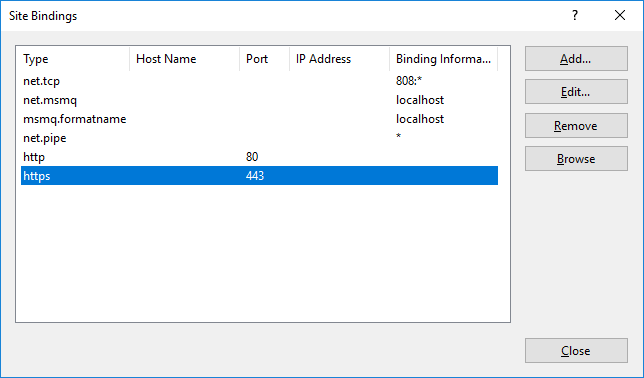
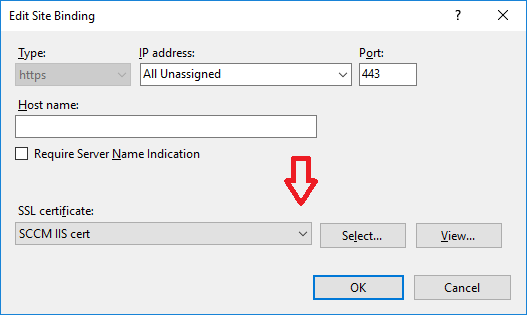
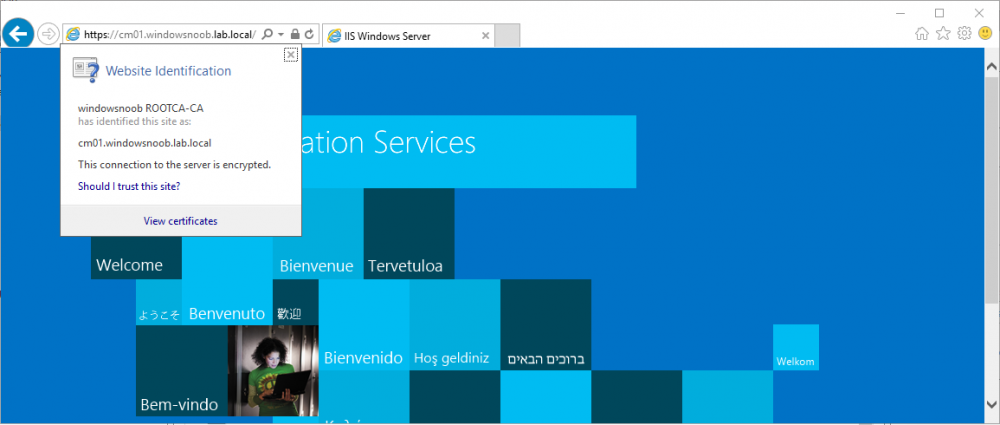
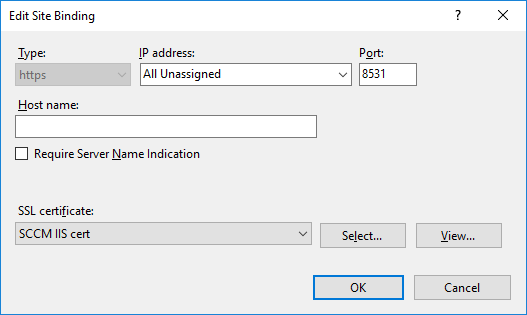
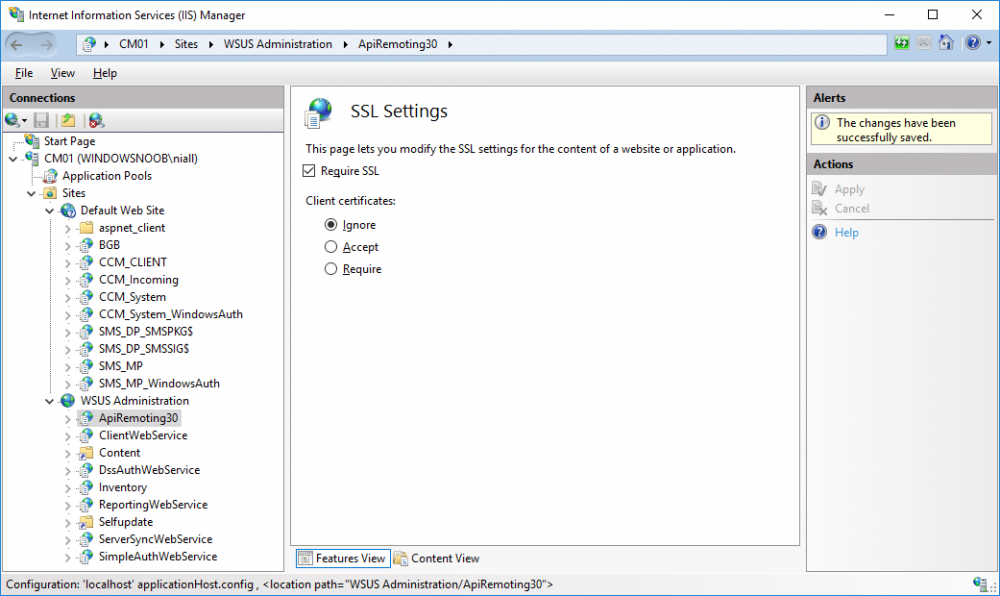
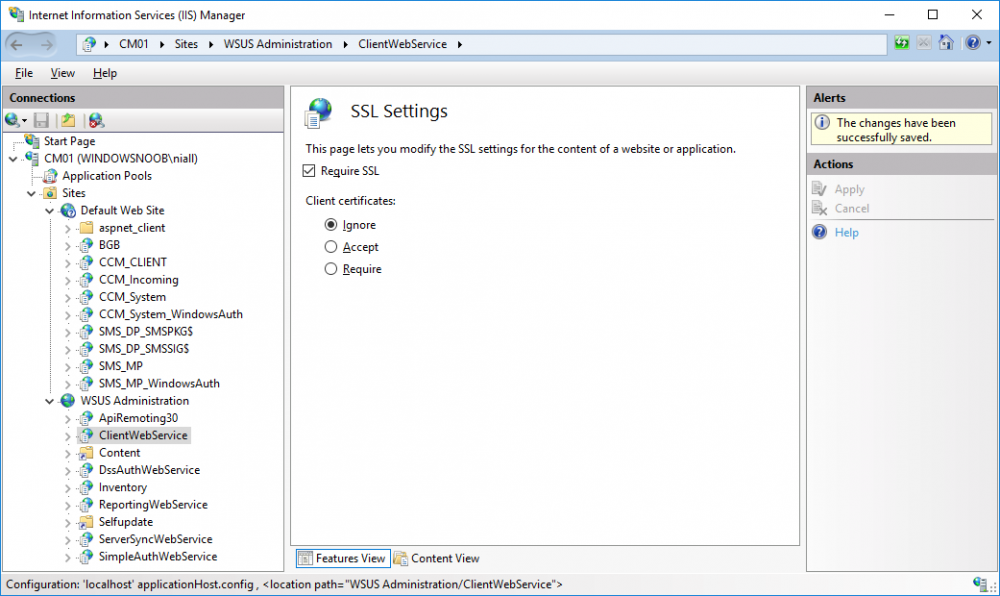
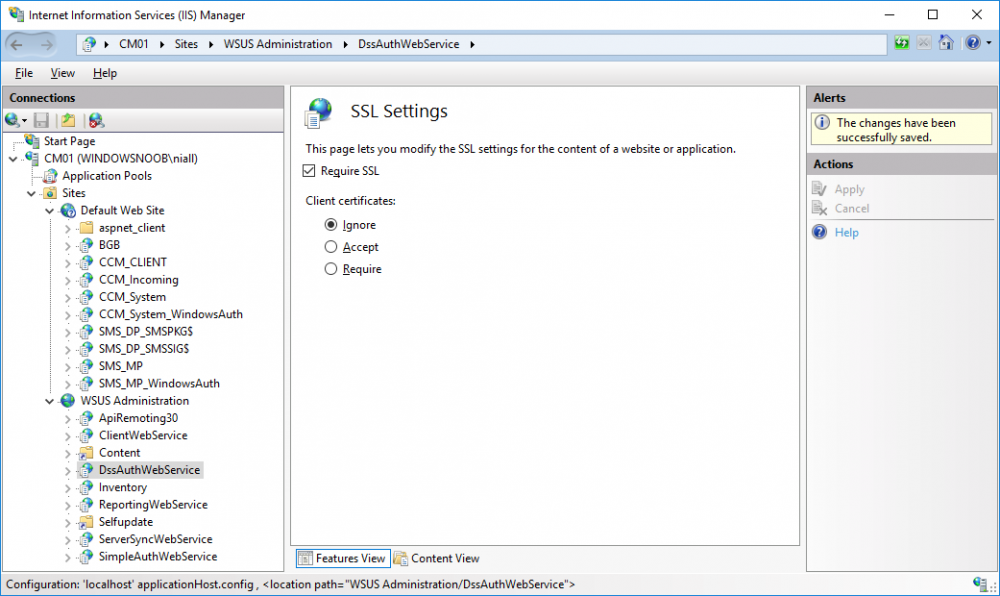
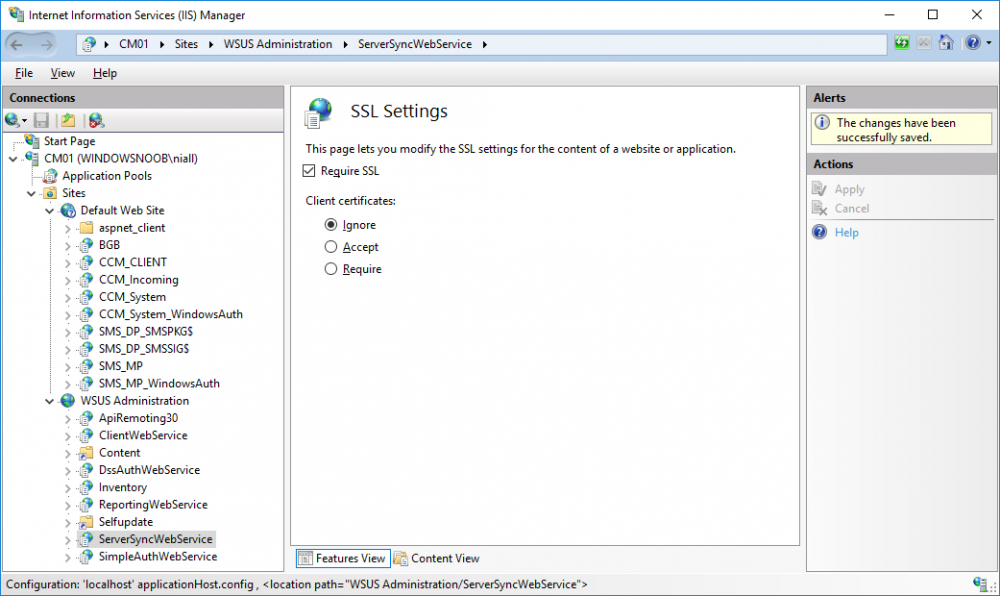
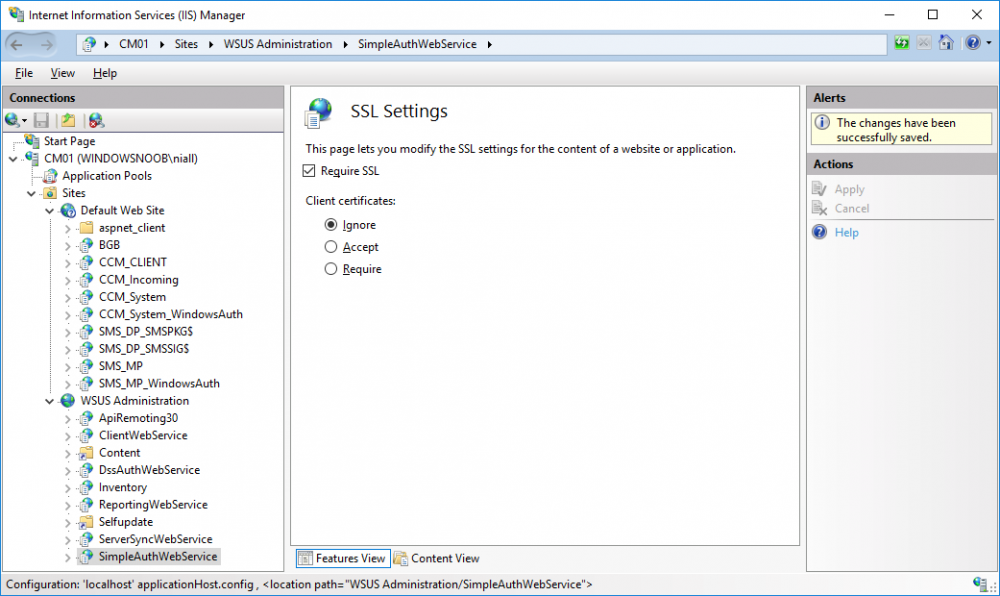
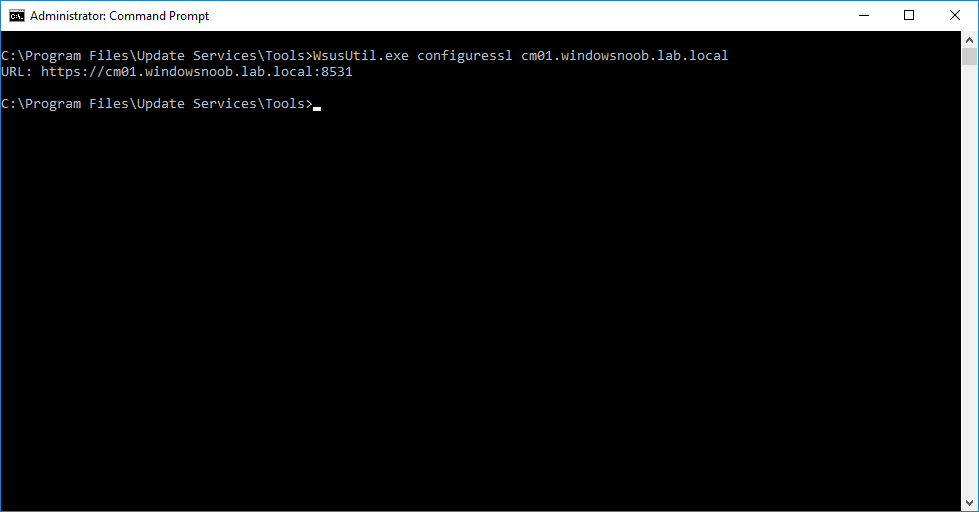
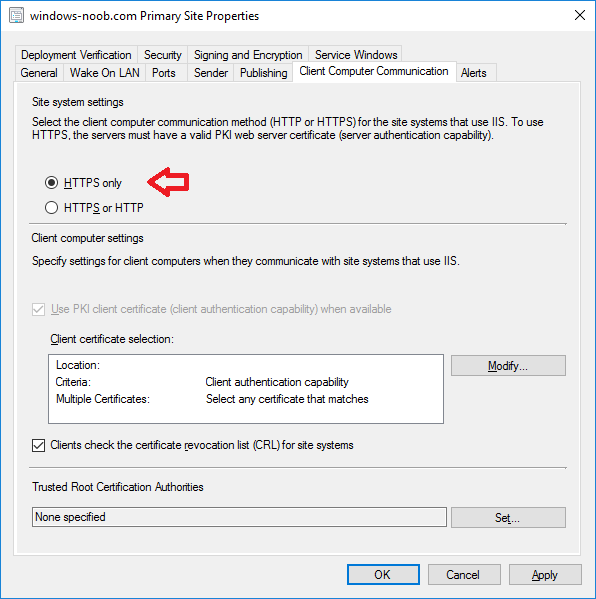
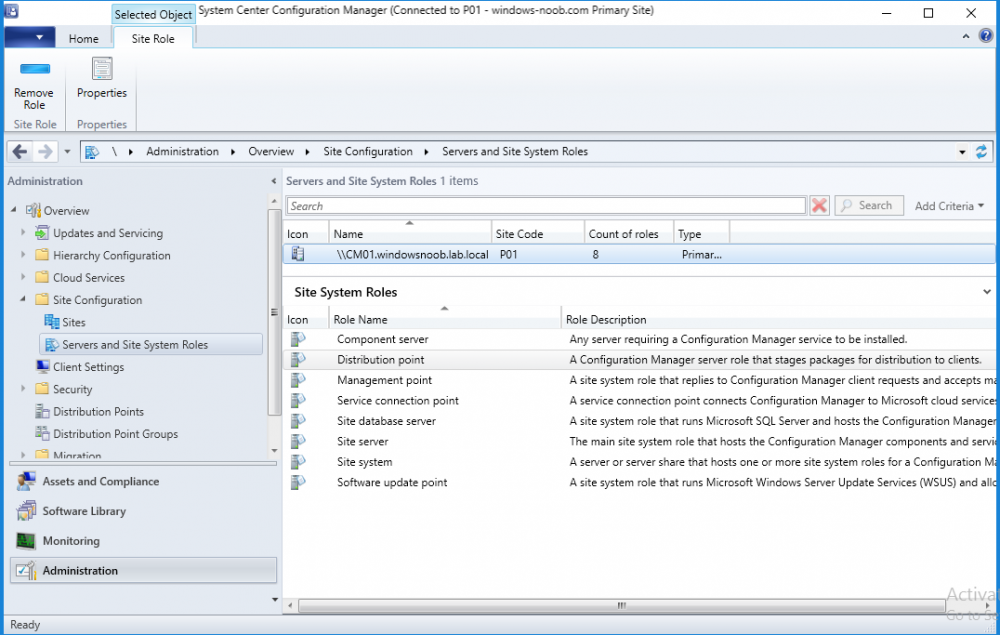
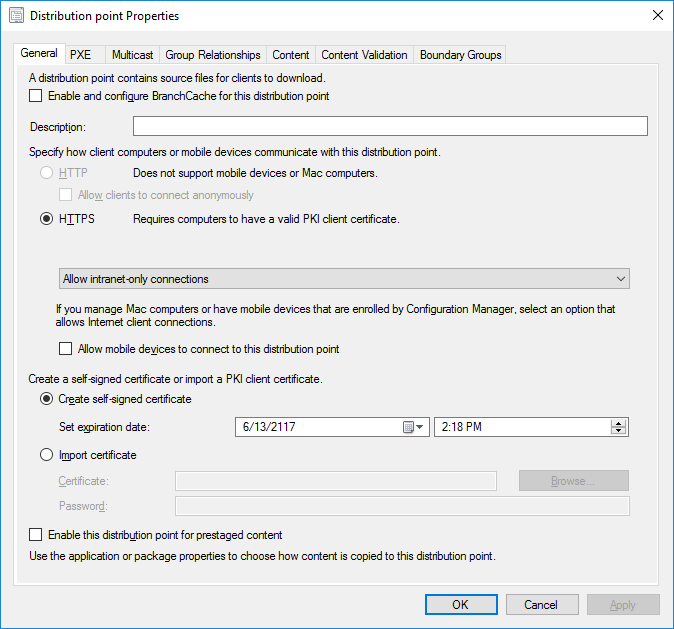
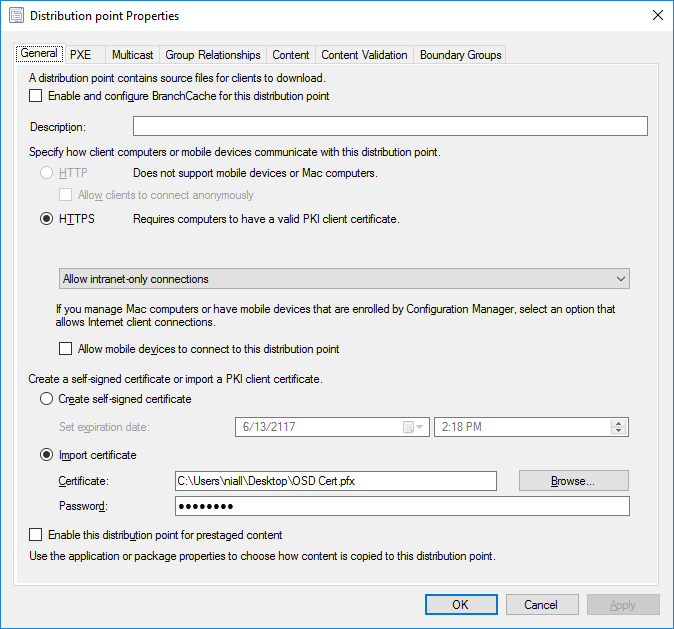
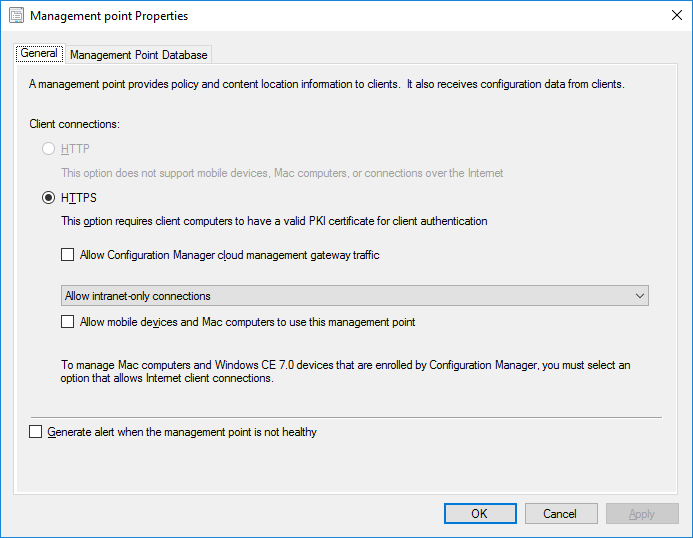
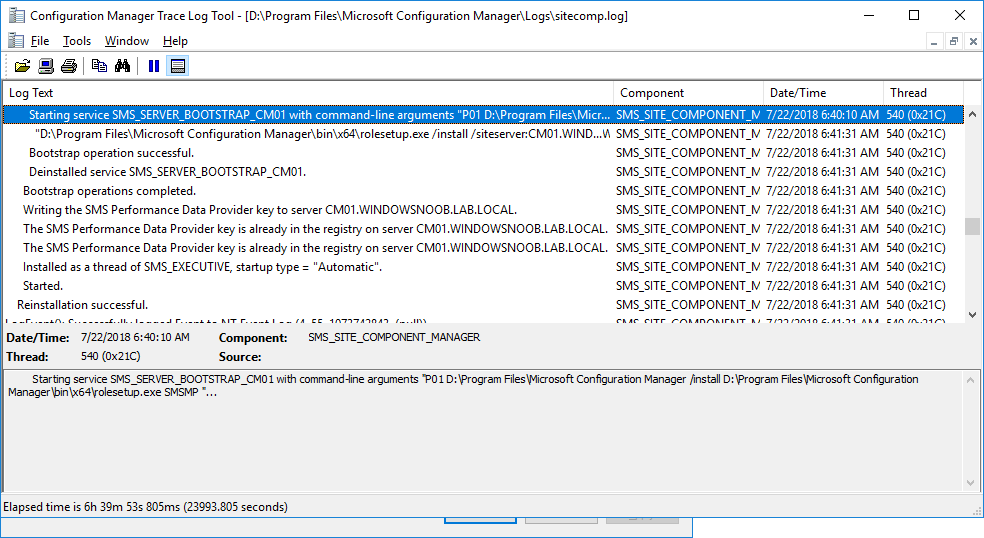
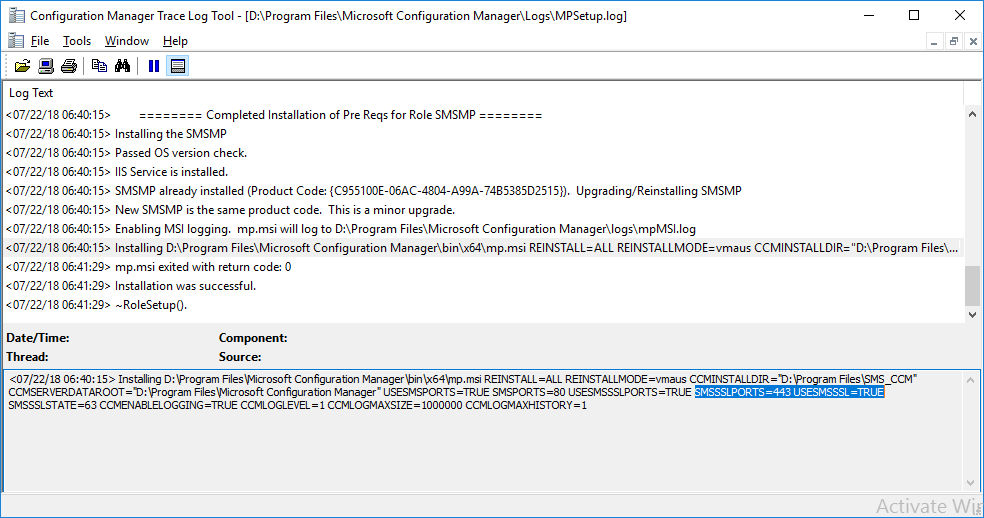
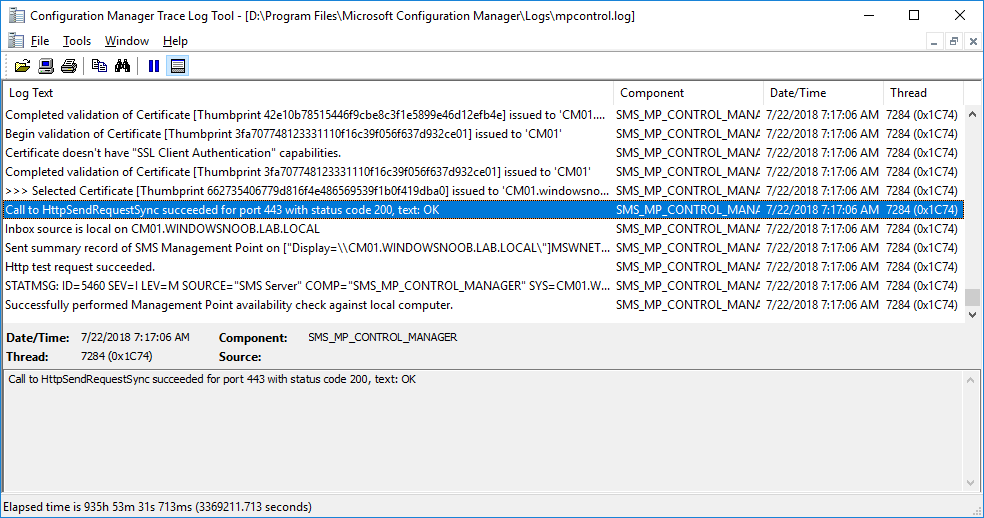
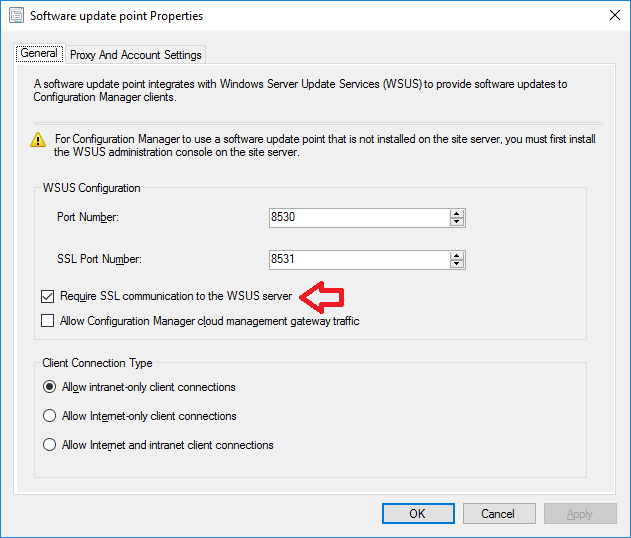
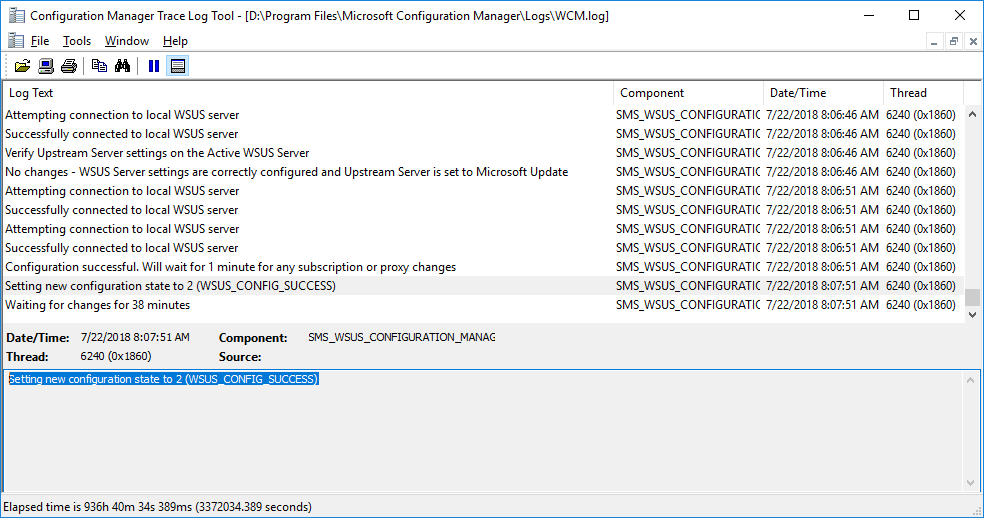
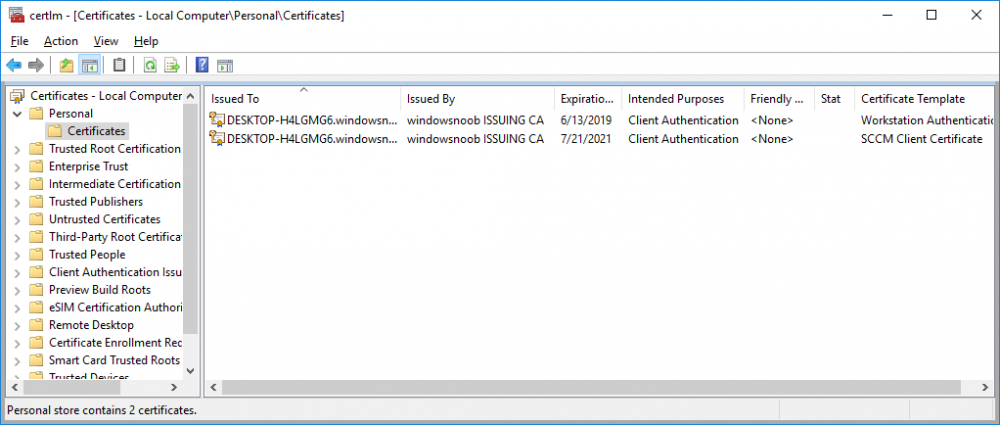
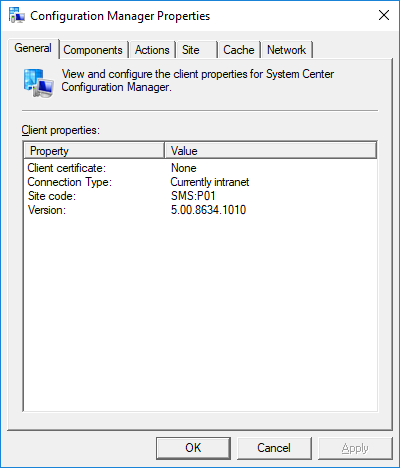
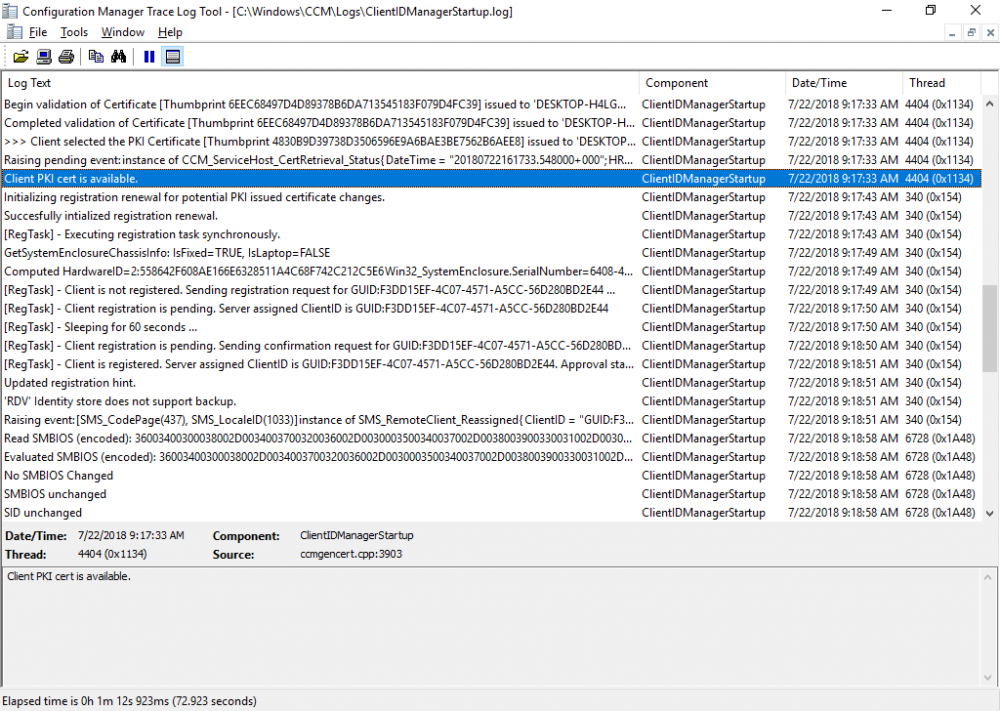
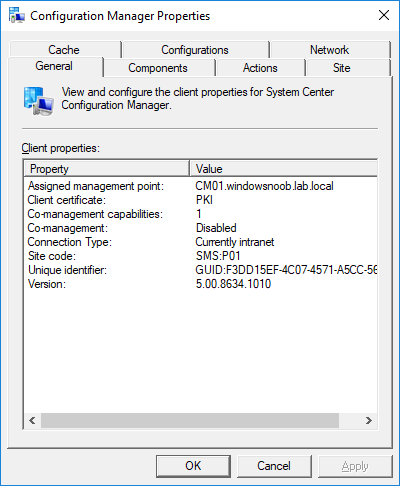
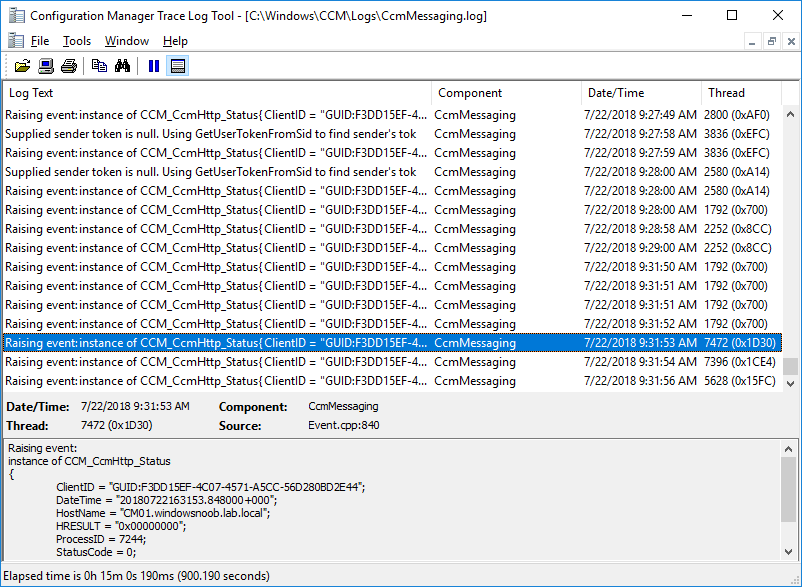
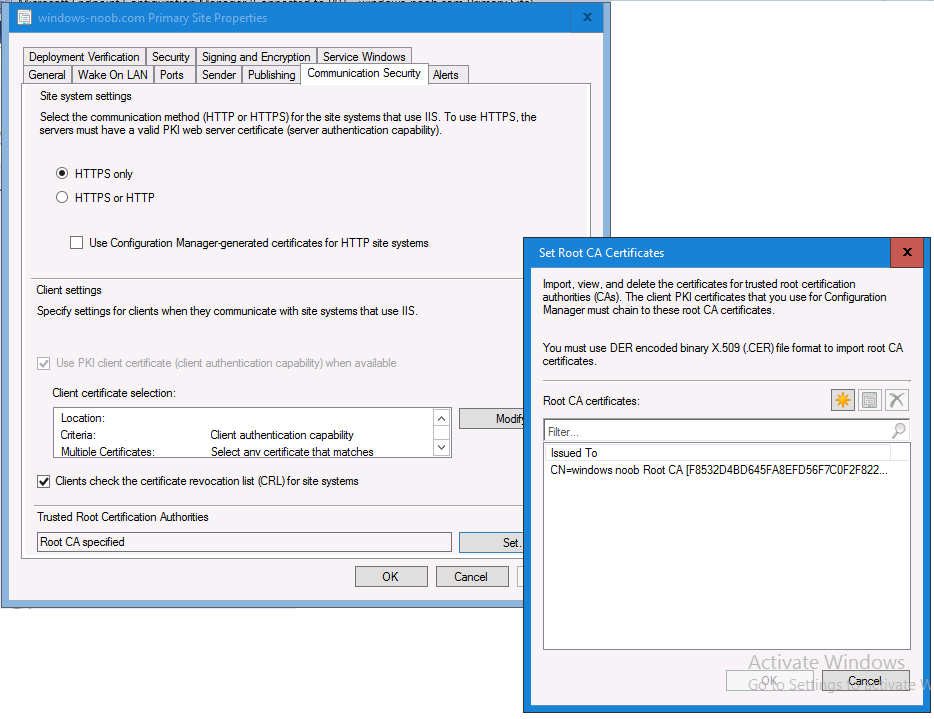
In a previous series of guides I showed you how to configure PKI in a lab on Windows Server 2016. In another series, I also showed you how to install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1802 on Windows Server 2016 with SQL Server 2017. In this lab, I will show you how to configure SCCM to utilize that PKI environment. This series is based upon an excellent video by the talented former Microsoft Premier Field Engineer Justin Chalfant here. If you haven't seen it yet, do check it out. The intention here is that after you've completed this PKI enabled SCCM lab you can then use this in future guides, and to dig deeper into new technologies from Microsoft, for example enabling a Cloud Management Gateway and/or Cloud Distribution Point and using later on, using Co-Management. Note: To complete this lab you must first complete the PKI Lab series (8 parts) and then install a new virtual machine within that PKI lab running System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1802 utilizing this series (4 parts), that installation of Configuration Manager will be in HTTP mode. In addition, you must configure the Software Update Point role (in HTTP mode) on CM01 See this guide (step 2 onward) for details. For details how to configure that, see this post. It will take some time to setup but you'll be glad you did. Also, don't do this in production without consulting with a PKI Expert. I don't claim to be one, I'm just helping you get it up and running in a lab. This is intended for use in a lab only. In part 1 of this series you created an Active Directory Security Group to contain your SCCM servers that host IIS based roles such as Distribution Point, Management Point and Software Update Point, you then rebooted that server after adding it (CM01) to the group. You then created 3 certificate templates for SCCM on the Issuing CA server (IssuingCA) and issued them so that they could be available to applicable computers. You verified that you had a GPO in place for AutoEnrollment before requesting the IIS and DP/OSD Certificates on the IIS Site System (CM01) using certlm.msc. Step 1. Edit bindings in IIS for the Default Web Site and WSUS Administration Websites On the SCCM server (CM01), start Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager, expand Sites so that you can see the Default Web Site and the WSUS Administration websites listed. Select the Default Web Site, this web site is where the management point, distribution point and other SCCM roles such as Application Catalog can be found (if they are installed). Edit bindings on the Default Web Site Right click on the Default Web Site and choose Edit Bindings from the options available. In the window that appears, select the https section (port 443) and choose Edit. In the SSL certificate dropdown menu, select SCCM IIS Cert. Click OK and then click Close. Verify changes made Once done, you can open up Internet Explorer and verify that it's reporting back in HTTPS mode for the default web site by browsing to the following addresses to verify the Netbios name and FQDN resolve in HTTPS mode. Click on the Lock in the address bar to get info about the connection. https://cm01 https://cm01.windowsnoob.lab.local/ Edit bindings on the WSUS Administration Web Site Repeat the above operation, on the WSUS Administration website (note that it uses port 8531 for https mode). click OK and Close when done. Step 2. Modify WSUS Administration SSL Settings WSUS itself requires some additional changes documented here (1) that we need to configure to allow WSUS to use HTTPS. In the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager, expand sites and selct WSUS Administration. Select ApiRemoting30 under the WSUS Administration web site, in the right pane, click on SSL Settings and select Require SSL and verify that Ignore is selected before clicking Apply. Next, select ClientWebService under the WSUS Administration web site, in the right pane, click on SSL Settings and select Require SSL and verify that Ignore is selected before clicking Apply. Next, select DSSAuthWebService under the WSUS Administration web site, in the right pane, click on SSL Settings and select Require SSL and verify that Ignore is selected before clicking Apply. Next, select ServerSyncWebService under the WSUS Administration web site, in the right pane, click on SSL Settings and select Require SSL and verify that Ignore is selected before clicking Apply. Finally, select SimpleAuthWebService under the WSUS Administration web site, in the right pane, click on SSL Settings and select Require SSL and verify that Ignore is selected before clicking Apply. Step 3. Configure WSUS to require SSL In an administrative command prompt on CM01, browse to the location of WSUS installation files. cd C:\Program Files\Update Services\Tools Next issue the following command where CM01.windowsnoob.lab.local is the Fully qualified domain name of your ConfigMgr server hosting WSUS. WsusUtil.exe configuressl cm01.windowsnoob.lab.local The results are shown below: Step 4. Configure SCCM to use HTTPS In this step you will configure SCCM to operate in HTTPS mode. To do that, first bring up the site properties in the SCCM Console on CM01. To bring up the site properties, select the Administration workspace, select Site Configuration, select your site and in the ribbon choose Properties. Next, click on Client Computer Configuration, select HTTPS only from the options and then select Apply. Note: If you have both HTTP and HTTPS site systems in your environment, keep the second box checked (HTTPS or HTTP) and enable the Use PKI client certificate (client authentication capability) when available check box. Step 5. Configure Trusted Root Certification Authorities Note: If you fail to add the Root CA (ROOTCA_windows noob Root CA.crt) specified here, PXE boot will fail to download policy after entering the PXE password. In the site properties screen, click on Communication Security and then click on Set beside Trusted Root Certification Authorities, and click on the yellow star to add your Root CA, in this case, the Root CA for your lab (from the offline root ca), in other words point it to the ROOTCA_windows noob Root CA.crt file which is the Trusted Root Certificate for this site (the Root CA cert). Step 6. Verify that the Distribution Point, Management Point and Software Update Point are using SSL Next you need to verify the DP (and perform some additional configuration), MP and SUP roles are using SSL. To do this, select the Administration workspace in the console, click Site Configuration, select Servers and Site System roles, and select the Distribution Point role. Right click it and choose Properties to bring up the Distribution Point role properties. You should see that it is already configured for HTTPS. Next you need to add the certificate used by clients being imaged by operating system deployment in WinPE or for WorkGroup based clients, to do so, click on Import Certificate and select Browse, browse to the location where you saved the OSD Cert.pfx file (which you created in Step 5 of part 1 here), enter the password you specified, and click Apply. Click OK to close the Distribution Point role properties. For more info on the DP Cert requirements see - https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/plan-design/network/pki-certificate-requirements Next, select the Management Point role properties, they are shown below, again, HTTPS is selected by default as you set it site wide with the HTTPS only option. When you selected HTTPS Only in the Client Computer Communication of the site properties, this initiated the Management Point to reinstall itself with the new settings, as you can see here in the sitecomp.log. In addition in the mpsetup.log you can see that it's configured for SSL Finally you can check mpcontrol.log this log logs the status of your Management Point, and in there you can verify that the Management Point is up and running and communicating OK in HTTPS mode and that it has successfully performed Management Point availability checks. Next, double click the Software Update Point role to review it's properties. Place a check in the Require SSL communication to the WSUS Server check box. Click Apply and click OK to close the Software Update Point properties. At this point open the WCM.log and look for a line that reads Step 7. Verify Client Received Client Certificate and SCCM Client Changes to SSL Logon to the Windows 10 1803 client and start and administrative command prompt, from there launch certlm.msc to bring up Certificates on the Local Machine. Browse to Personal and Certificates, and you should see the SCCM Client Certificate listed. Note: I assume you've already installed the ConfigMgr client agent using whatever method your prefer on the Windows 10 1803 virtual machine. Next, open the Control Panel and locate the Configuration Manager client agent in System and Security, and open it. If the client was just installed the Client Certificate will probably state Self-Signed (or None if you have just installed the client..). After a couple of minutes, close and then reopen the client and you should see that the Client Certificate states PKI. At this point, open the ClientIDManagerStartup.log in C:\Windows\CCM\Logs and you can see Client PKI cert is available. You can also verify client communication to the Management Point in the CCMMessaging.log and we can see it's successful in that communication. Job done ! You've successfully converted SCCM from HTTP to HTTPS using your PKI lab, and you've verified that the client is operating in HTTPS mode. In the next parts we'll look at the Cloud Management Gateway and Cloud Distribution Point. Recommended reading (1) - https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb633246.aspx https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sccm/core/plan-design/network/pki-certificate-requirements https://www.enhansoft.com/how-to-setup-ssrs-to-use-https-part-1/
-
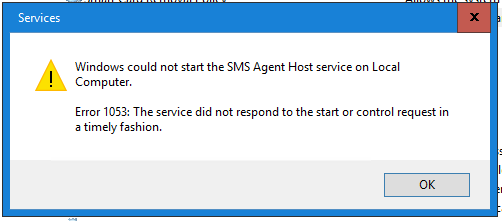
Good morning My MP is showing the following error in MPcontrol.log. As well, in monitoring/system status/site status, the Management Point role is showing the following: Total 0 bytes. Also, the service "ccmexec" is stopped, and will not start. When attempting to start it I get the following error: Event viewer shows error 10005 DCOM got error "1053" attempting to start the service CcmExec with arguments "-Service" in order to run the server: {B82CF833-7A61-4B84-9D69-C63E7B6DE6C0} I'm currently running Server 2016, Configuration Manager 1902. I've also attached the MPcontrol.log file. Http test request failed, status code is 500, 'Internal Server Error'. Http test request failed, status code is 500, 'Internal Server Error'. SMS_MP_CONTROL_MANAGER 4/30/2019 9:51:42 AM 9428 (0x24D4) Is my Management Point hosed? Should I just reinstall the role? mpcontrol.log
-
I am running into issues with enabling HTTPS for my site. All my clients are utilizing a PKI certificate, my DP is using a certificate that meets the requirements. I first switch my MP to HTTPS, and no errors in logs on the server, however, communication between server-client doesn't work. I checked CCMmessaging.log and these are the errors. Raising event: instance of CCM_CcmHttp_Status { ClientID = "GUID:39c25844-fdcd-4128-ad02-afbbbb7da681"; DateTime = "20180306185215.125000+000"; HostName = "Servername-hidden"; HRESULT = "0x87d0027e"; ProcessID = 724; StatusCode = 403; ThreadID = 300; }; CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 12:52:15 PM 300 (0x012C) Successfully queued RefreshSecuritySettingsEvent event. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 12:52:15 PM 300 (0x012C) Successfully queued event on HTTP/HTTPS failure for server 'Servername-hidden'. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 12:52:15 PM 300 (0x012C) Post to http://Servername-hidden/ccm_system_windowsauth/request failed with 0x87d00231. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 12:52:15 PM 300 (0x012C) [CCMHTTP] ERROR: URL=http://Servername-hidden/ccm_system/request, Port=80, Options=480, Code=0, Text=CCM_E_BAD_HTTP_STATUS_CODE CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:14:47 PM 4980 (0x1374) Raising event: instance of CCM_CcmHttp_Status { ClientID = "GUID:39c25844-fdcd-4128-ad02-afbbbb7da681"; DateTime = "20180306191447.628000+000"; HostName = "Servername-hidden"; HRESULT = "0x87d0027e"; ProcessID = 724; StatusCode = 503; ThreadID = 4980; }; CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:14:47 PM 4980 (0x1374) Successfully queued event on HTTP/HTTPS failure for server 'Servername-hidden'. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:14:47 PM 4980 (0x1374) Post to http://Servername-hidden/ccm_system/request failed with 0x87d00231. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:14:47 PM 4980 (0x1374) [CCMHTTP] ERROR: URL=http://Servername-hidden/ccm_system/request, Port=80, Options=480, Code=0, Text=CCM_E_BAD_HTTP_STATUS_CODE CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:16:47 PM 11316 (0x2C34) Raising event: instance of CCM_CcmHttp_Status { ClientID = "GUID:39c25844-fdcd-4128-ad02-afbbbb7da681"; DateTime = "20180306191647.300000+000"; HostName = "Servername-hidden"; HRESULT = "0x87d0027e"; ProcessID = 724; StatusCode = 503; ThreadID = 11316; }; CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:16:47 PM 11316 (0x2C34) Successfully queued event on HTTP/HTTPS failure for server 'Servername-hidden'. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:16:47 PM 11316 (0x2C34) Post to http://Servername-hidden/ccm_system/request failed with 0x87d00231. CcmMessaging 3/6/2018 1:16:47 PM 11316 (0x2C34) So, I went ahead and switched the MP back to HTTP, and the clients still cannot communicate with the server. Help please. excerpt_ccmmessaging_log.log
-
HTTPS to HTTP issues
jtelling posted a topic in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch)
Running into an issue that I cannot wrap my head around. We recently switched from HTTPS to HTTP and now clients will not talk to remote MPs or DPs on Secondary Sites. Talking back to MP on Stand Alone Primary works fine. I have revoked certs from CA and removed certs from servers but all of my Secondary sites are having issues with MPs and DPs (no PXE Boot Filename Received). Also removed Secondary Site, WDS, WSUS, all prereqs and reinstalled. Tried PXE booting to WDS + MDT 2013 and that works, but once SCCM PXE boot is turned on, I get the error. Boot images are distributed to DPs and Task Sequences have correct boot image assigned. Has anyone run into this type of problem before? Everything looks fine the mpsetup.log and mpcontrol.log files. MPControl.log STATMSG: ID=5460 SEV=I LEV=M SOURCE="SMS Server" COMP="SMS_MP_CONTROL_MANAGER" SYS=KEL-APPS.******.****** SITE=KEL PID=2840 TID=5188 GMTDATE=Mon Mar 13 16:23:37.001 2017 ISTR0="" ISTR1="" ISTR2="" ISTR3="" ISTR4="" ISTR5="" ISTR6="" ISTR7="" ISTR8="" ISTR9="" NUMATTRS=0 Successfully performed Management Point availability check against local computer. Applied D:P(A;CIOI;GA;;;SY)(A;CIOI;GA;;;BA)(A;CIOI;GR;;;LS)(A;CIOI;GR;;;S-1-5-17) to folder C:\Program Files\Microsoft Configuration Manager\Client SSL is not enabled. Call to HttpSendRequestSync succeeded for port 80 with status code 200, text: OK Sent summary record of SMS Management Point on ["Display=\\KEL-APPS.******.******\"]MSWNET:["SMS_SITE=KEL"]\\KEL-APPS.******.******\ to \\KEL-APPS.******.******\SMS_KEL\inboxes\sitestat.box\7d1dtt14.SUM, Availability 0, 733641724 KB total disk space , 681200880 KB free disk space, installation state 0. Http test request succeeded. STATMSG: ID=5460 SEV=I LEV=M SOURCE="SMS Server" COMP="SMS_MP_CONTROL_MANAGER" SYS=KEL-APPS.******.****** SITE=KEL PID=2840 TID=5188 GMTDATE=Mon Mar 13 16:28:37.013 2017 ISTR0="" ISTR1="" ISTR2="" ISTR3="" ISTR4="" ISTR5="" ISTR6="" ISTR7="" ISTR8="" ISTR9="" NUMATTRS=0 Successfully performed Management Point availability check against local computer. SMS_MP_CONTROL_MANAGER 3/13/2017 12:28:37 PM 5188 (0x1444) -
This list of guides is a living index covering Windows 365 Cloud PC, Microsoft Intune or Configuration Manager. The Configuration Manager Current Branch releases are meant for your production deployments and the Technical Preview releases are for testing new upcoming features in the product, and are aimed at Lab use only. The PKI guides are added as https communication within ConfigMgr and Intune is desired. These guides are broken down into different sections: Windows 365 Microsoft Intune Configuration Manager - Current Branch Configuration Manager - Technical Preview Setting up PKI Note: The guides in each section are (mostly) sorted in the direction of oldest first. Windows 365 How can I delete a Windows 365 Cloud PC How can I use multiple monitors with Windows 365 Using Windows 365 with Linux Introducing the Windows 365 App How can I resize a Windows 365 Cloud PC USA Windows 365 User Group session – video available Windows 365 – Your connection failed – Error Code 0x3000047 How can I configure alerts for Windows 365 activity in Intune Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 1. Introduction Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 2. Provisioning an Azure Ad Joined Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 3. Provisioning a Hybrid Azure Ad Joined Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 4. Connecting to your Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 5. Managing your Cloud PC Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 6. Point in time restore Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 7. Patching your Cloud PCs with Windows Autopatch Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 8. Windows 365 boot Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 9. Windows 365 switch Getting started with Windows 365 - Part 10. Windows 365 offline Windows 365 app not connecting try this Using alternate ANCs in your Windows 365 provisioning policy Location redirection with Windows 365 Troubleshooting Windows 365 connection issues via the troubleshoot option in the Windows 365 app A quick look at some of the new features in the Windows 365 app An update about location redirection on Windows 365 Cloud PCs Windows 365 end user improvements - open in browser, open in desktop app Windows 365 web client can now use your camera New video: Windows 365 Switch in action Windows 365 boot and Windows 365 switch go GA! Automating Windows 365 part 1 - Introducing Graph and setting up Visual Studio code Automating Windows 365 part 2 - Using Graph X-Ray Automating Windows 365 part 3 - Provisioning Cloud PC's Automating Windows 365 part 4 - Managing your Cloud PC Automating Windows 365 part 5 - Cloud PC reports A quick look at Windows 365 Boot dedicated mode A quick look at Windows 365 Boot shared mode Getting more out of Windows 365 – Windows 365 Boot Getting more out of Windows 365 – Windows 365 GPU Getting more out of Windows 365 – Windows 365 Frontline Getting more out of Windows 365 – Windows 365 Switch Getting more out of Windows 365 – Securing your Windows 365 PC’s Updating the Windows app to the latest version A quick look at using Windows 365 Cloud PC’s via Motorola Thinkphone Automated Provisioning of Windows 365 Cloud PCs: Advanced Scripts Moving one or more Windows 365 Cloud PCs to another location Recovering a Windows 365 Cloud PC that was de-provisioned due to license expiration How healthy are your Windows 365 or Azure Virtual Desktop PC’s ? Using remediation scripts in Intune to grab Windows 365 health check logs Windows 365 and the External Identity preview – using a guest account to access Cloud PCs Cloudy With a Chance of Apps Microsoft Intune How can I find out version info about Intune Preview in Azure ? How can I unlock Windows Holographic for Business features in Intune Preview? How can I determine how long a blade loads in Intune Preview in Azure ? How can I check the status of my Intune service ? Intune Preview in Azure get’s a new look and Software Updates for Windows 10 ! What is Windows Information Protection and how can I use it to protect Enterprise data on Windows 10 devices using Intune Using Intune to enable WIP to protect Enterprise data on Windows 10 devices (MAM-WE) Getting started with Microsoft Graph and using PowerShell to automate things in Intune How can I integrate Microsoft Store for Business with Intune in Azure How can I create a dynamic group containing all Windows 10 version 1709 in Intune in Azure ? How can I enable MDM auto-enrollment in Azure How can I customize the start screen in Windows 10 using Intune How can I use Windows AutoPilot with a Proxy ? Troubleshooting “Something went wrong error 801c0003” during enrollment via Windows AutoPilot and Microsoft Intune Configuring BitLocker in Intune - Part 1. Configuring BitLocker Configuring BitLocker in Intune - Part 2. Automating Encryption Configuring BitLocker in Intune - Part 3. Testing the scripts How can I send notification messages using PowerShell in Microsoft Intune How can I deploy custom favorites in Microsoft Edge to Windows 10 devices using Microsoft Intune Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 1 – new features) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 2 – iOS) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 3 – Android) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 4 – macOS) Managing devices with Microsoft Intune: What’s new and what’s next – my notes (Part 5 – Windows) Learn how to leverage Intune support for Microsoft Graph and PowerShell to enable powerful automation and IT security- my notes How Microsoft uses Intune internally to manage Windows devices Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 1. Partnerships Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 2. Deployment Scenarios Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 3. Dedicated device management Android device management with Microsoft Intune – Part 4. Coming soon and what’s new How can I create dynamic groups for different HoloLens devices in Microsoft Intune Troubleshooting app deployment in Windows Autopilot Configuring the Registered Owner and Organization in Windows Autopilot delivered PCs Removing company data from Endpoint Manager enrolled phones Office 365 issues after Windows Autopilot Displaying a welcome page after Windows Autopilot completes Adding devices to an Azure AD group after Windows Autopilot is complete - part 1 Adding devices to an Azure AD group after Windows Autopilot is complete - part 2 Gathering logs and sending an email when resetting Windows Autopilot - part 1 Gathering logs and sending an email when you need to reset Windows Autopilot - part 2 Gathering logs and sending an email when you need to reset Windows Autopilot - part 3 Adding devices or users to an Azure AD group after Windows Autopilot is complete but only when the device is marked as Compliant Using the updated & secure Retire My PC app via Company Portal Prompting standard users to confirm or change Regional, Time Zone and Country settings after Windows Autopilot enrollment is complete Encrypting devices during Windows Autopilot provisioning (WhiteGlove) - Part 1 Encrypting devices during Windows Autopilot provisioning (WhiteGlove) - Part 2 Encrypting devices during Windows Autopilot provisioning (WhiteGlove) - Part 3 https://www.niallbrady.com/2024/04/06/pc-buyback-for-windows-autopilot-devices-part-2/ PC Buyback for Windows Autopilot devices – part 1 PC Buyback for Windows Autopilot devices – part 2 PC Buyback for Windows Autopilot devices – part 3 Deploying KB5030310 to devices as a Win32 app for Copilot Using remediation scripts to automate a setting for Copilot How can I disable Copilot ? Getting started with Azure Key Vault Expediting updates using Windows Autopatch August Cumulative update causing Windows reset problems Configuration Manager Current Branch Installation - How can I install System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Configuring Discovery - How can I configure discovery for System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Configuring Boundaries - How can I configure boundaries in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Using Updates and Servicing in Offline mode - How can I use Updates and Servicing in Offline mode in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Using Updates and Servicing in Online mode - How can I use Updates and Servicing in Online mode in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Setting up the Software Update Point - How can I setup Software Updates in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Installing the Client agent - How can I configure client settings and install the ConfigMgr client agent in System Center Configuration Manager Current Branch Upgrading to System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1602 from System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1511 How can I use the Upgrade Task Sequence in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) ? How can I use servicing plans in System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) to upgrade Windows 10 devices ? How can I deploy Windows 10 with MDT 2013 Update 2 integrated with System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) Setting up PKI Part 1 - Introduction and server setup Part 2 - Install and do initial configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 3 - Prepare the HTTP Web server for CDP and AIA Publication Part 4 - Post configuration on the Standalone Offline Root CA Part 5 - Installing the Enterprise Issuing CA Part 6 - Perform post installation tasks on the Issuing CA Part 7 - Install and configure the OCSP Responder role service Part 8 - Configure AutoEnroll and Verify PKI health How can I configure System Center Configuration Manager in HTTPS mode (PKI) - Part 1 How can I configure System Center Configuration Manager in HTTPS mode (PKI) - Part 2 New video: Fixing expired Root CA CDP and Crypt_E_REVOCATION_OFFLINE problems cheers niall
-
- 4
-

-

-
- current branch
- step by step
- (and 12 more)
-
When I try to deploy windows 8 updates follow Anyweb's guide SCCM 2012 RC Part 6 - Deploying Software Updates, Step Install Software Updates failed with 0X800705B4 while system join workgroup instead of domain. If I config system to join domain everything is fine. I have specified SMSMP=CM01.corp.viamonstra.com in installation properties of Configuration Manger Client ConfigMgr version is System Center 2012 ConfigMgr SP1, and config to use HTTPS for communication between server and client. I also try HTTP situation ,windows software can be installed successfully in infrastructure of workgroup and domain. I google for several days, still not found soulation. Logs.zip
- 2 replies
-
- 0x800705b4
- sccm 2012
-
(and 4 more)
Tagged with: