Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'sql server 2017'.
-
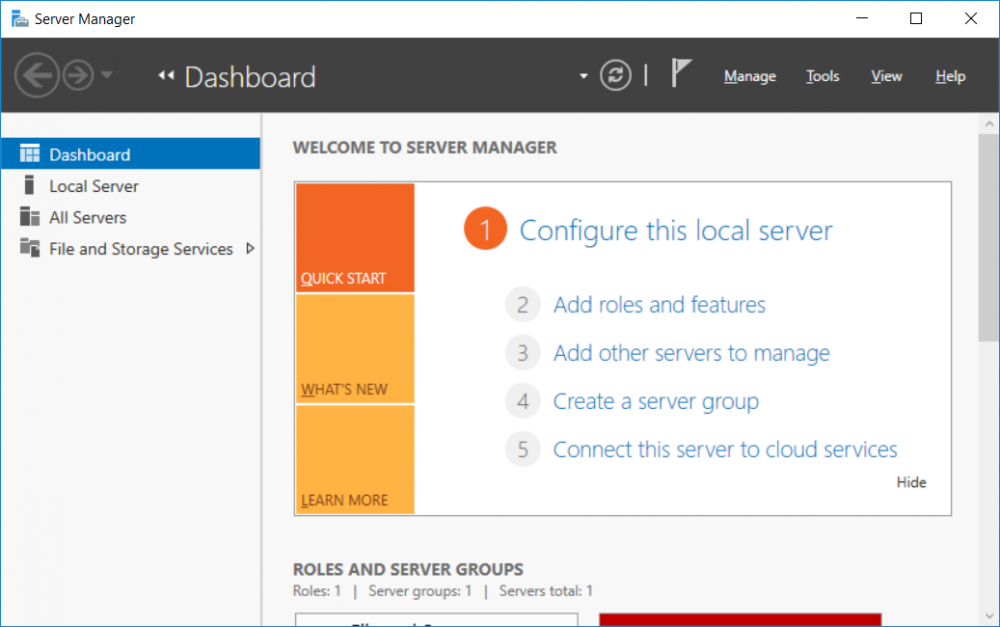
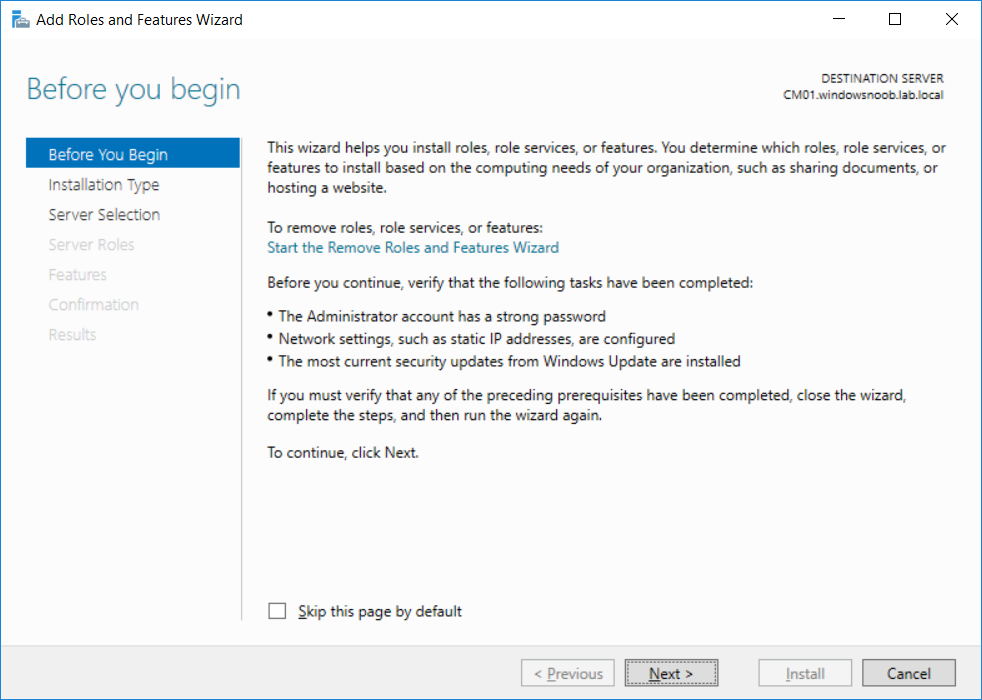
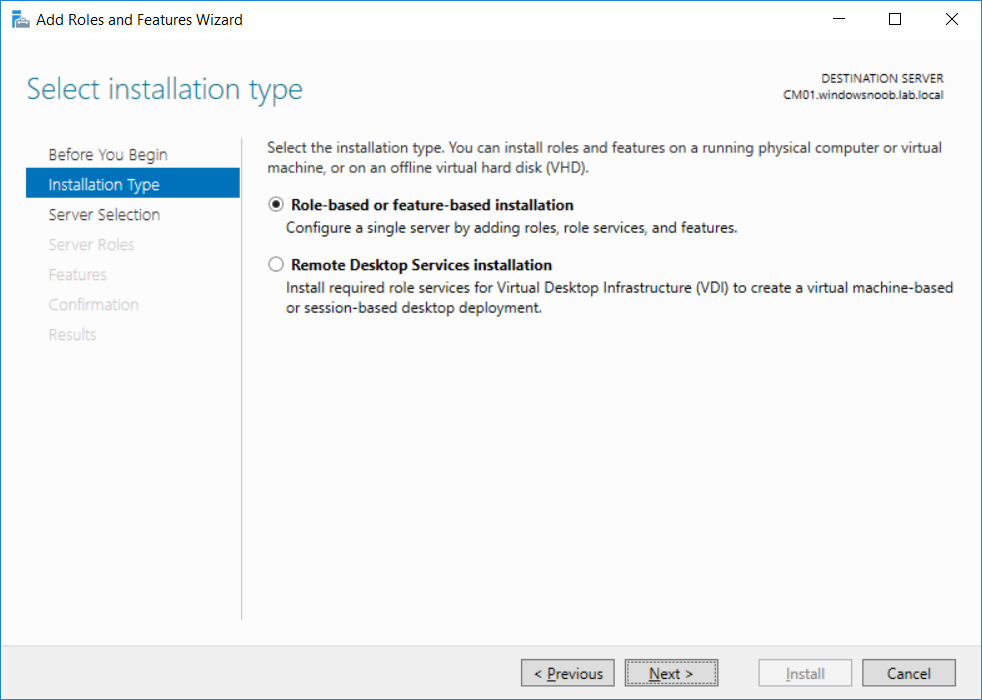
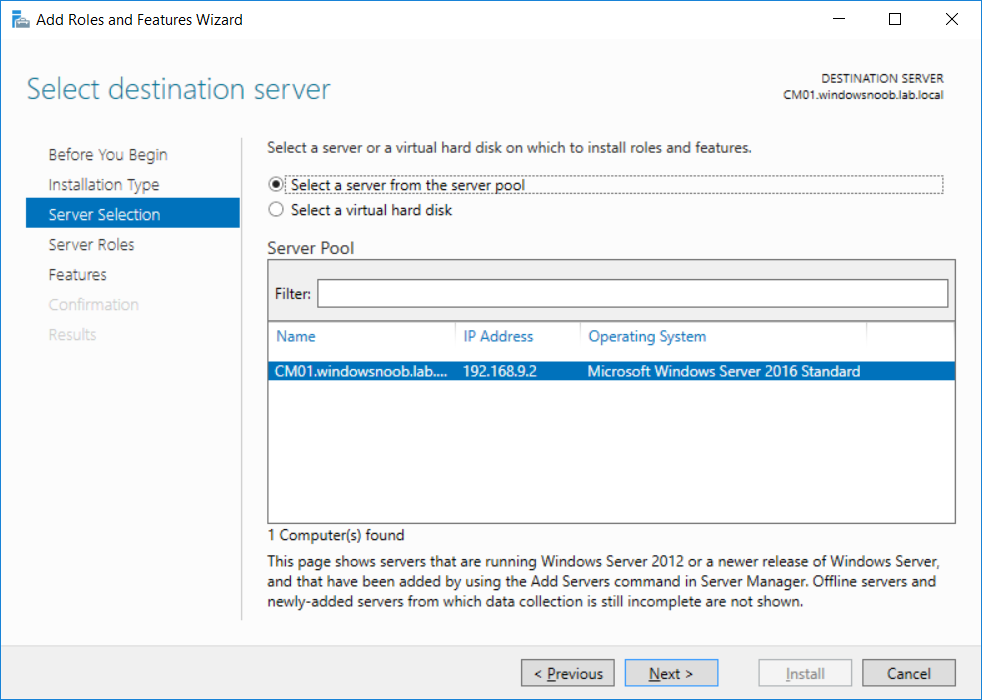
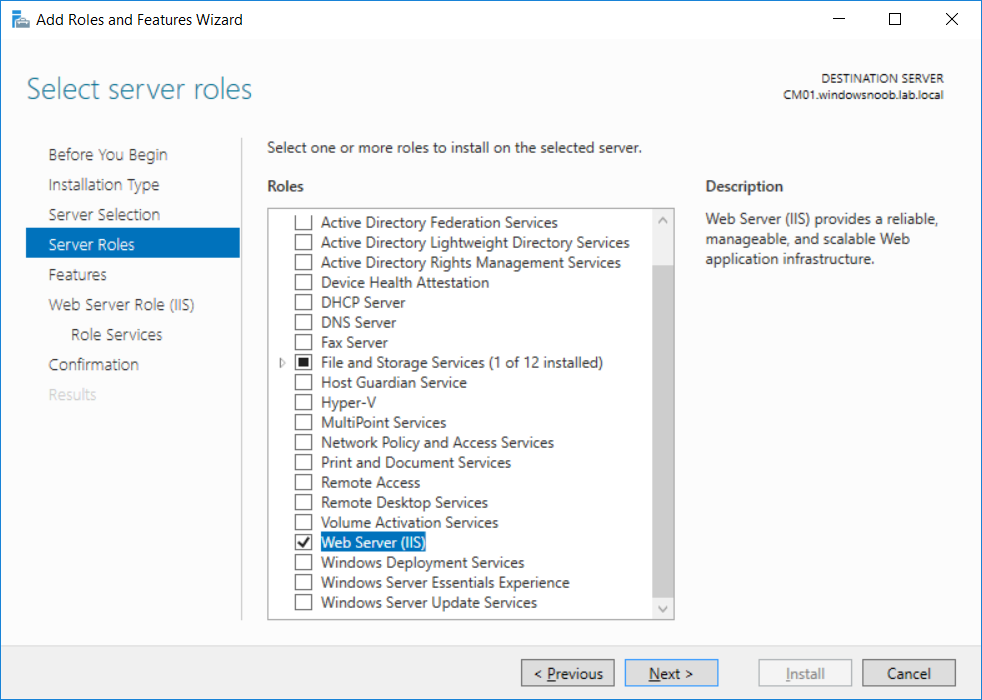
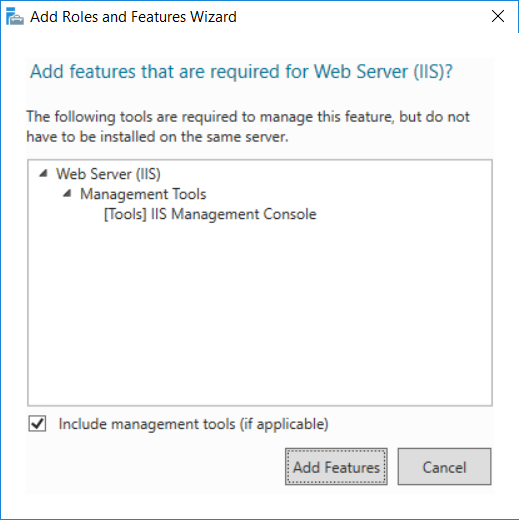
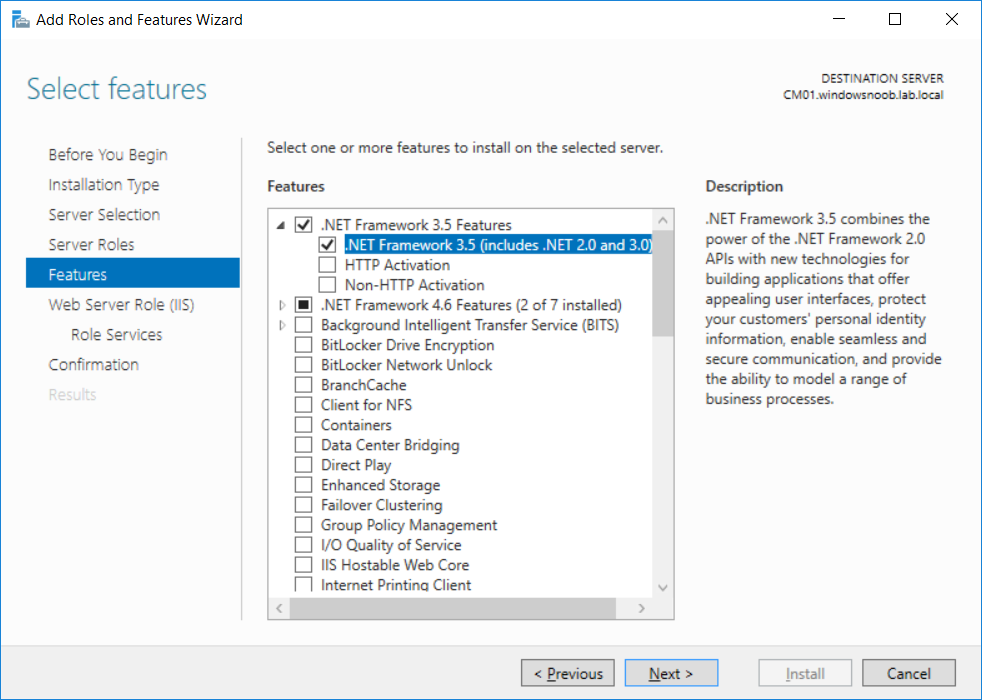
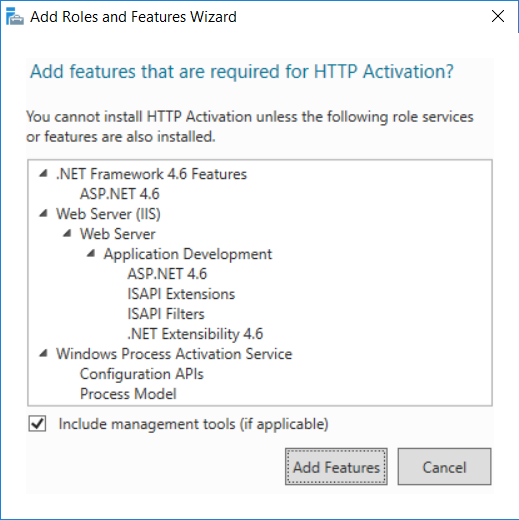
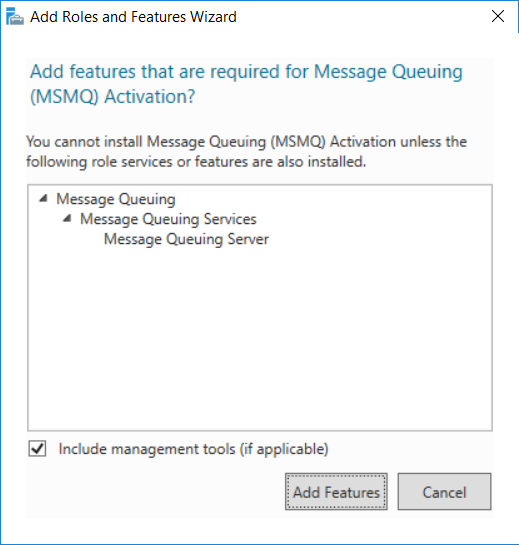
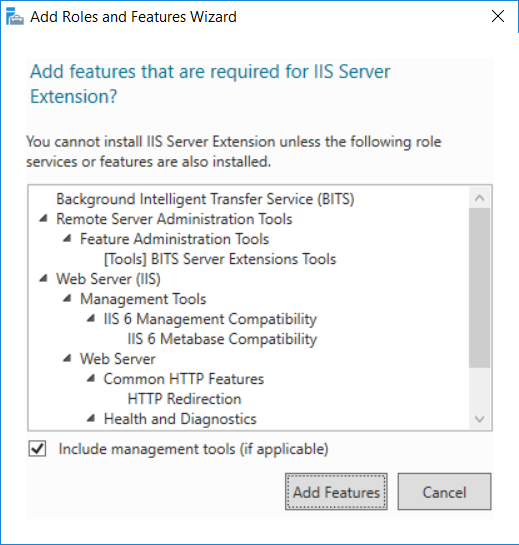
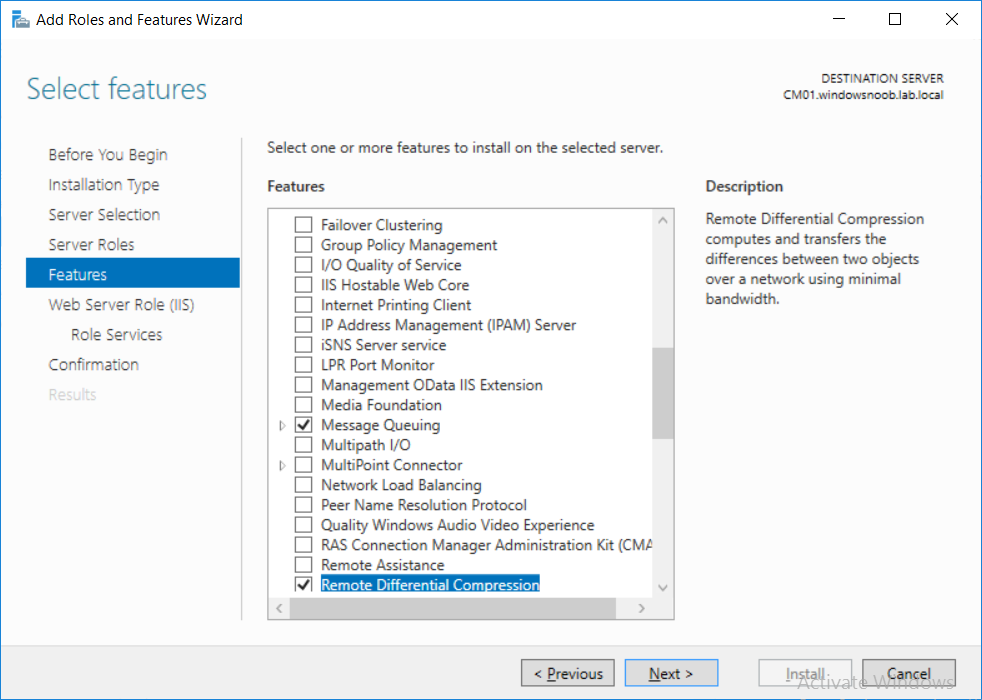
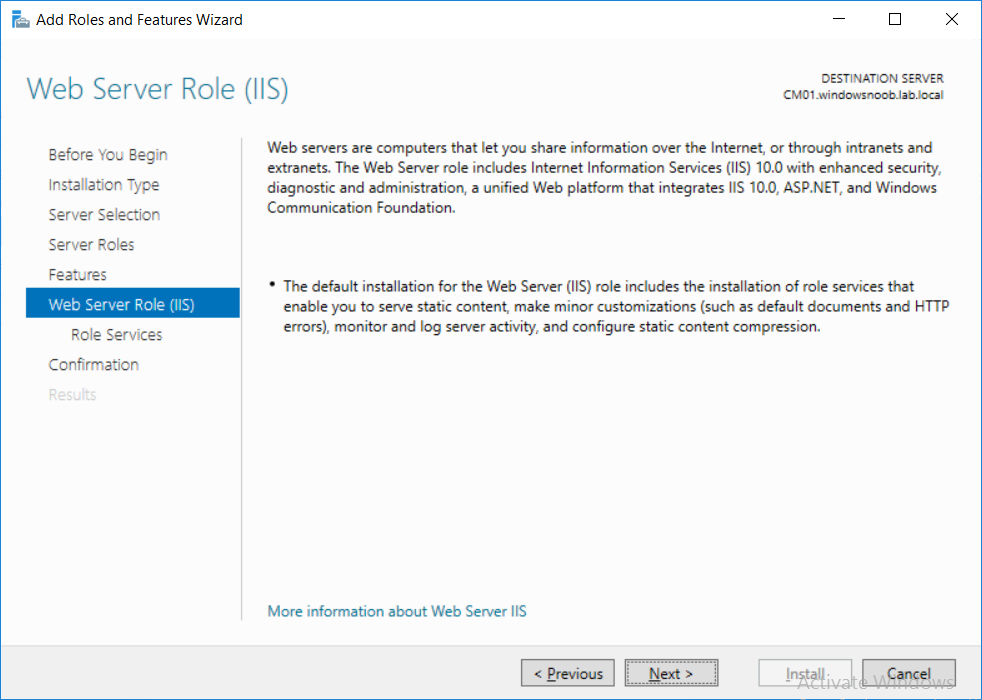
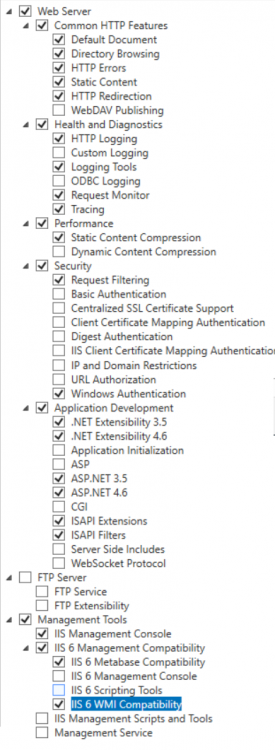
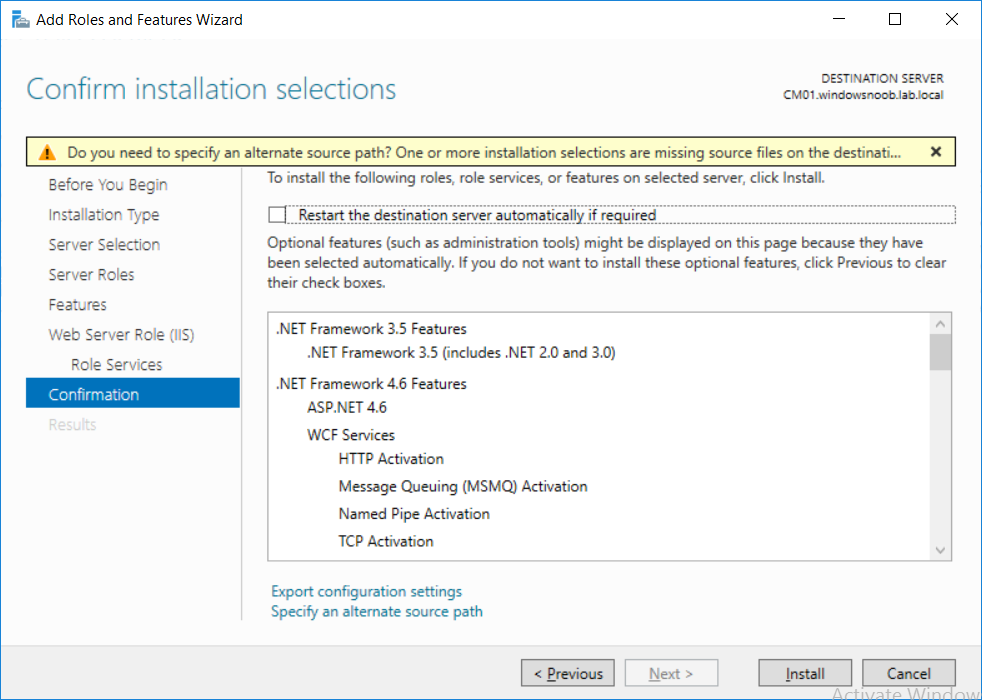
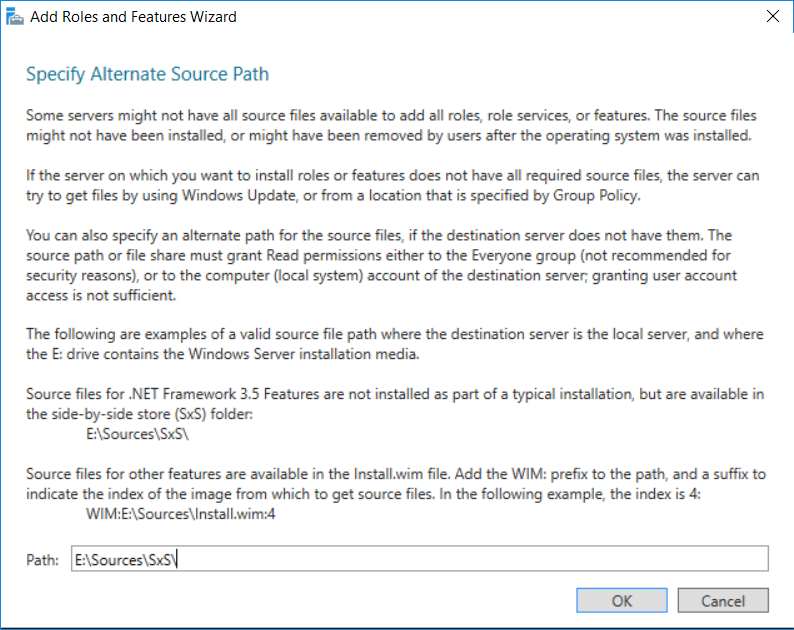
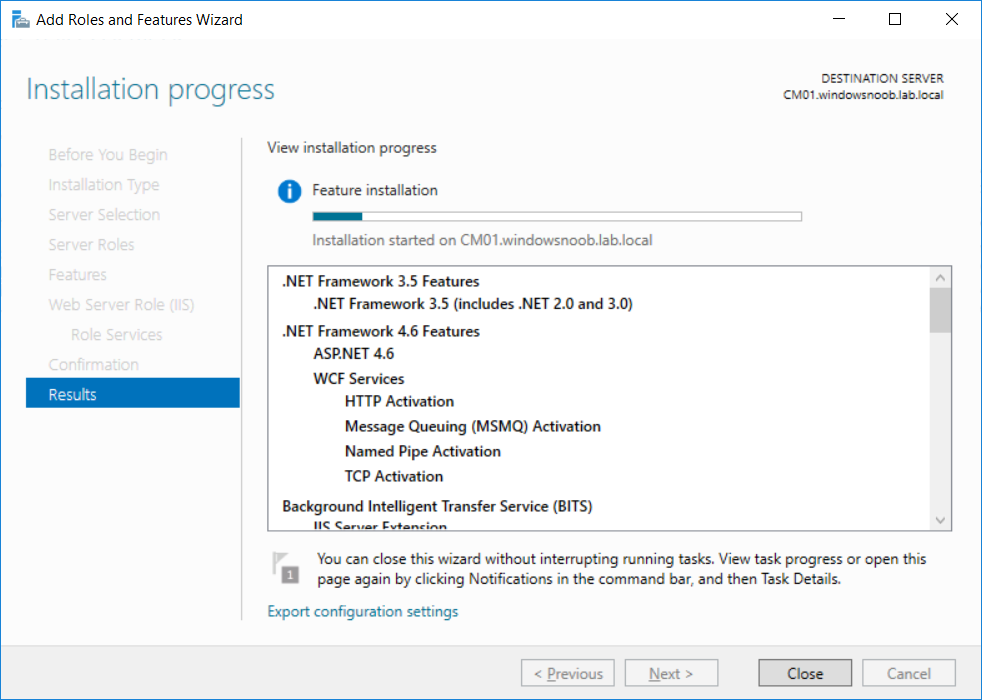
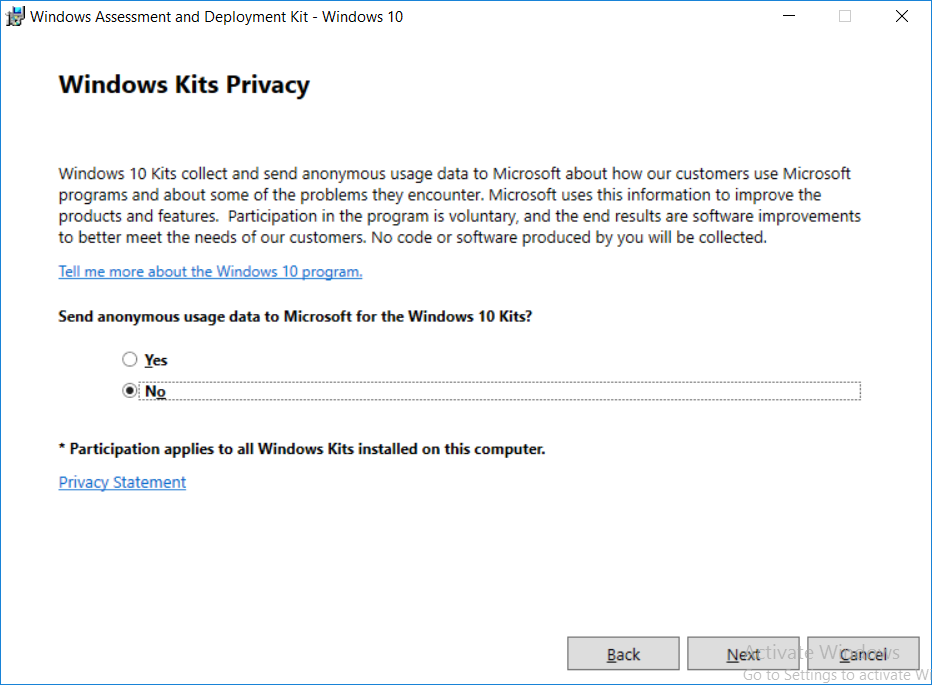
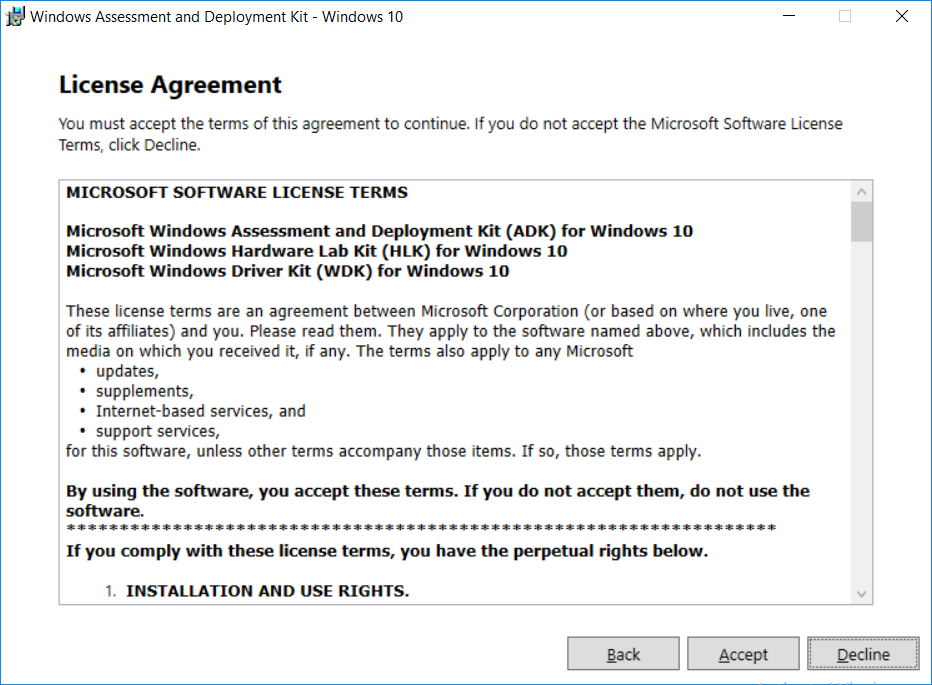
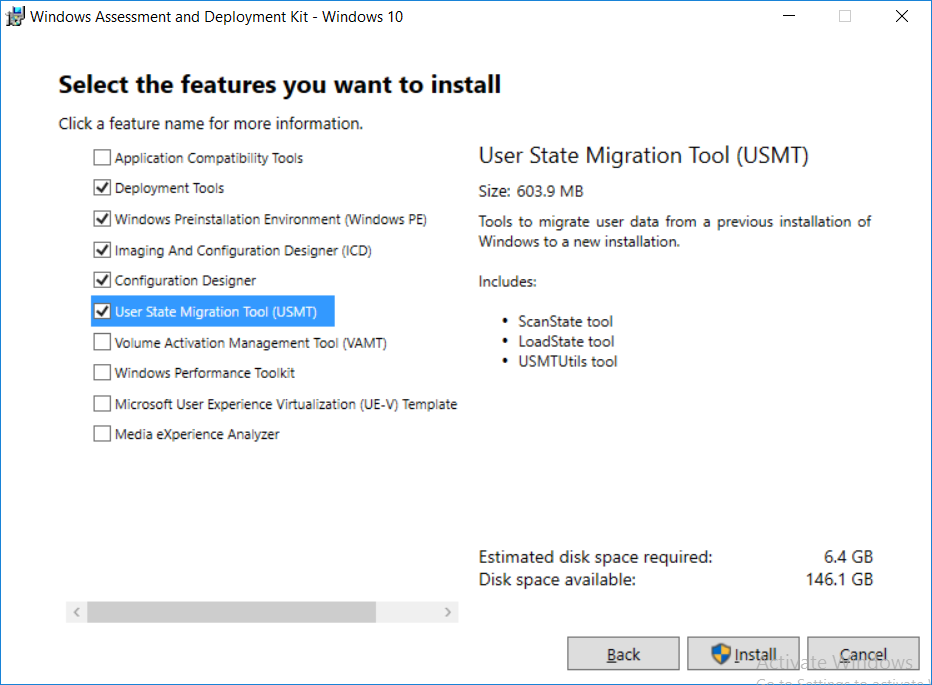
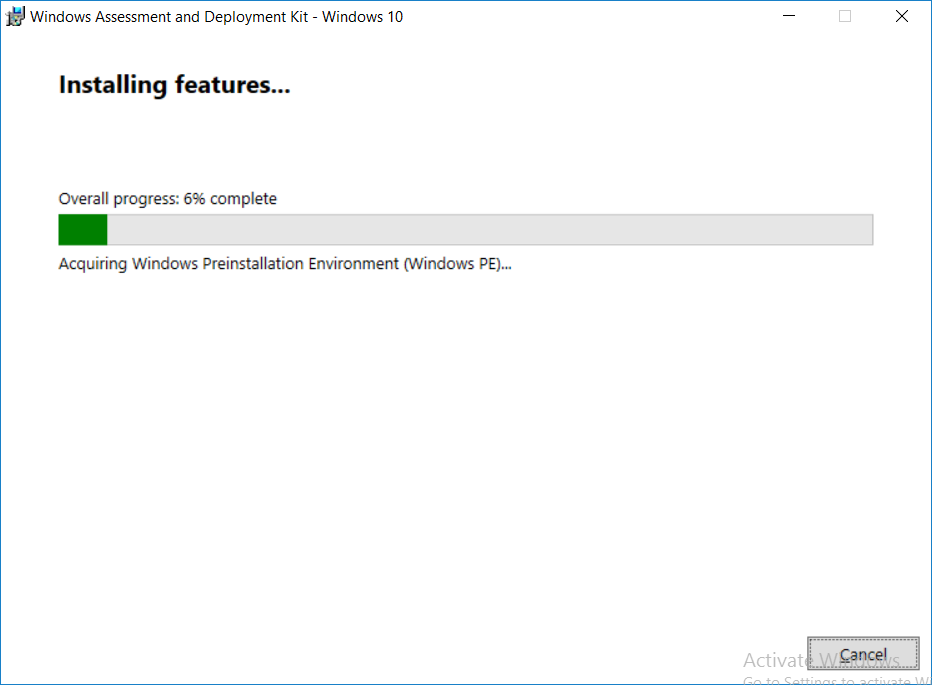
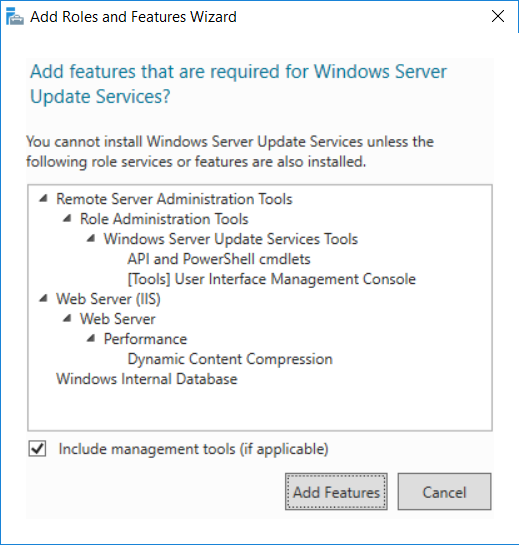
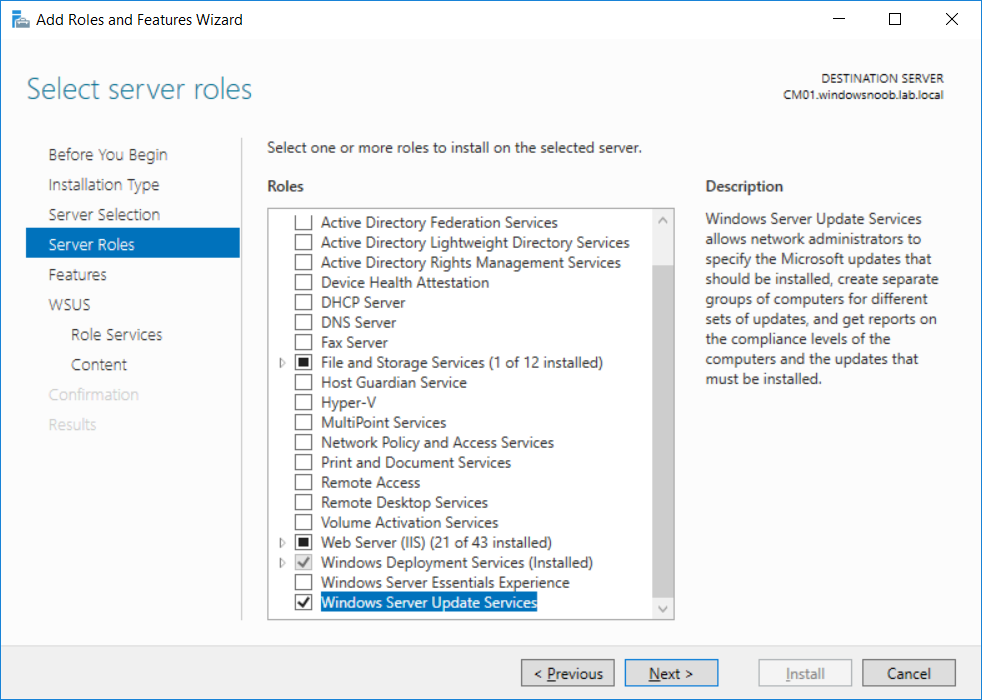
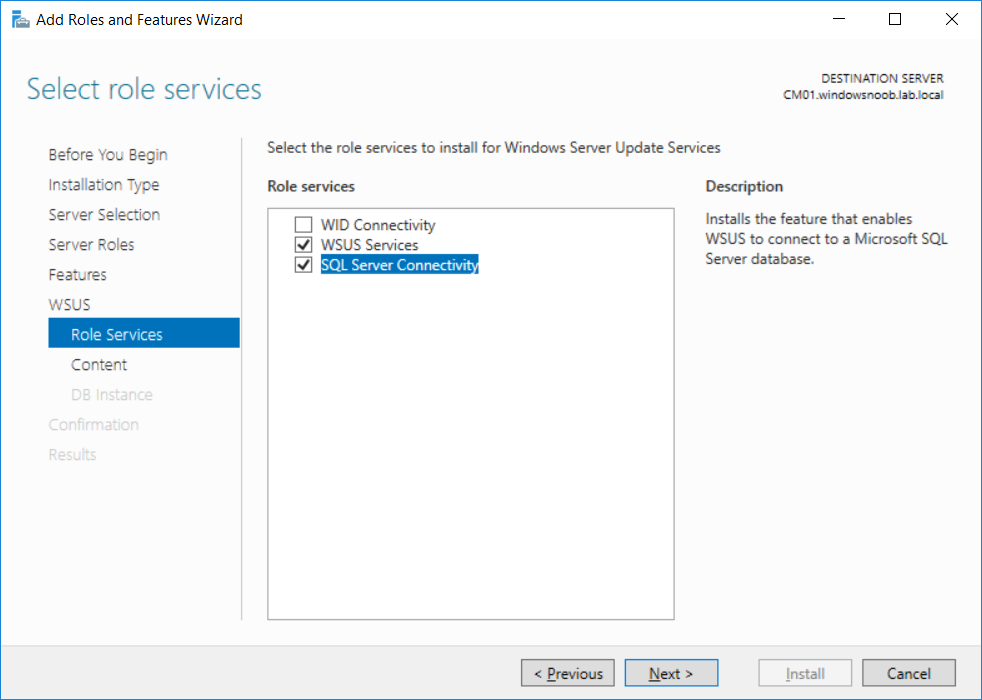
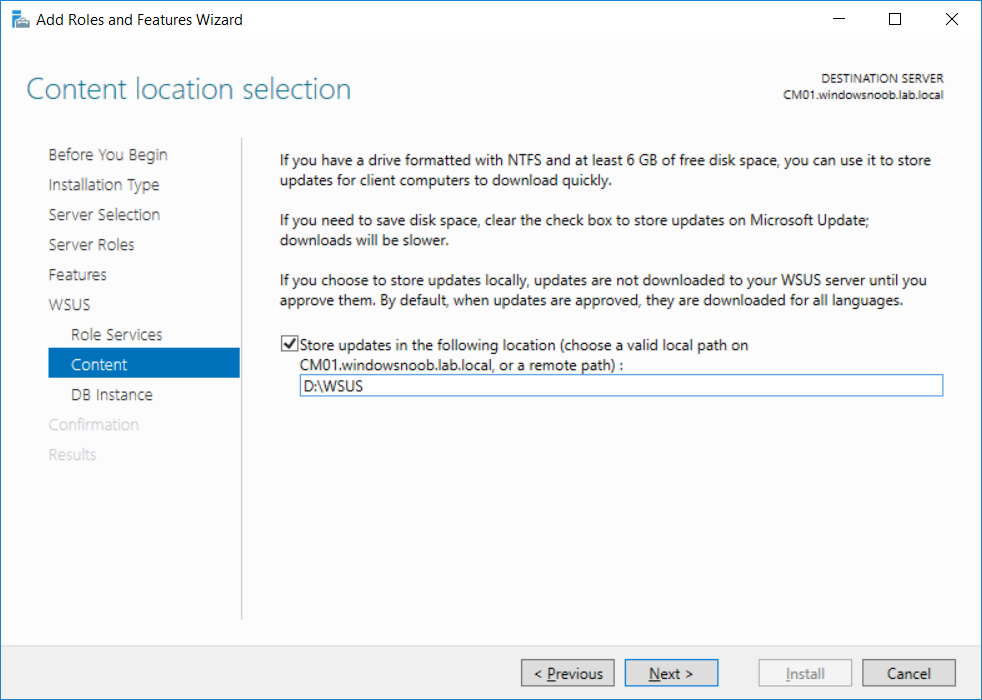
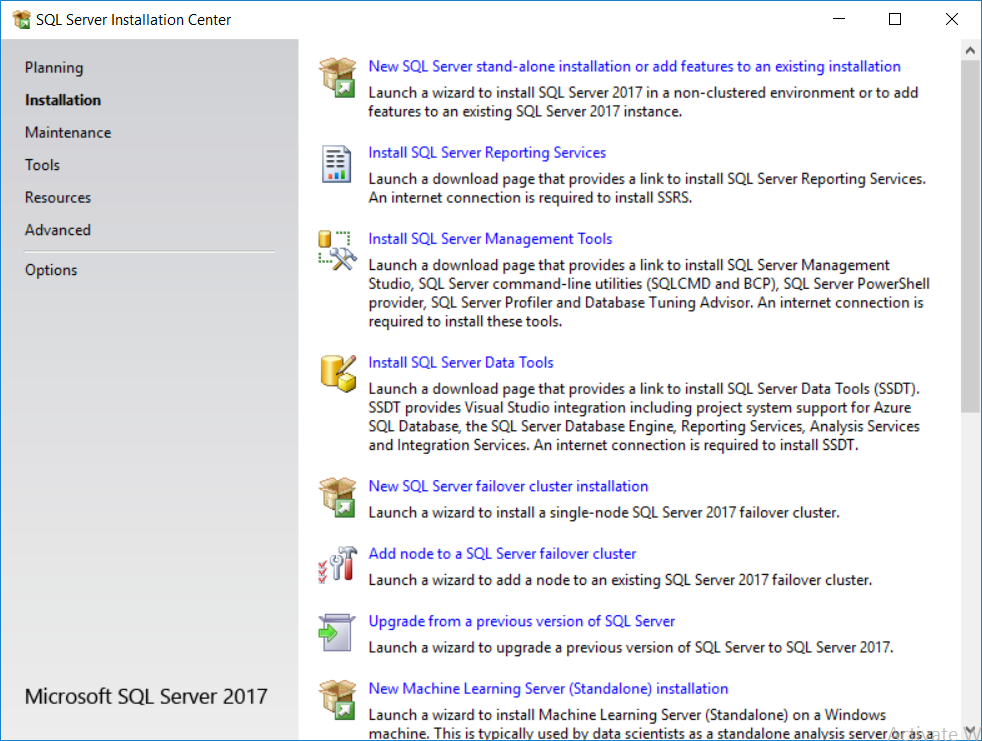
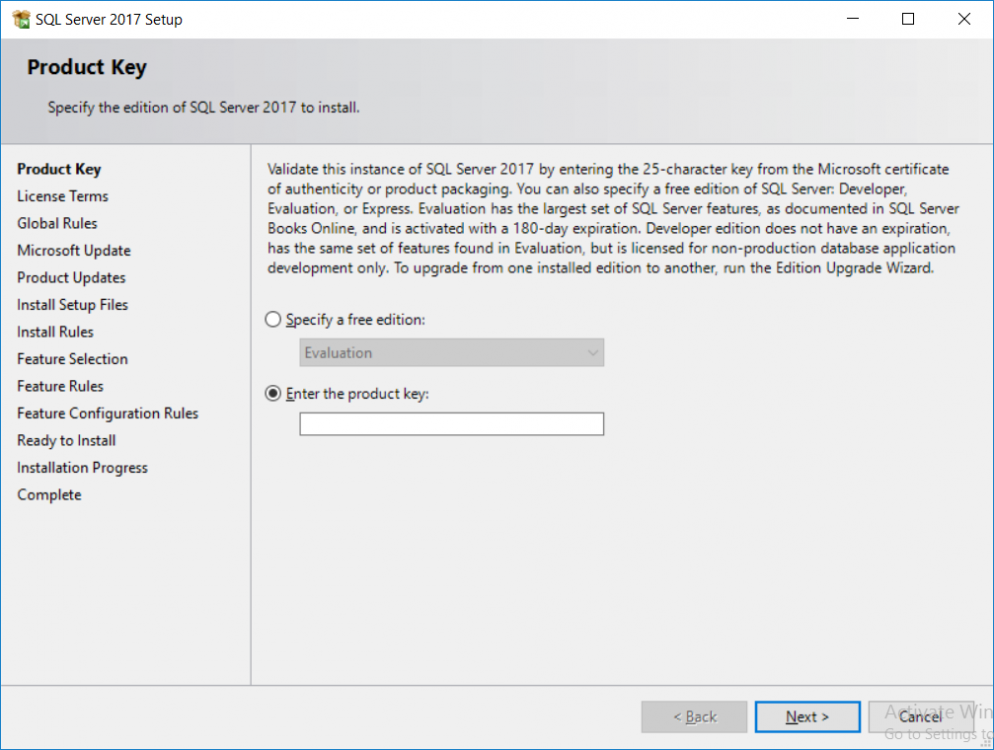
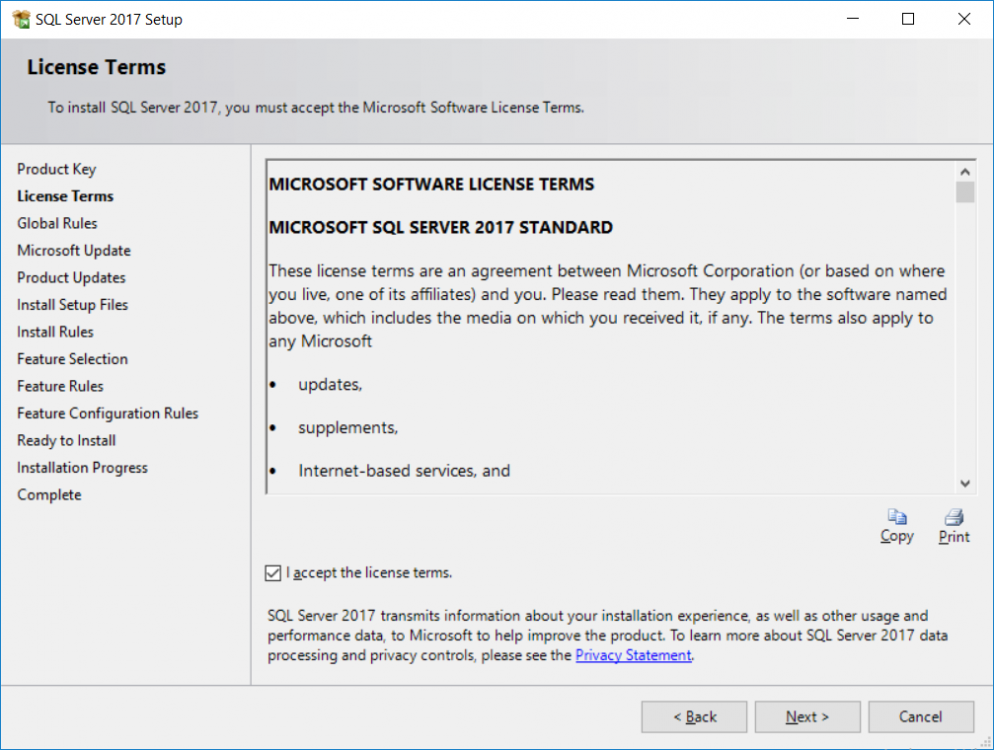
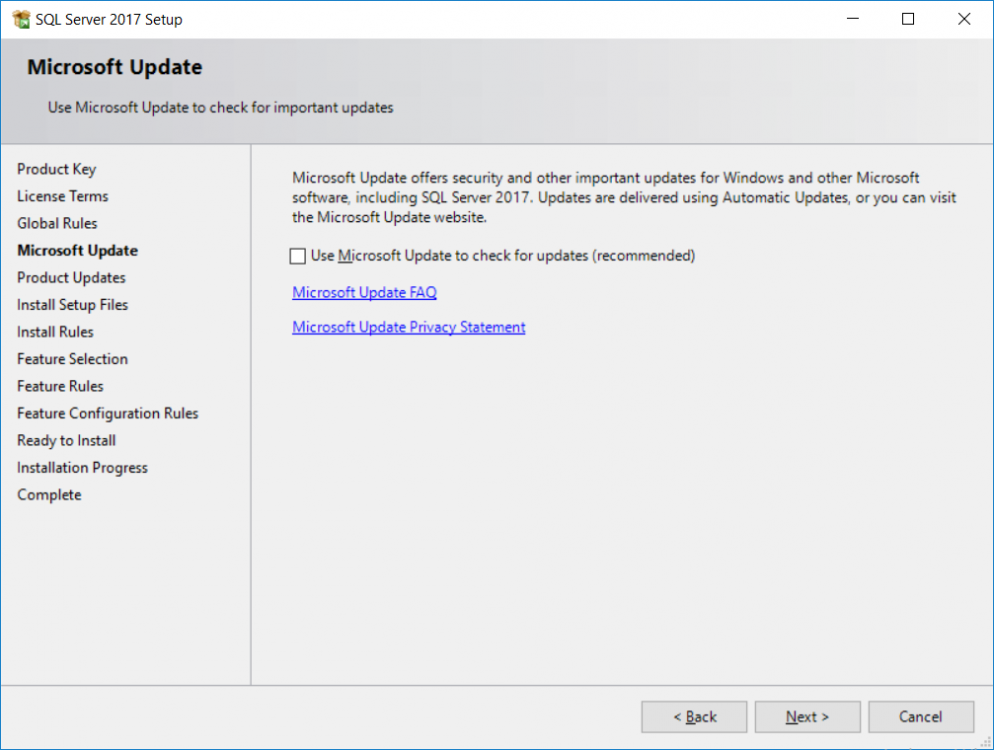
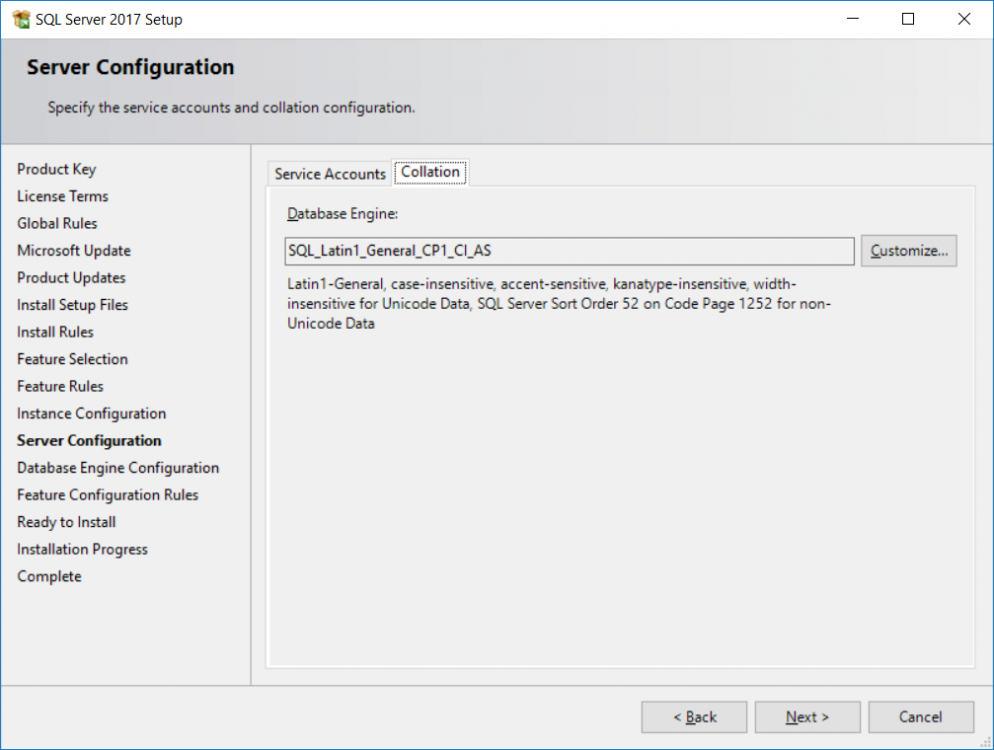
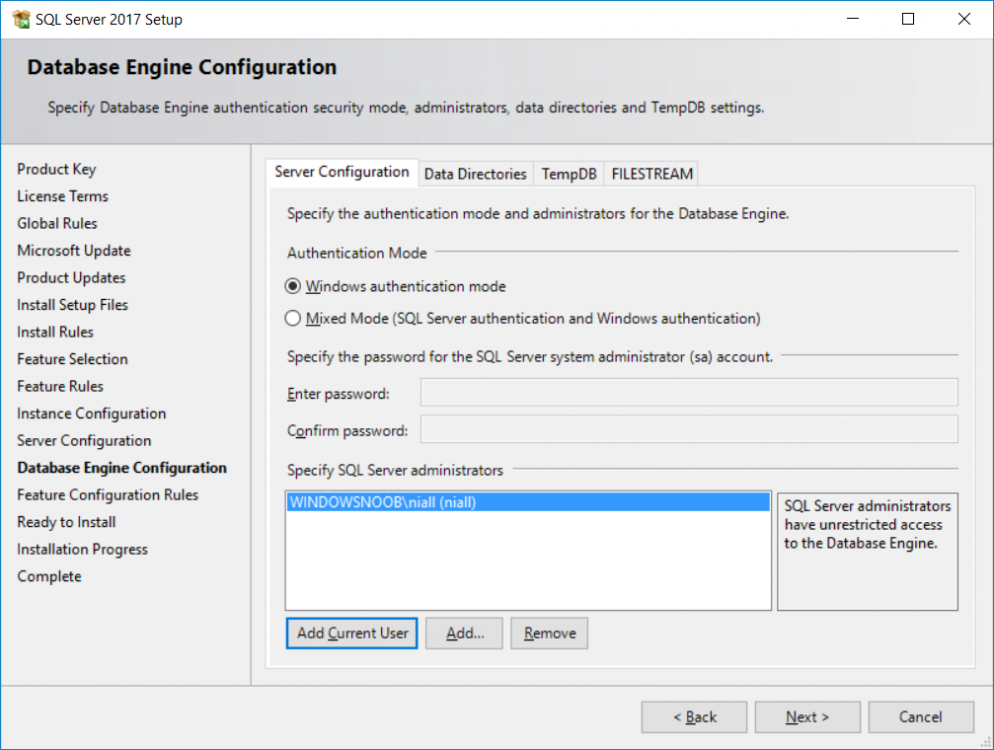
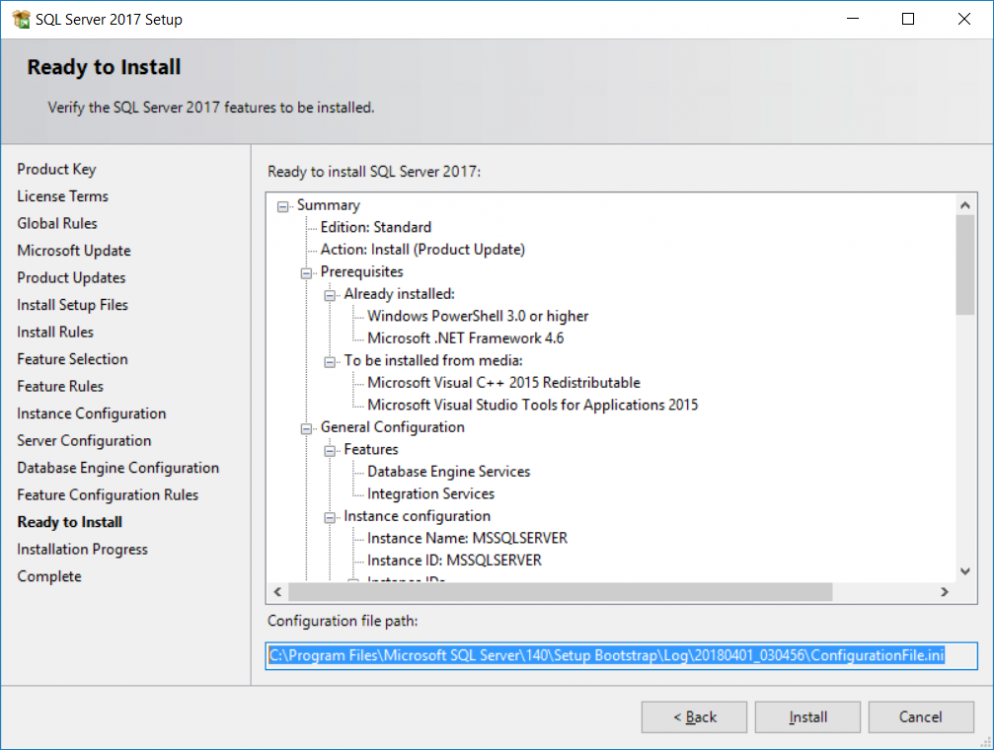
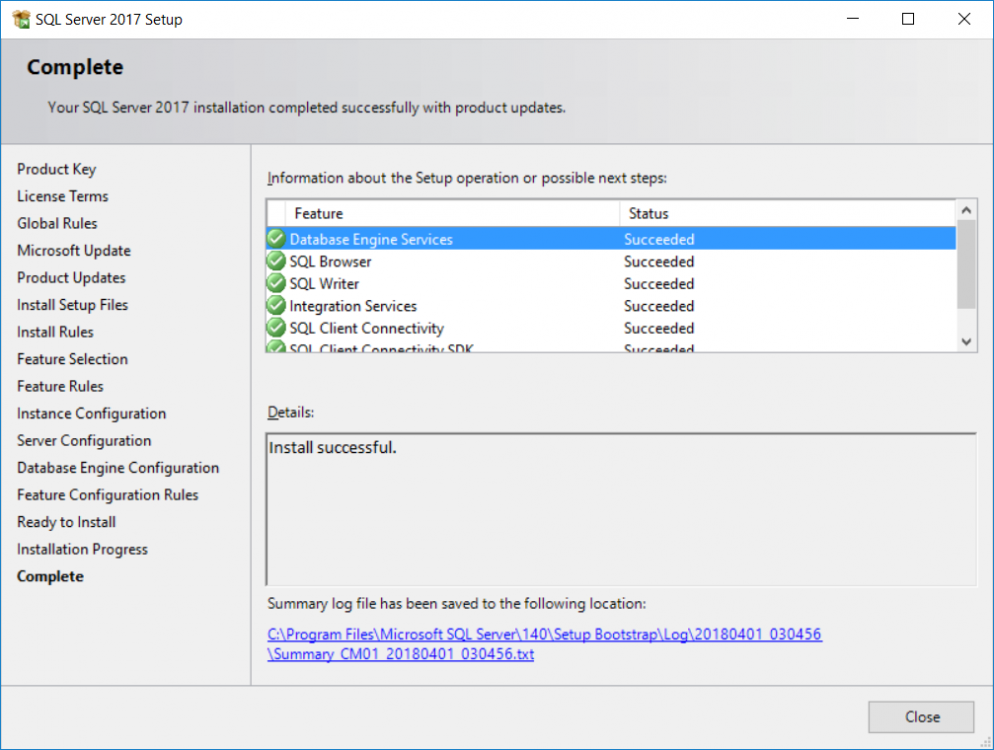
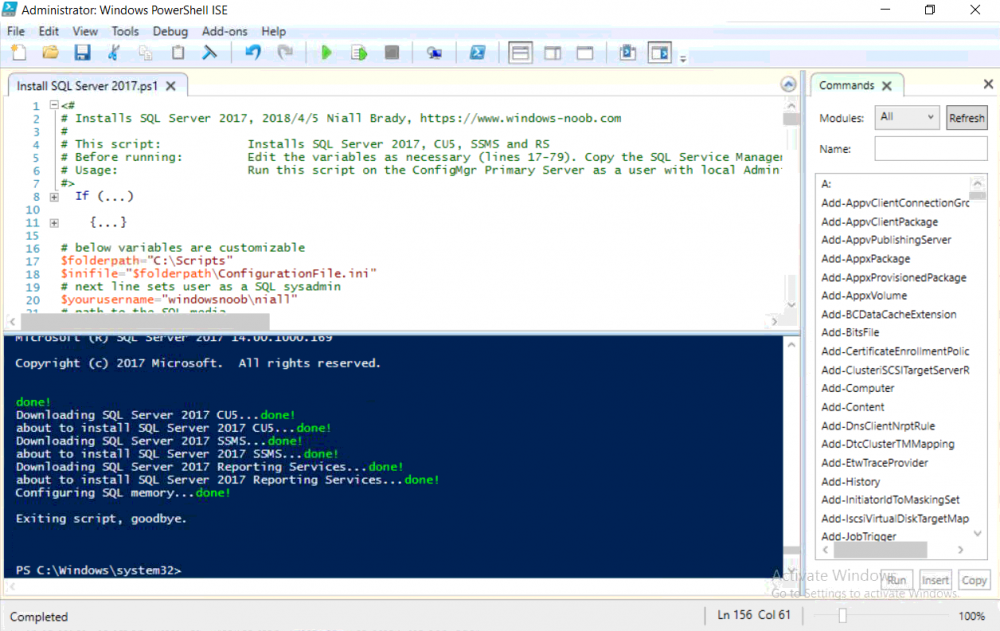
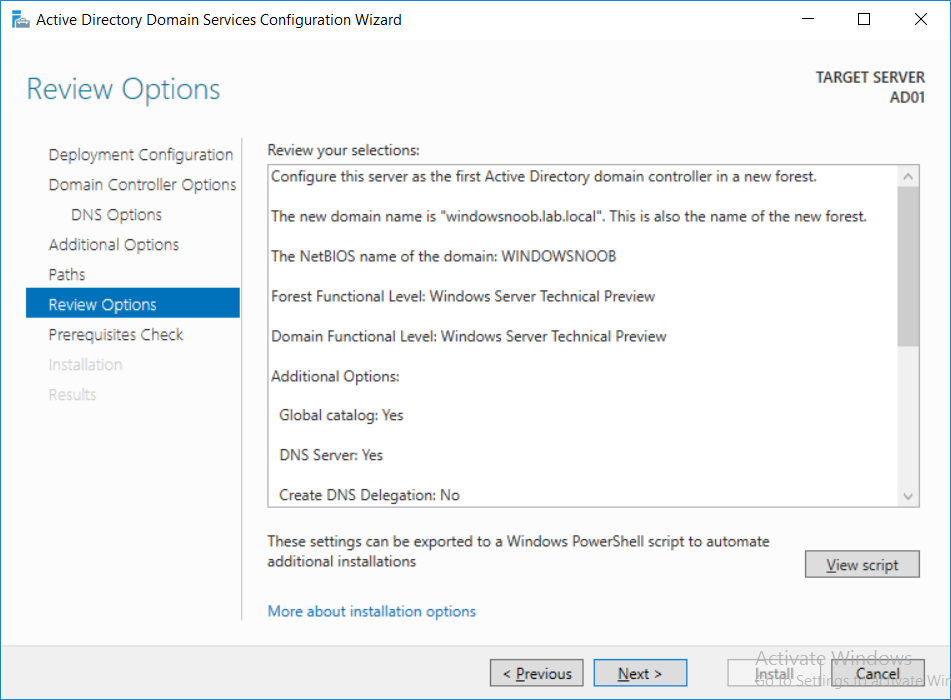
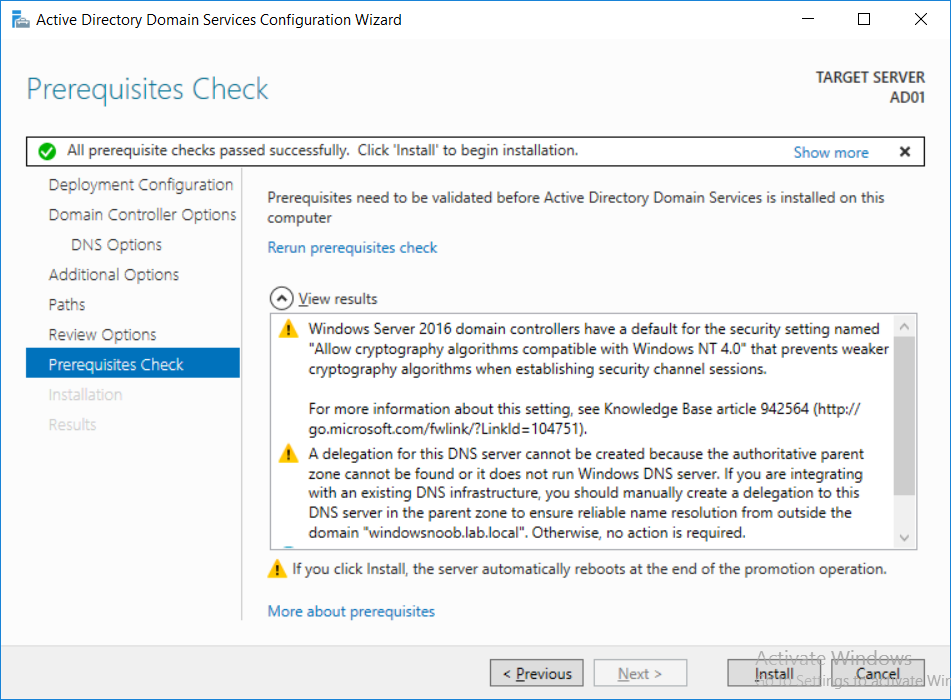
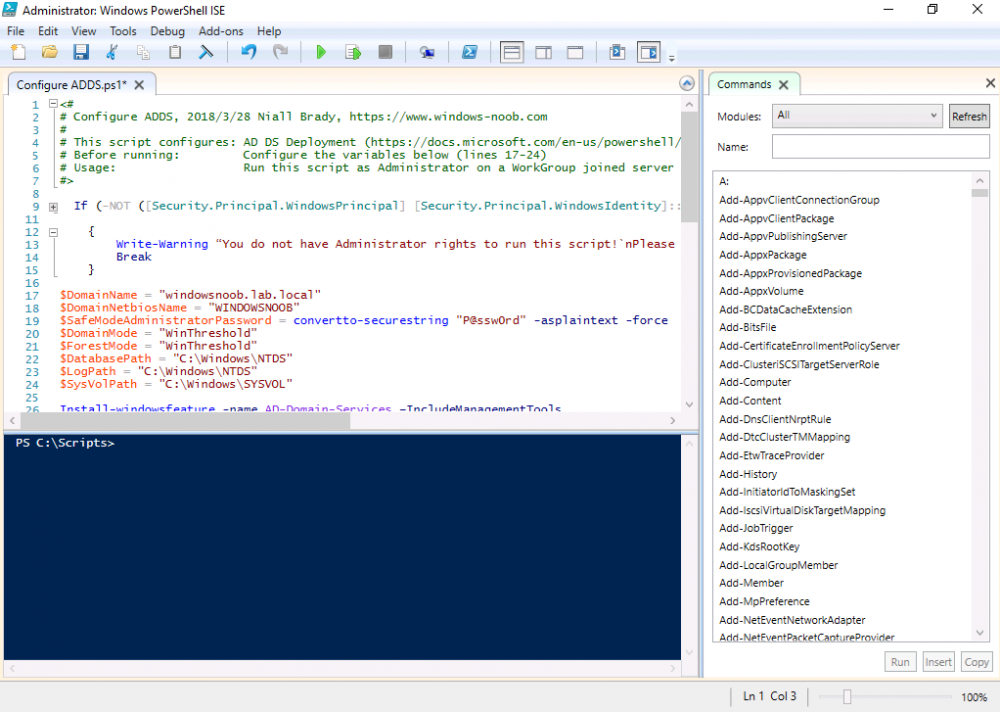
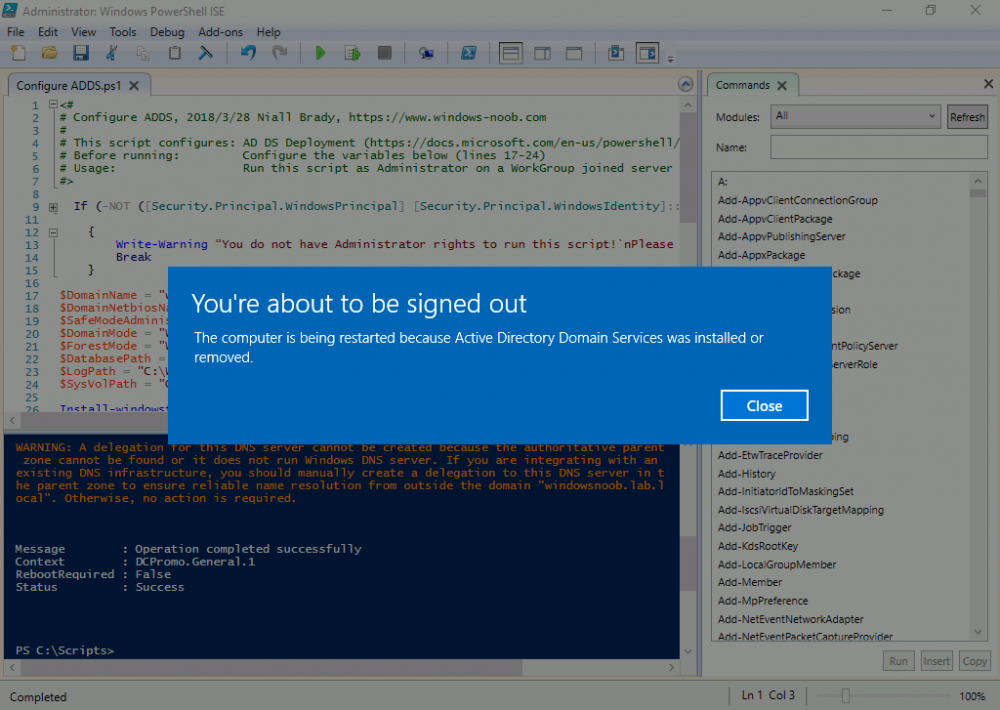
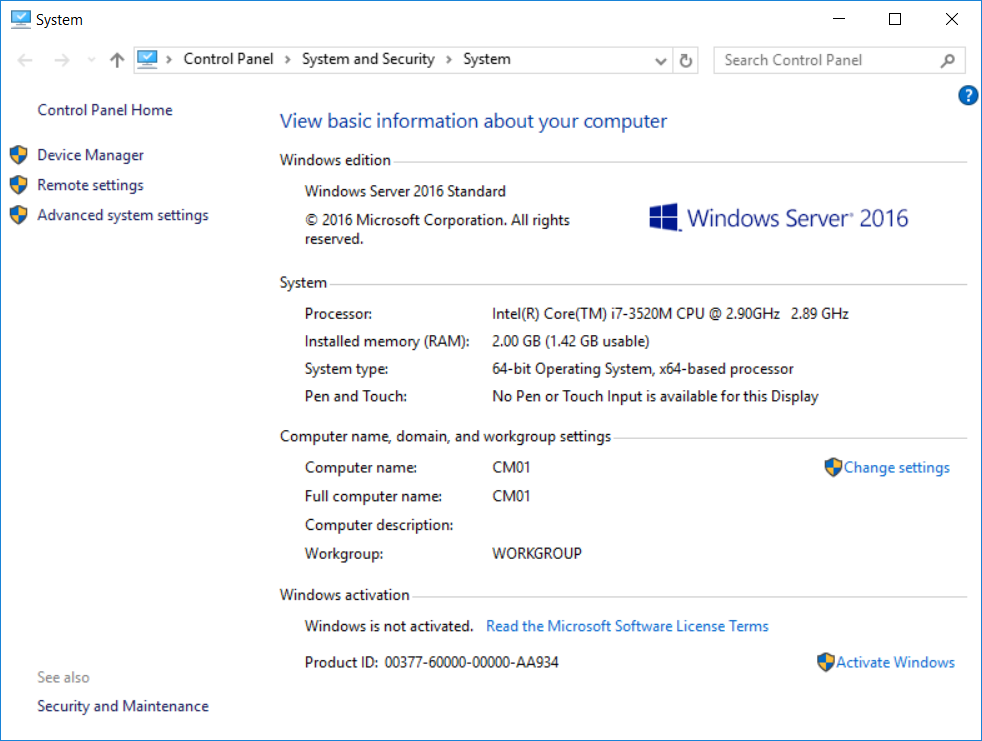
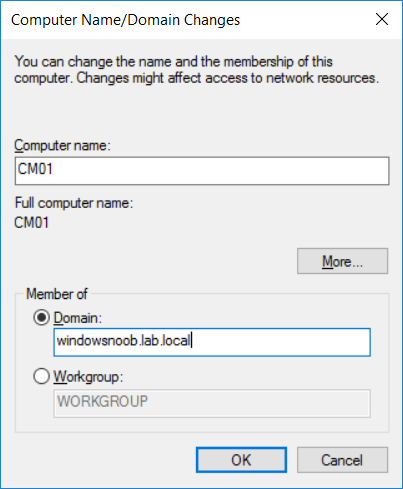
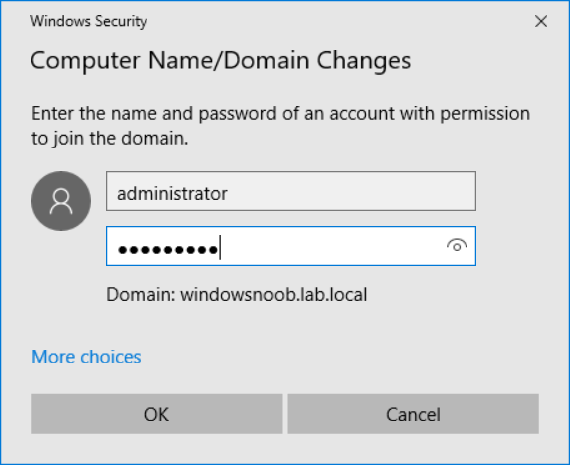
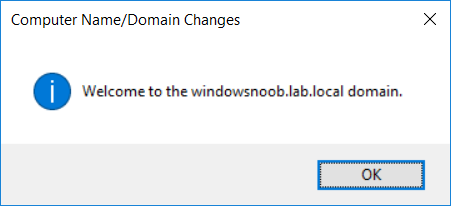
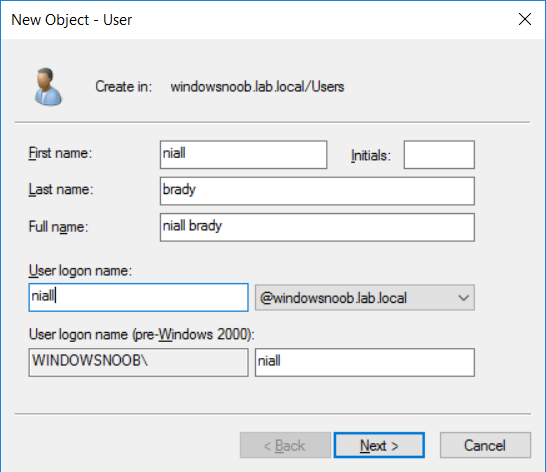
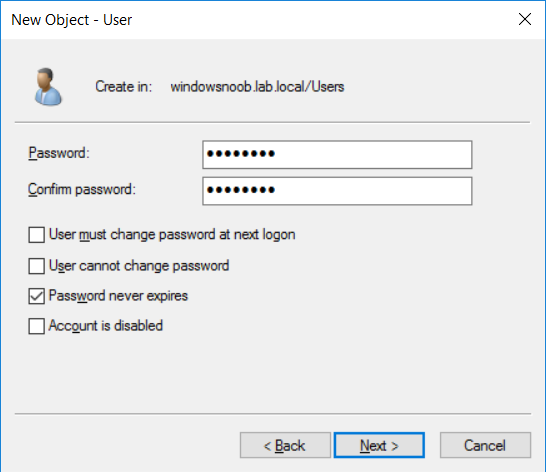
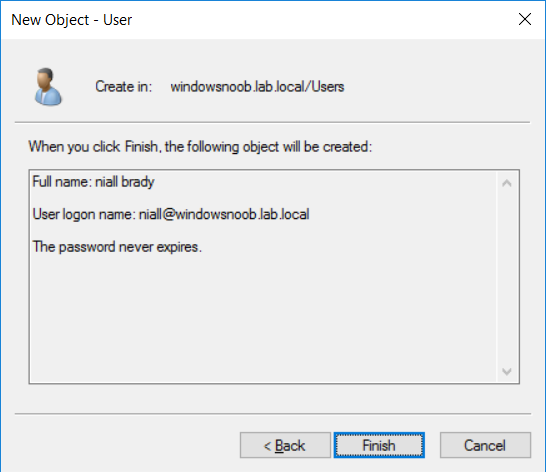
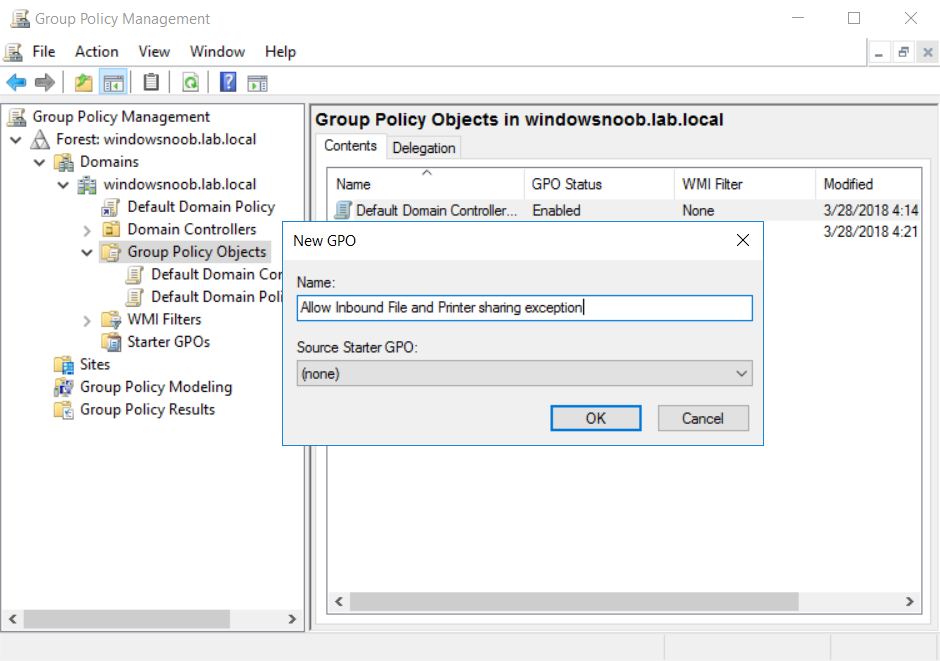
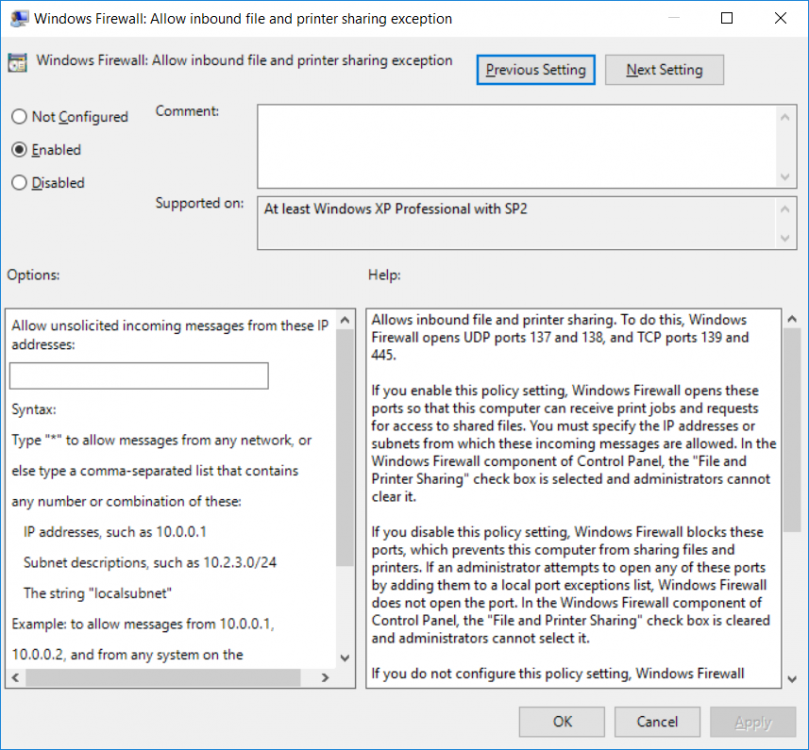
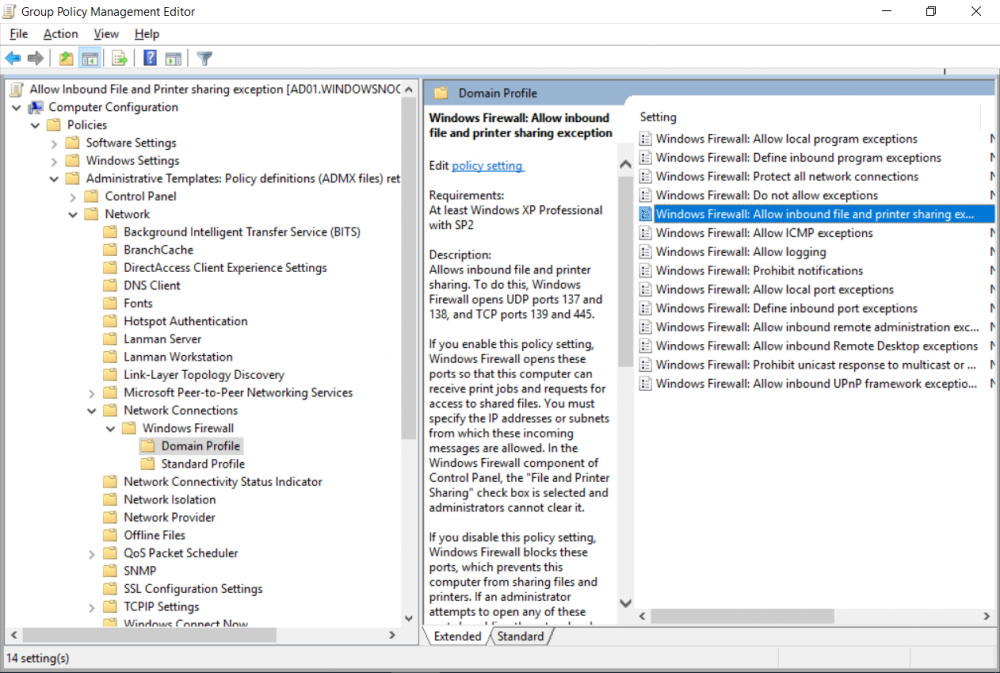
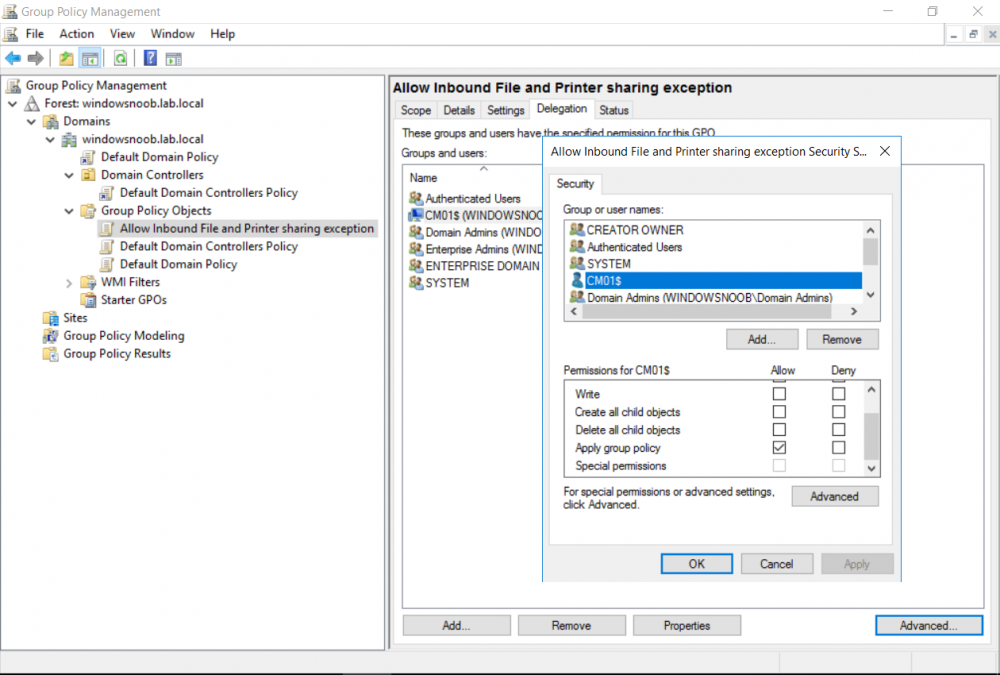
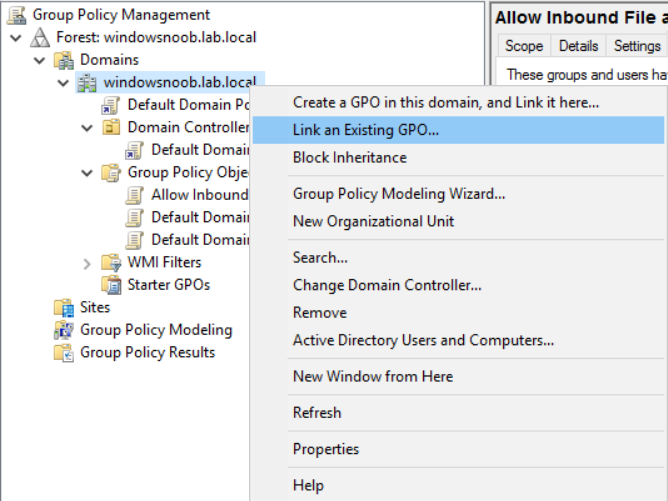
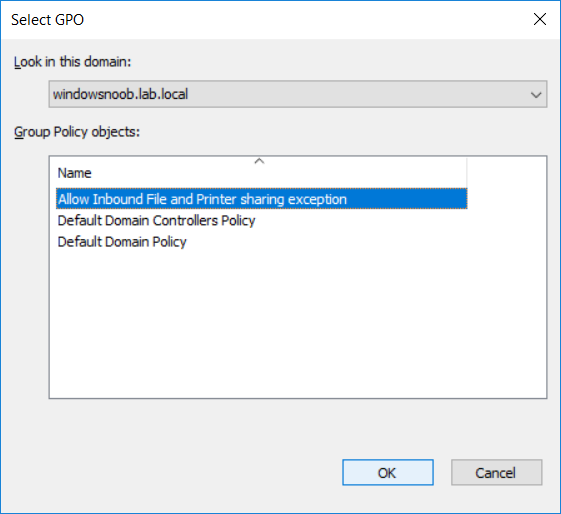
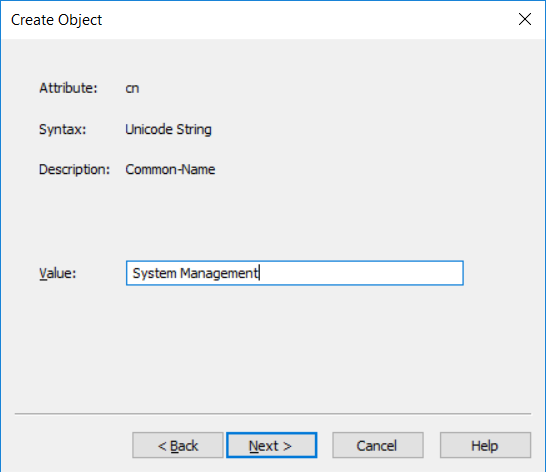
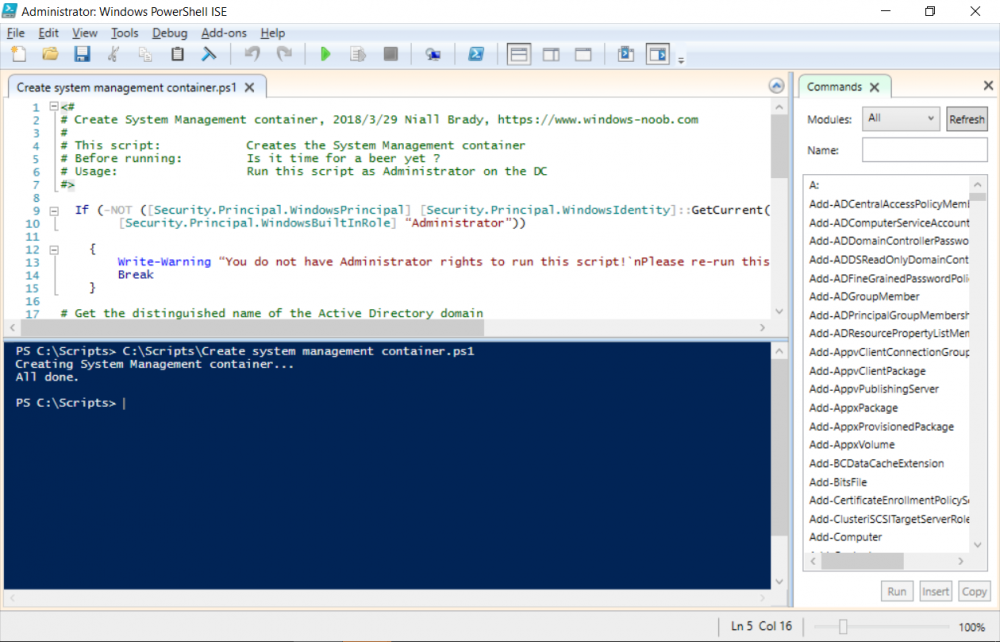
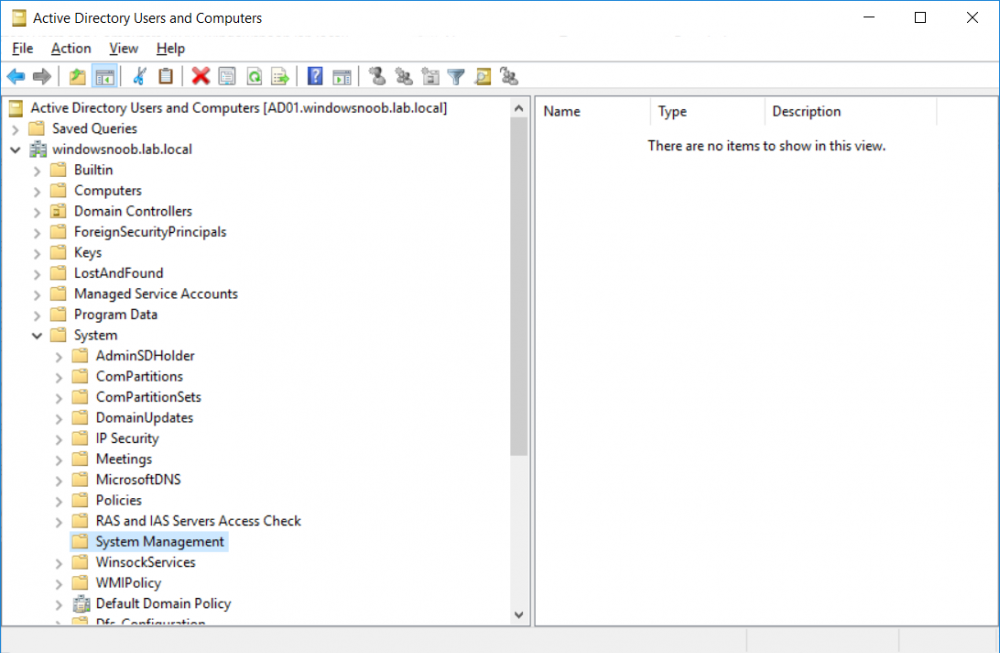
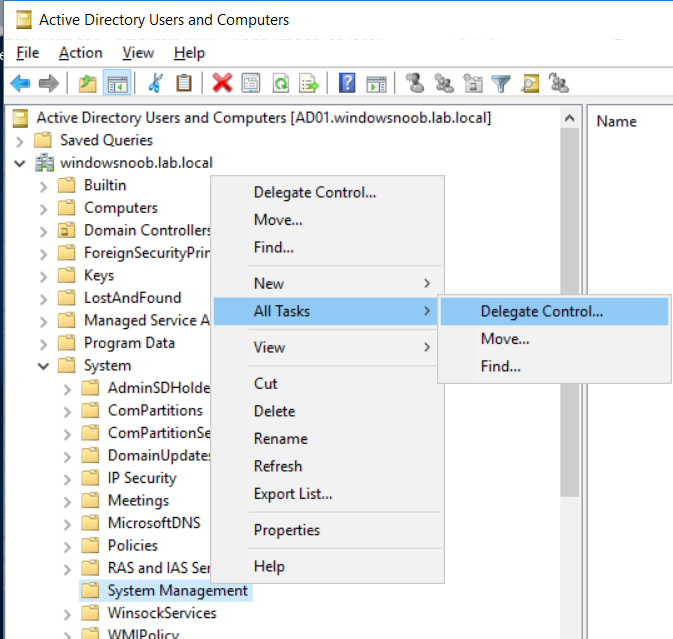
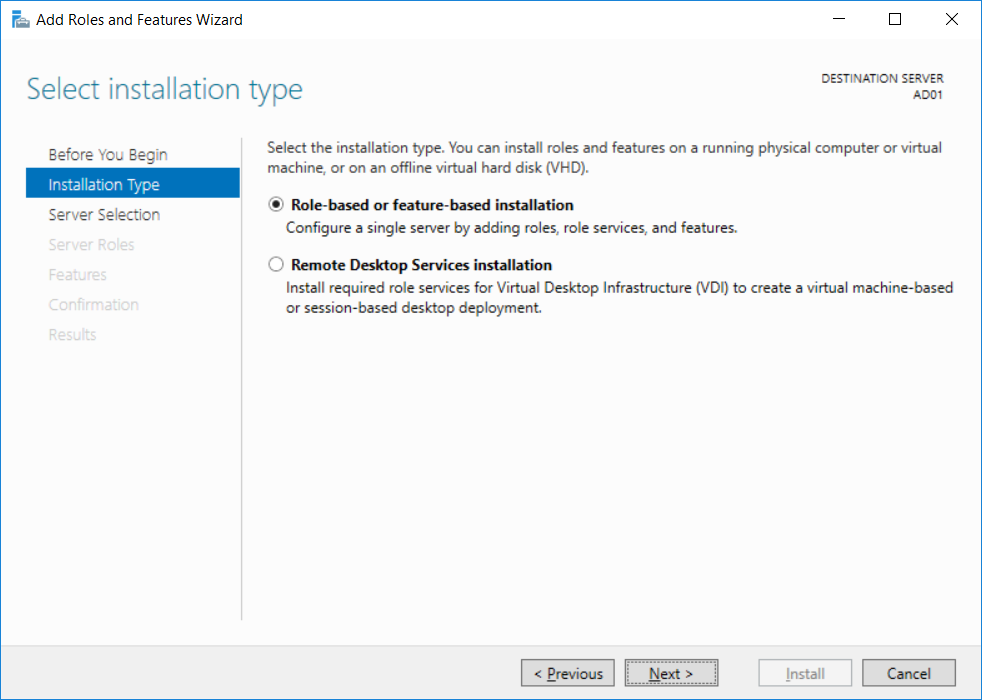
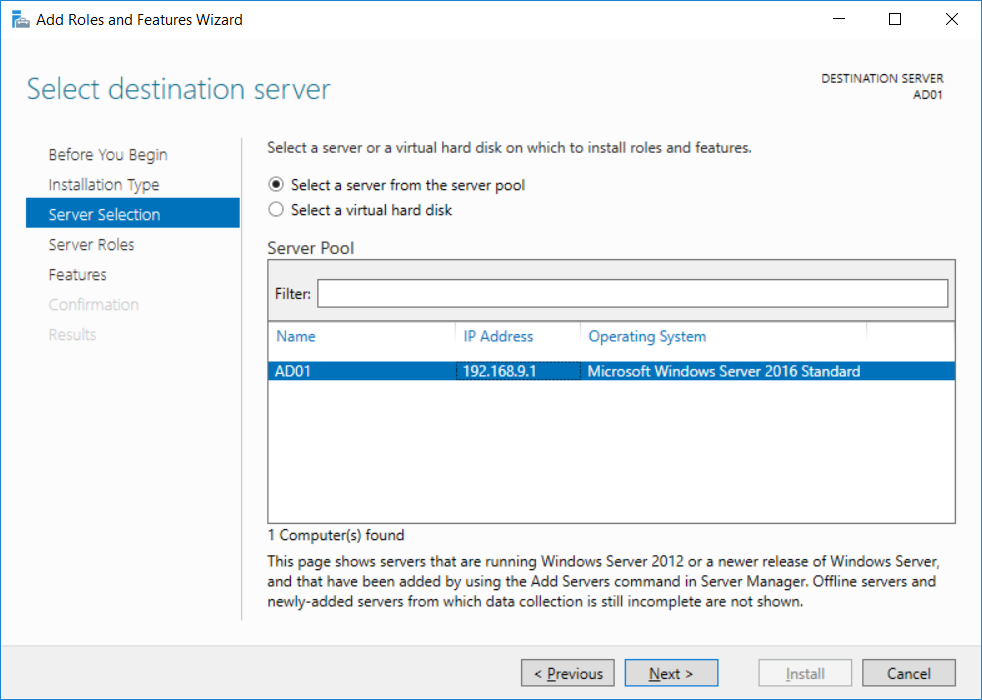
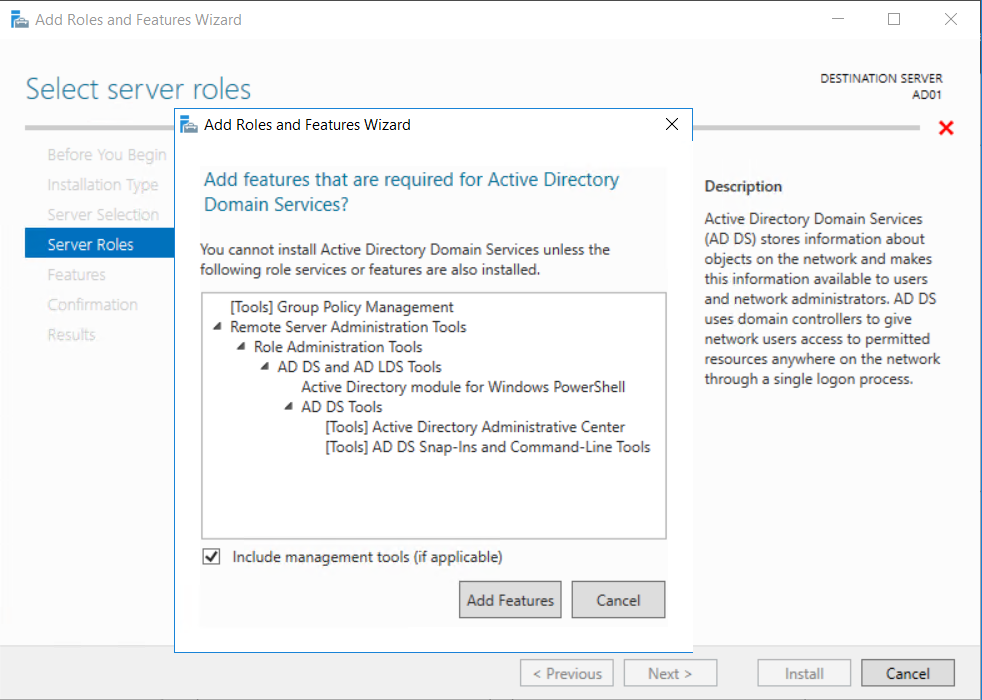
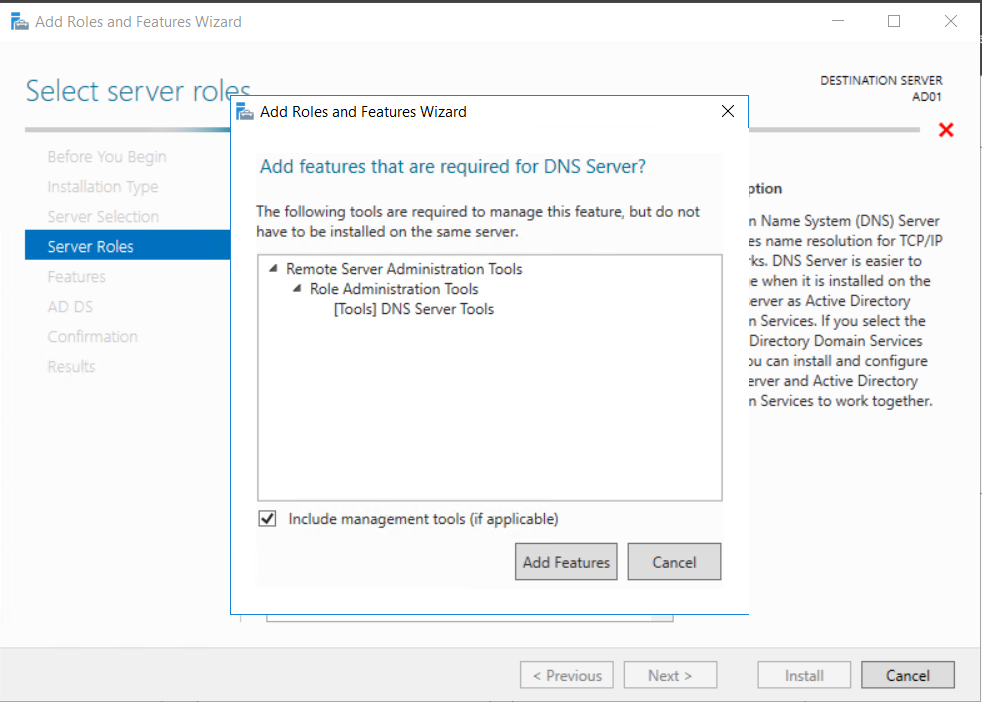
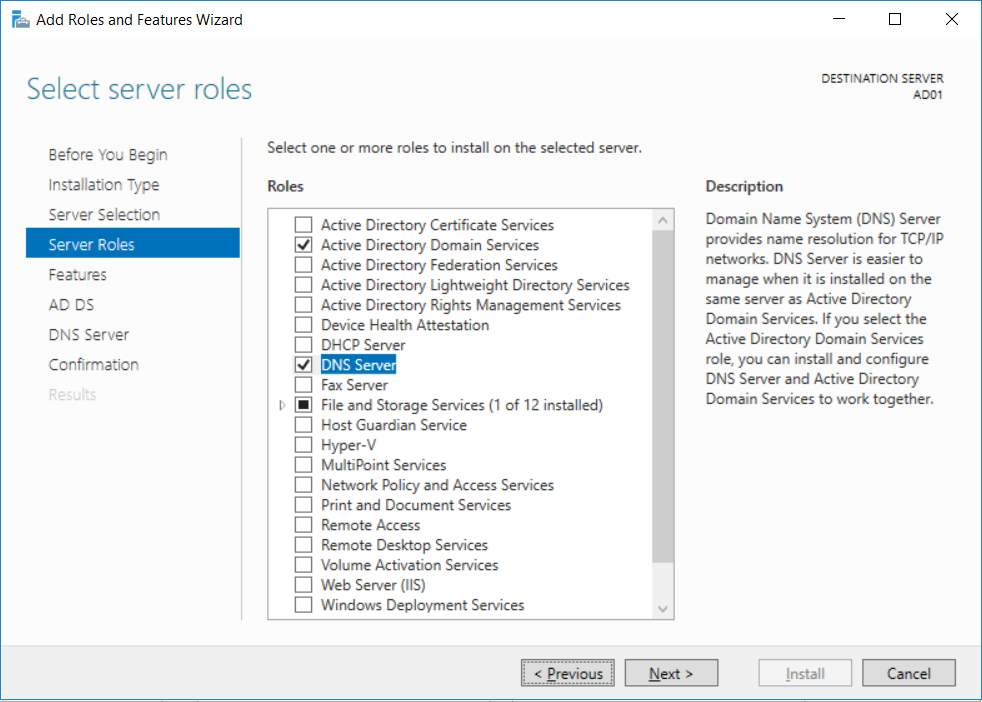
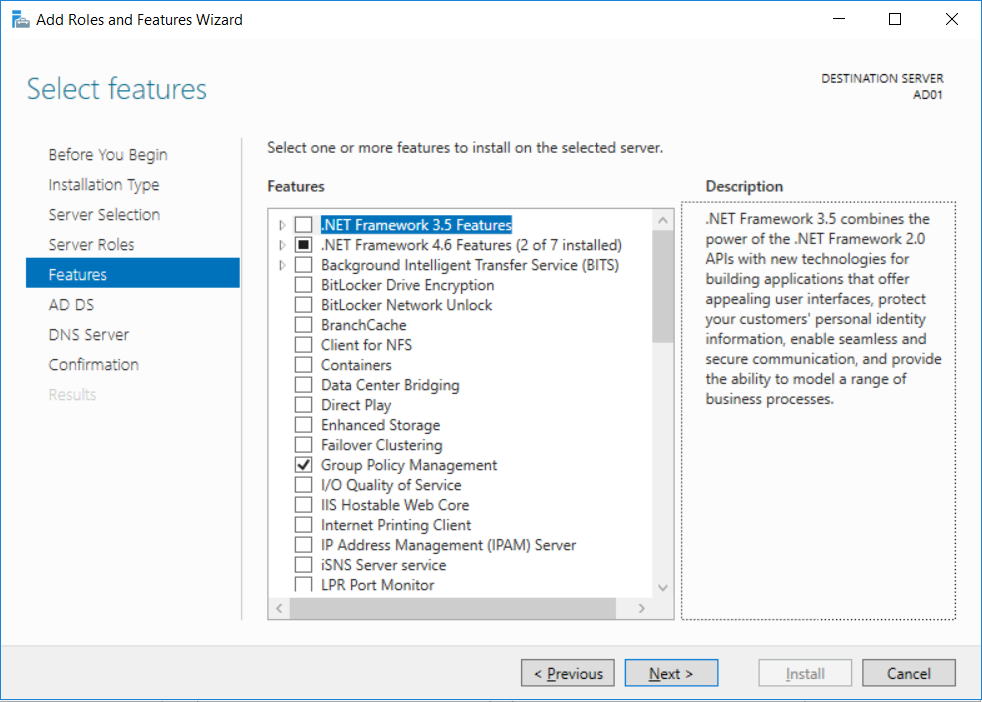
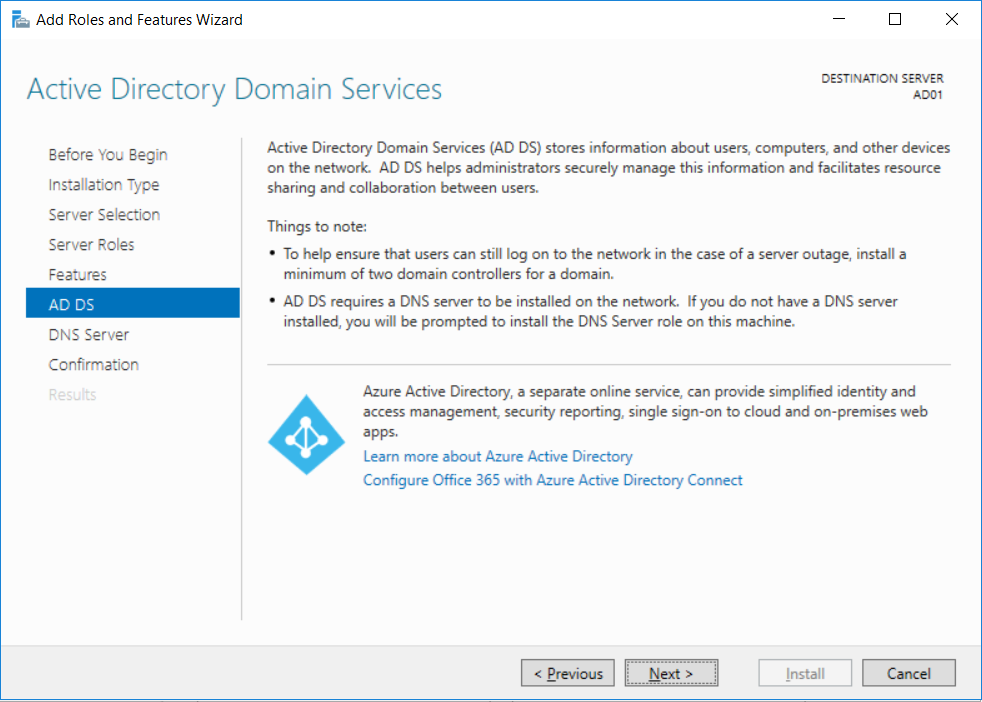
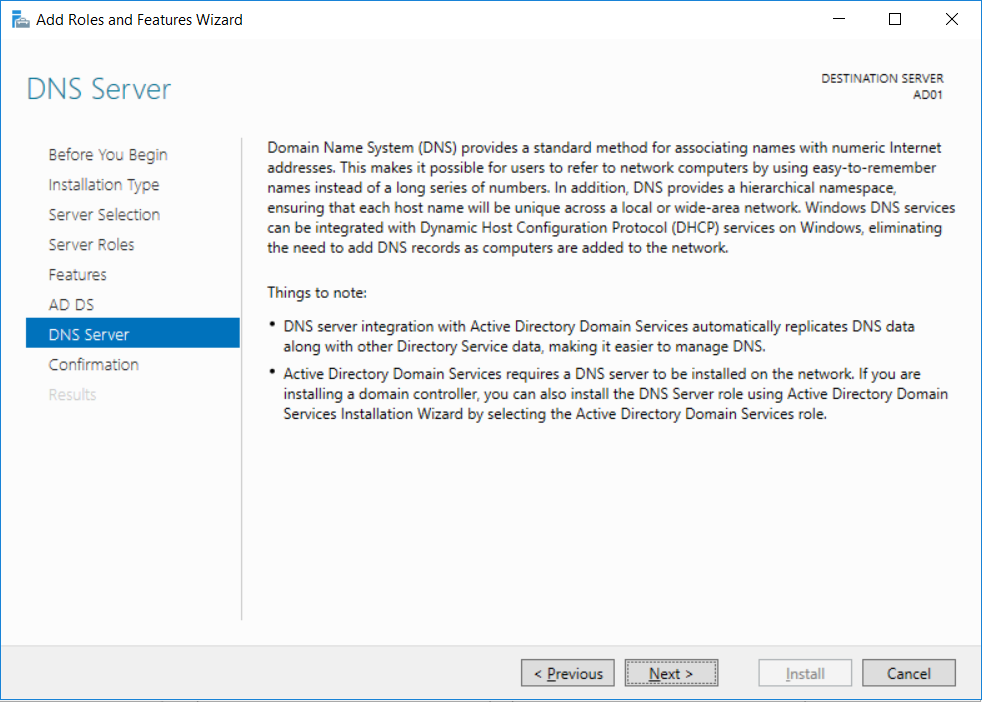
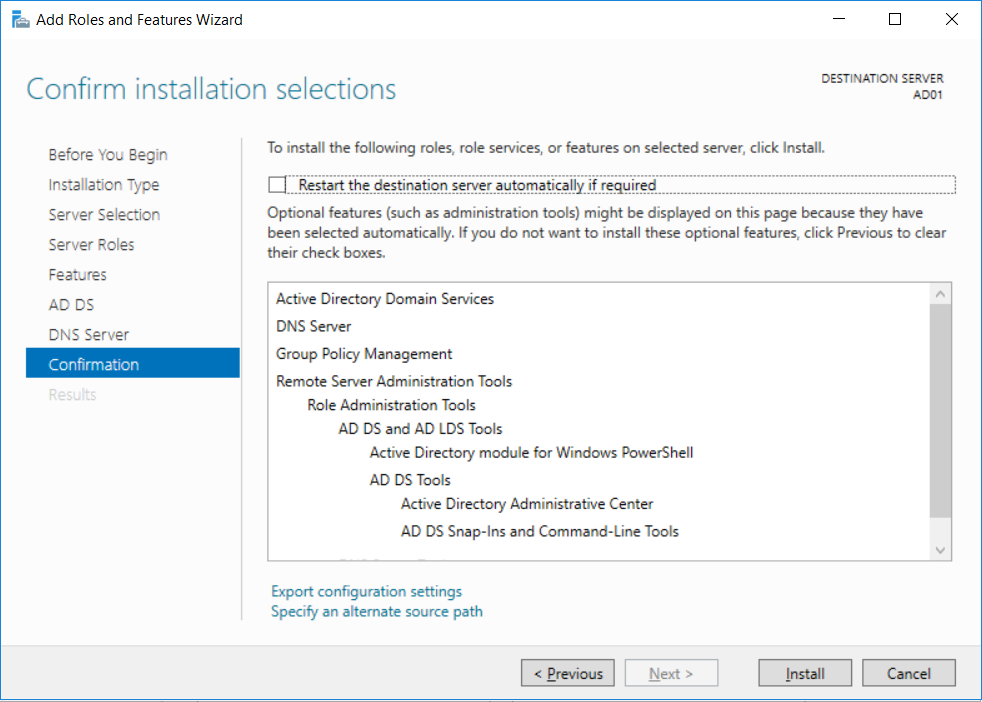
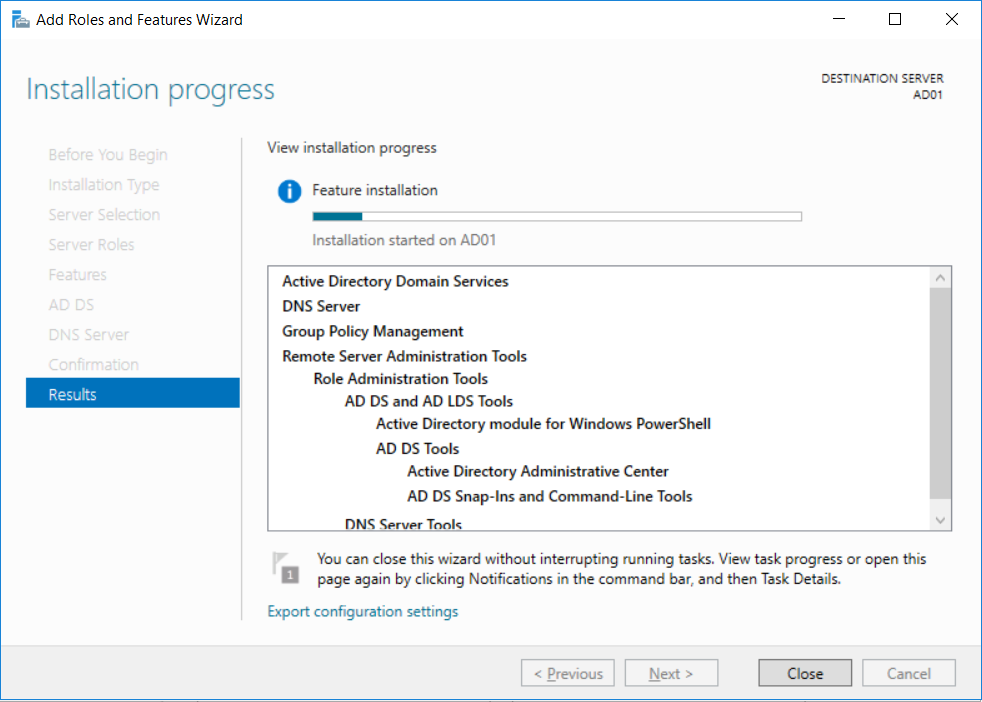
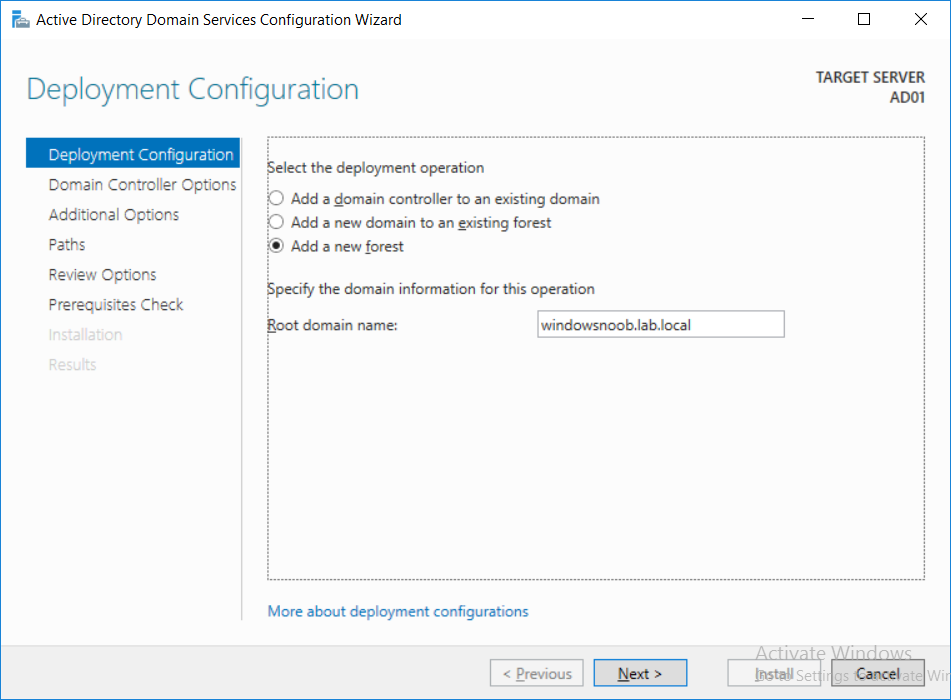
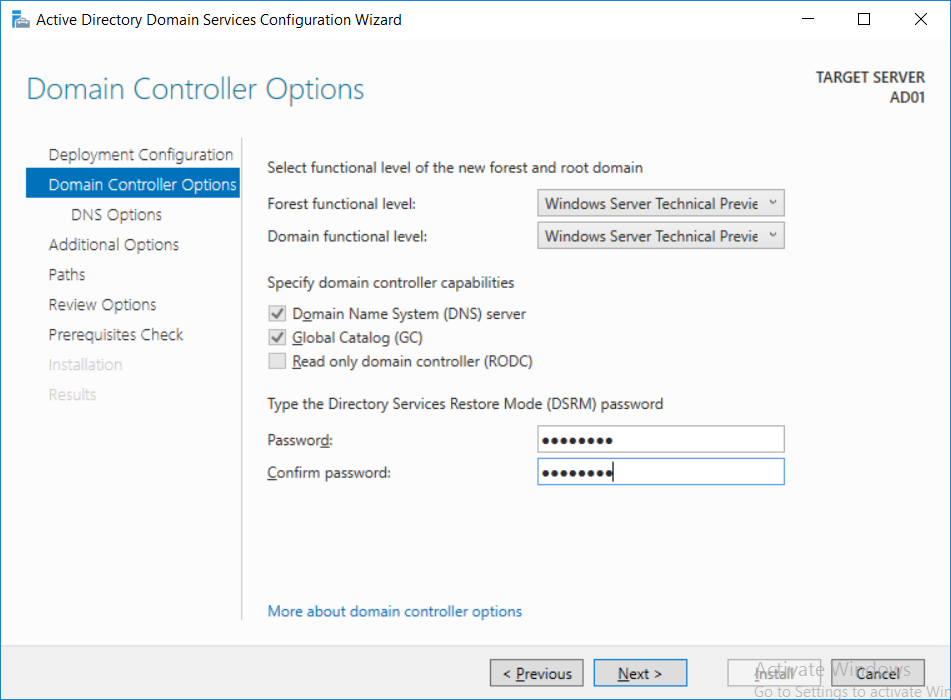
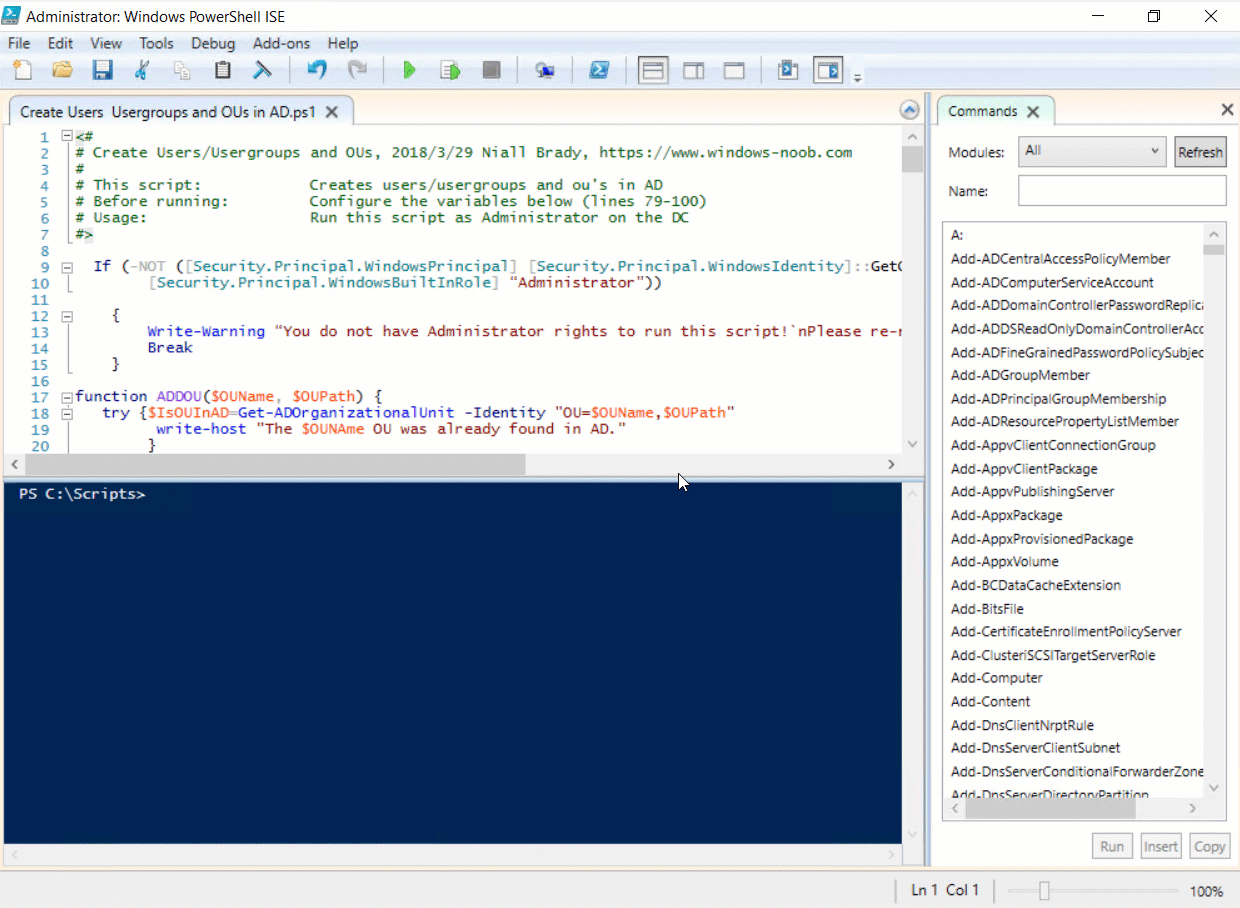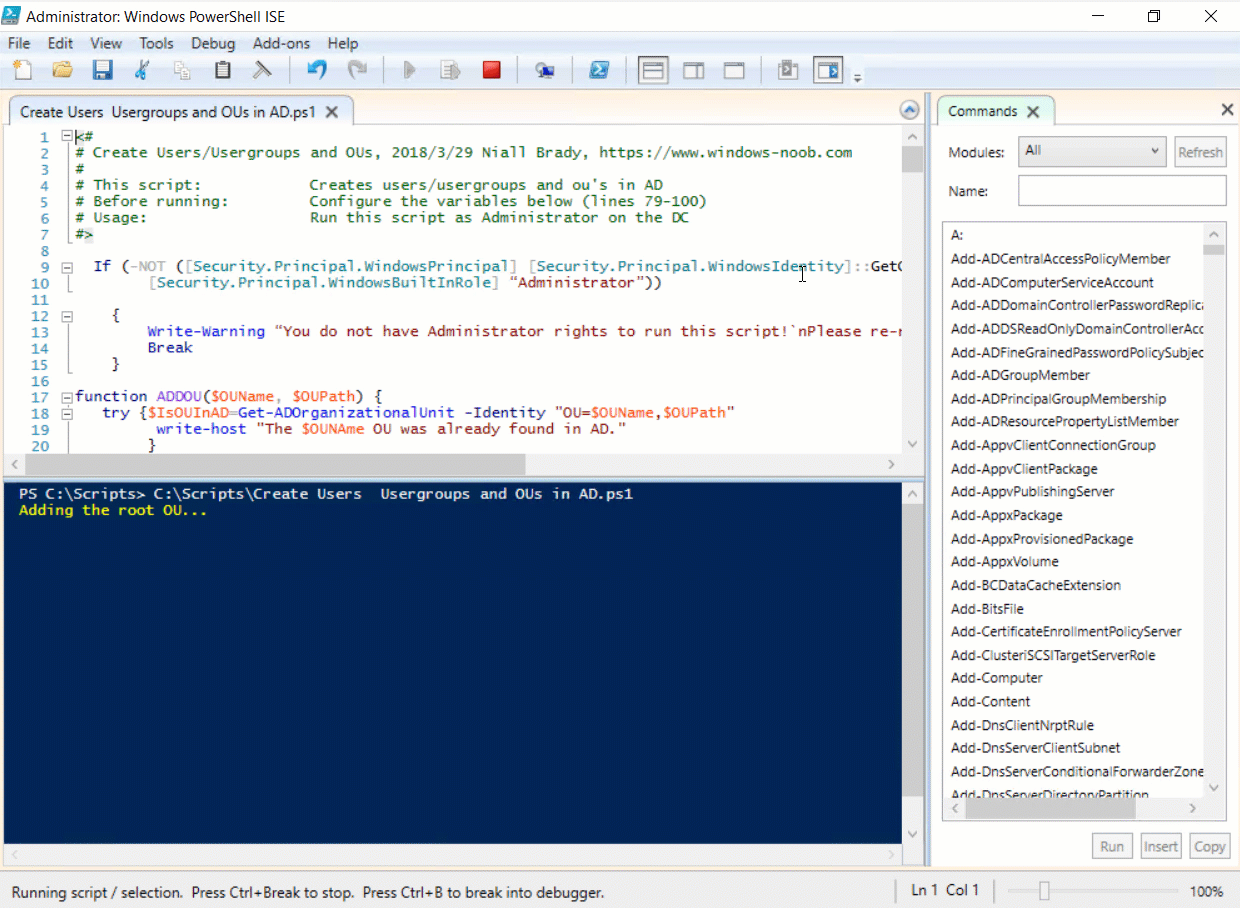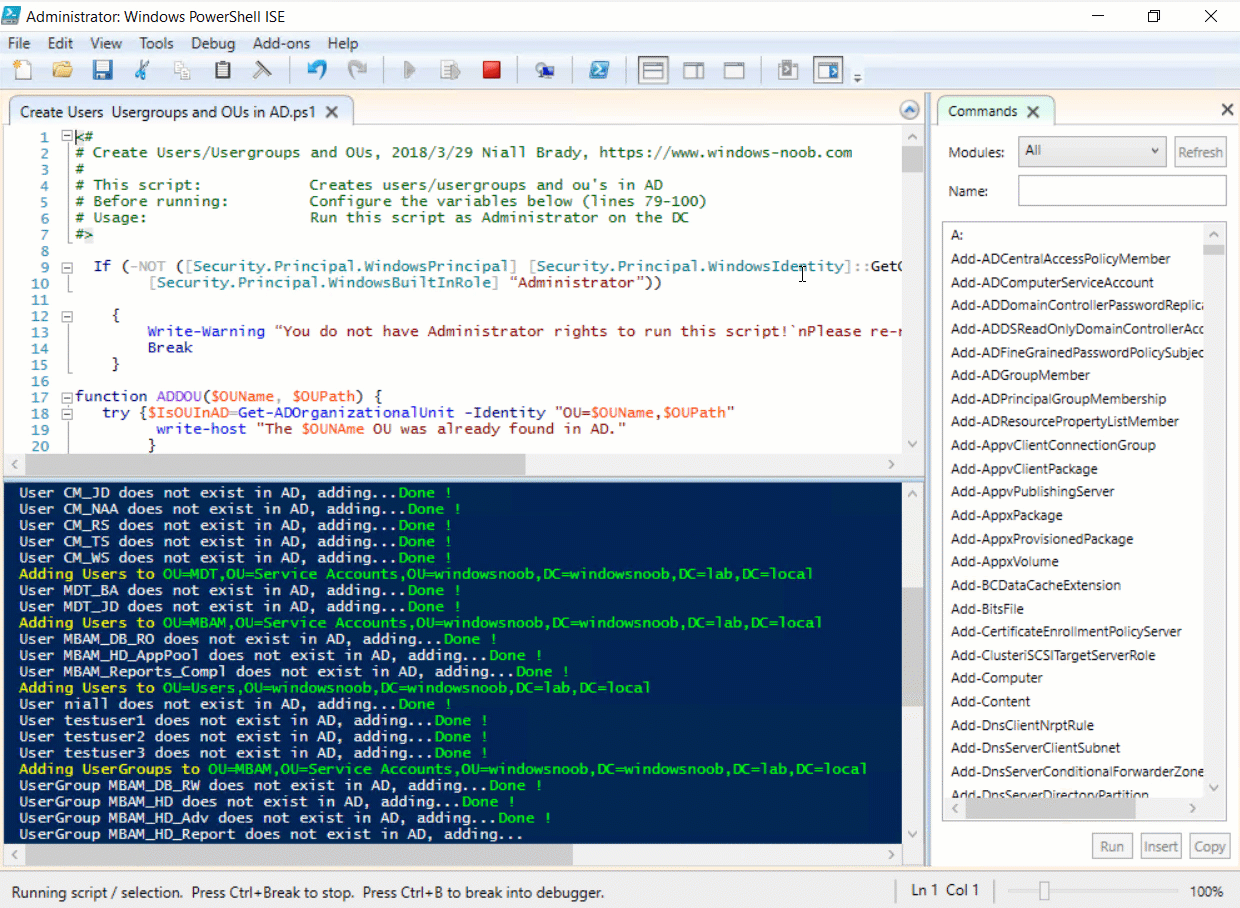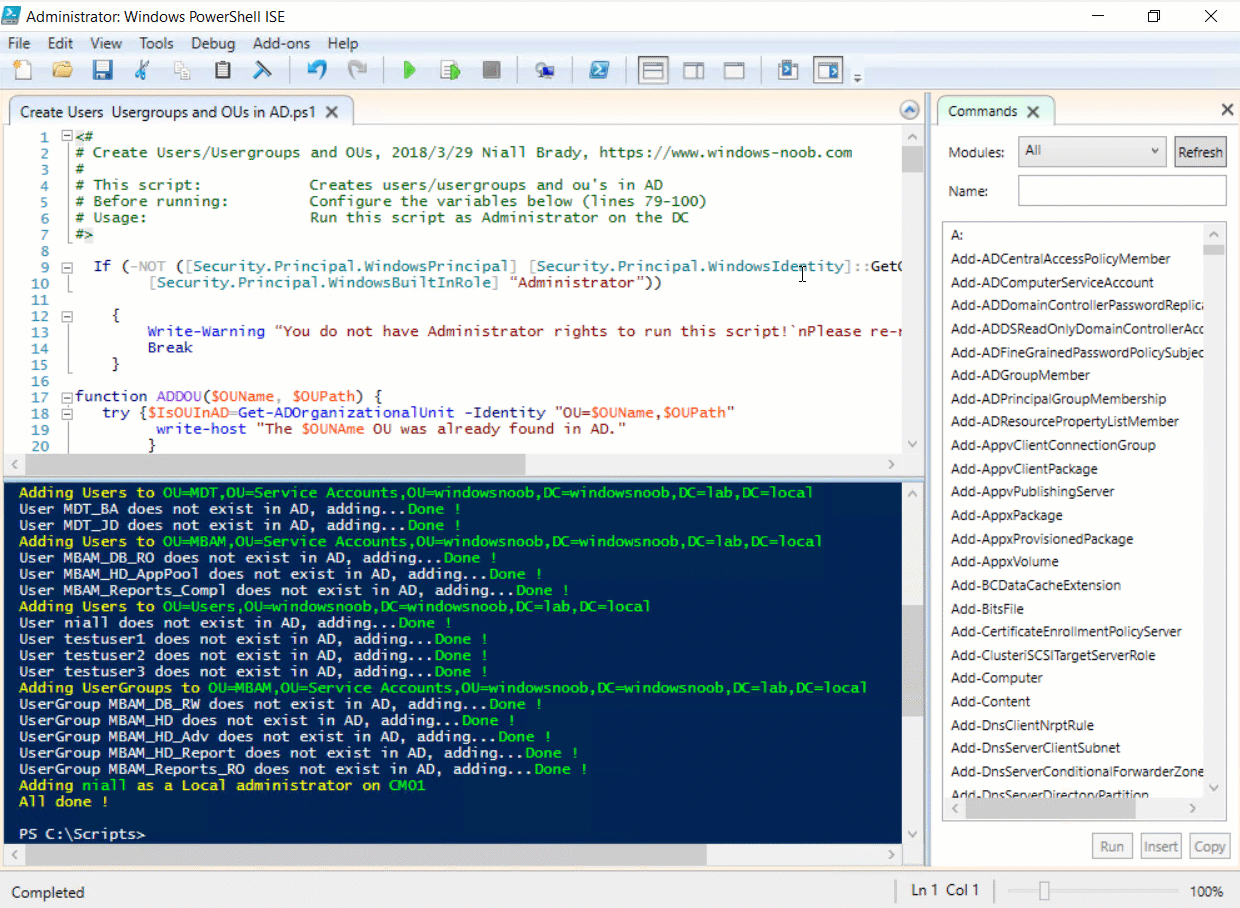
This multi-part guide will show you how to install the latest baseline version of Configuration Manager from Microsoft. The latest available baseline version is System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) version 1802 as of March 29th 2018. How can I install System Center Configurati...
- 20 replies
-
- sql server 2017
- powershell
-
(and 3 more)
Tagged with:
-
My reports are not showing up under my console. (Monitoring, Reporting, Reports). I've added Administrator User for the Reporting. And created a custom role for this purpose. When I go to reports in the console, it shows as: http://sccm2016/Reports_SCCMTEST16, and when it attempts to open, it...
- 3 replies
-
- sql server 2017
- sccm 1806
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
Introduction UPDATE: please use the newer version of this guide here. This multi-part guide will show you how to install the latest baseline version of Configuration Manager from Microsoft. The latest available baseline version is System Center Configuration Manager (Current Branch) vers...
- 5 replies
-
- sccm
- windows server 2016
-
(and 2 more)
Tagged with: